|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Amazon Athena is a serverless, interactive query service that easily analyzes large amounts of data stored in Amazon S3 using standard SQL. One of its powerful features, introduced in engine version 2, is parameterized queries. This capability allows users to run the same SQL statement with different input values safely and efficiently without rewriting the query each time.
In this blog, we will explore what parameterized queries are, how they work in Amazon Athena, the benefits they bring, and the key limitations to be aware of.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
What Are Parameterized Queries in Amazon Athena?
Parameterized queries use placeholders (?) within SQL statements, allowing values to be passed in separately at the time the query is executed. This means the SQL structure stays fixed, while the actual values can vary with each run.
For example, instead of writing:
|
1 |
SELECT * FROM sales WHERE region = 'West'; |
You can write:
|
1 |
SELECT * FROM sales WHERE region = ?; |
Then you provide the value ‘West’ during execution. This approach is safer and easier to manage, especially when dealing with user input or variable data.
Amazon Athena supports parameterized queries in the following SQL operations:
- SELECT
- INSERT INTO
- CTAS (Create Table As Select)
- UNLOAD
Note: This feature is available from engine version 2 onwards. Users on older versions will need to upgrade to use it.
How Parameterized Queries Work in Amazon Athena?
Amazon Athena offers two different methods to work with parameters, depending on how frequently the query is used and how much control is needed.
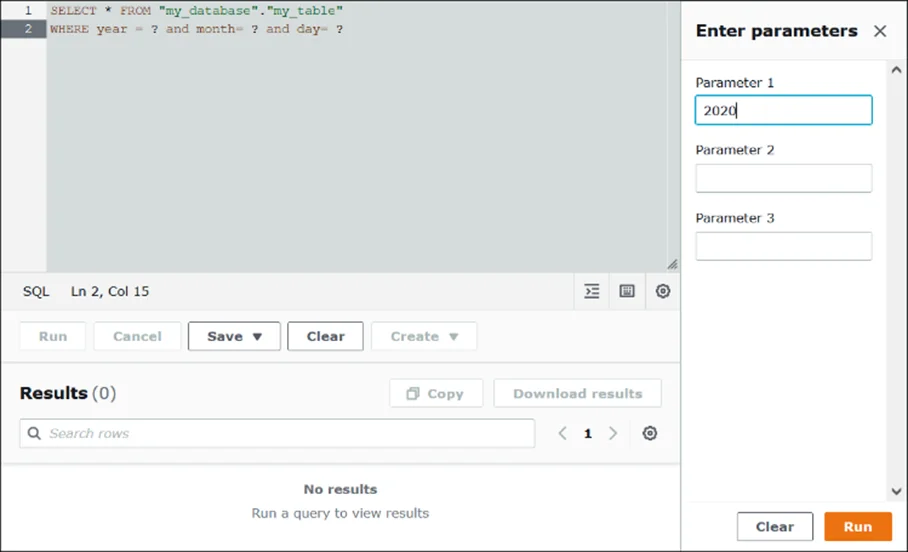
- Execution Parameters
This is a one-step process where you run the query with placeholders and pass in the values during execution via the Amazon Athena console, AWS CLI, or SDKs.
- No setup required
- Works across any workgroup
- Ideal for quick, temporary, or dynamic queries
- Prepared Statements
This method involves a two-step process: first, you define the query using a PREPARE command; then, you run it using EXECUTE … USING.
- Stored within a specific Amazon Athena workgroup
- Can be reused multiple times
- Hides input values from logs, making it suitable for sensitive environments
Benefits of Amazon Athena Parameterized Queries
- Improved Security
Parameterized queries treat inputs as fixed values, not executable SQL. This protects against SQL injection attacks and ensures queries are safely executed, especially when inputs come from users or external sources.
- Reusable Query Structure
With prepared statements, the SQL structure is written once and reused as needed. This reduces code duplication and simplifies long-term maintenance.
- Cleaner Audit Logs
Amazon Athena hides actual parameter values in logs like AWS CloudTrail when using prepared statements. Instead of showing sensitive details, it marks them as hidden for security, helping teams meet compliance requirements.
- Flexible Usage
Execution parameters are simple to use and don’t require any setup or stored metadata. They’re great for single-use queries or tools that span across multiple workgroups.
Limitations of Amazon Athena Parameterized Queries
While powerful, parameterized queries in Amazon Athena come with some important restrictions:
- Only certain SQL statements are supported: You can only use parameters with SELECT, INSERT INTO, CTAS, and UNLOAD. Statements like UPDATE or DELETE aren’t supported.
- Only positional placeholders: Named parameters (like :region) are not supported-values must be passed in the exact order they appear.
- Restricted to WHERE clause: You can’t use “?” in column names, table names, or SELECT lists—only in the WHERE clause.
- Limit of 25 parameters per query: Amazon Athena will return a syntax error if a query has more than 25 placeholders.
- No placeholders inside quotes: You cannot wrap? In quotes (like ‘?’). Placeholders must be outside quotes to work.
- Engine-specific behavior: Some earlier engine version 2 releases had bugs with parameter order in complex queries using CTEs (WITH clauses). These issues are fixed in the Amazon Athena engine version 3.
Use Cases of Amazon Athena Parameterized Queries
- Self-Service Dashboards
Business users can apply filters or date ranges without rewriting SQL queries, using safe and flexible parameter passing behind the scenes. - Web Applications
Backend services can reuse SQL logic by changing values like user IDs or dates and using prepared statements for added security. - Analytics Tools
Teams building automated reports or custom insights can reduce risk by avoiding direct string-based query building. - Audit-Sensitive Workloads
Organizations that require secure logging can use prepared statements to ensure sensitive values are not exposed in log data.
Conclusion
Amazon Athena’s parameterized queries provide a safer and more scalable way to execute SQL in serverless environments.
Whether building dynamic dashboards, supporting multiple teams, or working in a compliance-driven environment, Amazon Athena’s support for parameters offers the tools you need to work efficiently and securely. Just be mindful of the limits, like WHERE-only usage and parameter count, and you can make the most of this feature.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Amazon Athena and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Why can’t I use “?” in table names or SELECT fields?
ANS: – Because placeholders are designed for values only, table and column names must be known before the query runs, so Athena does not allow them to be dynamic.
2. Can I pass more than 25 values using parameters?
ANS: – No. Amazon Athena currently allows a maximum of 25 positional parameters (?) per query. You must split your logic or reduce parameter usage if you exceed this.
3. Is this feature available in all Amazon Athena versions?
ANS: – No. Parameterized queries are supported only in engine version 2 and later. For the most stable experience and bug fixes, engine version 3 is recommended.

WRITTEN BY Anusha
Anusha works as a Subject Matter Expert at CloudThat. She handles AWS-based data engineering tasks such as building data pipelines, automating workflows, and creating dashboards. She focuses on developing efficient and reliable cloud solutions.


 Login
Login


 September 1, 2025
September 1, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments