|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
AWS LakeFormation is a fully managed service that helps organizations build, secure, and manage data lakes on Amazon Web Services (AWS). It simplifies the process of setting up and managing data lakes by providing capabilities for data ingestion, storage, and data access. One key feature of AWS Lake Formation is its fine-grained permission model, which allows organizations to have granular control over data access and security.
The fine-grained permission model in AWS Lake Formation enables organizations to define precise access controls at different levels, including databases, tables, columns, and rows. This level of granularity ensures that data is accessed only by authorized users or groups, protecting sensitive information and maintaining data privacy and compliance. Amazon Athena can be used to query data that is registered with AWS LakeFormation. Here we are taking an example of Amazon Athena, but one can very well use Amazon QuikSight, Amazon Redshift, Amazon EMR, and Amazon SageMaker with Amazon LakeFormation.
Athena User Request Workflow

Source: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/images/athena/latest/ug/images/lake-formation-athena.png
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
Let's understand how a query is initiated in Amazon Athena
Step 1: Register the S3 bucket in AWS LakeFormation
Step 2: Once registered, you can set up user access for the data.
Step 3: When a user fires a query using Amazon Athena to access the data, it sends the user credentials to AWS LakeFormation
Step 4: AWS LakeFormation validates the credentials and provides a temporary token to access the data
Step 5: The user then gets access to data based on the temporary token
Reference Architecture for Demonstration

So, we have two IAM users,
- Nehal – Administrator User
- Tina – Customer User
Step 1: Both users initiate a query request via Amazon Athena with their individual IAM roles.
Step 2: Using the get data access permission, AWS LakeFormation requests temporary credentials to access the data.
Step 3: It then checks whether the AWS LakeFormation Service role has access to the data in S3 or not.
Step 4: Based on the access, it gets a temporary token.
Step 5: Then this temporary token is passed back to Amazon Athena, which assumes the AWS LakeFormation service role.
Step 6: Finally, S3 Get Object API call is made through the AWS LakeFormation service role, and data is written back to the user.
Demonstration

The goal is that Nehal being the administrator user, should get access to the entire dataset while Tine being a consumer, used to be able to access only selected fields like name, phone number, dob, address, and city.

Step 1: Create 2 IAM users, one being Nehal having Administrator access and Tina being a consumer with the following set of permissions.
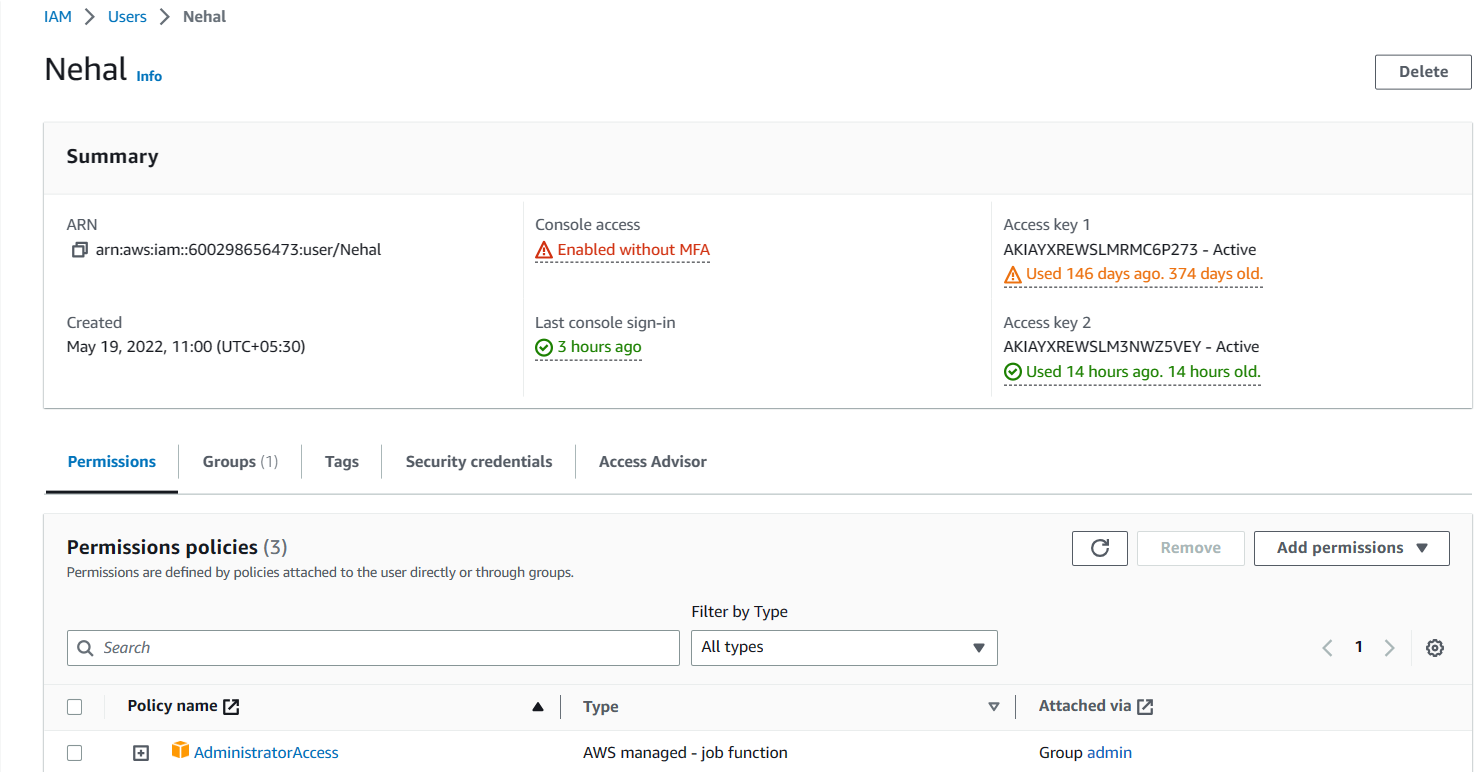

Step 2: Next, we create an S3 bucket and upload the sample data to a data folder.
 Our sample data looks like this.
Our sample data looks like this.

Step 3: Next, we set up the AWS LakeFormation to build our data lake.

Step 4: First will create a database inside AWS LakeFormation

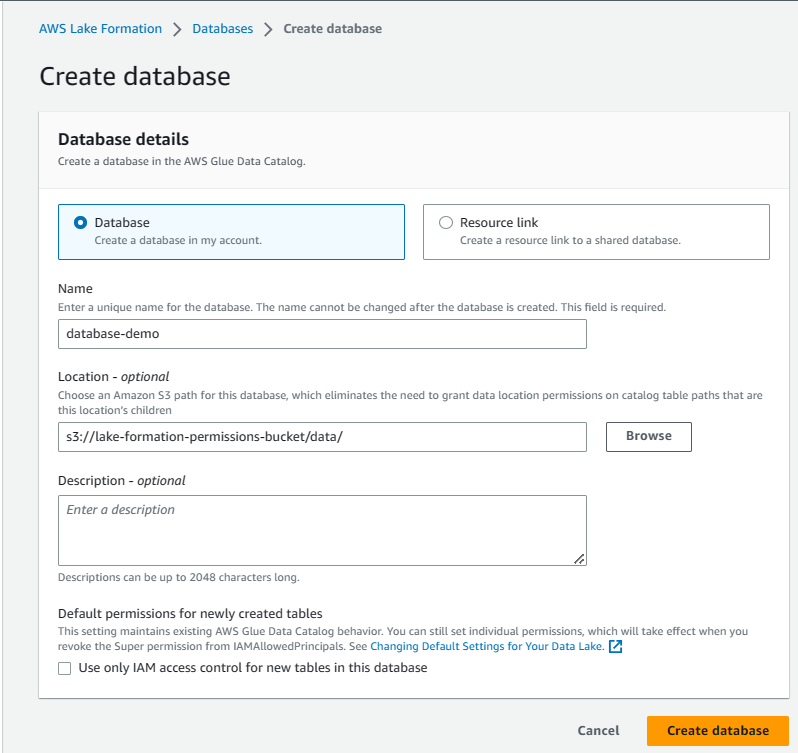
Step 5: Next step in AWS Lake Formation, register our S3 bucket using AWS Lake Formation Service Role.

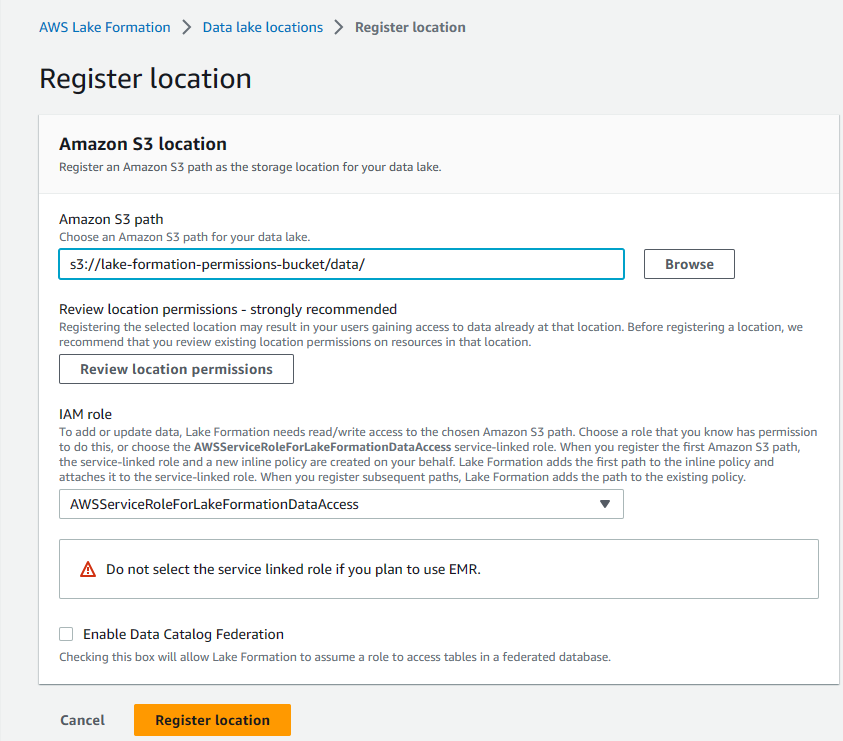
Step 6: Next, we will grant Glue Role onto the database we created so that once we run the Glue Crawler, the Glue Crawler is able to populate the tables inside this database.



Step 7: Here, we create a Glue Crawler to catalog the data present inside S3
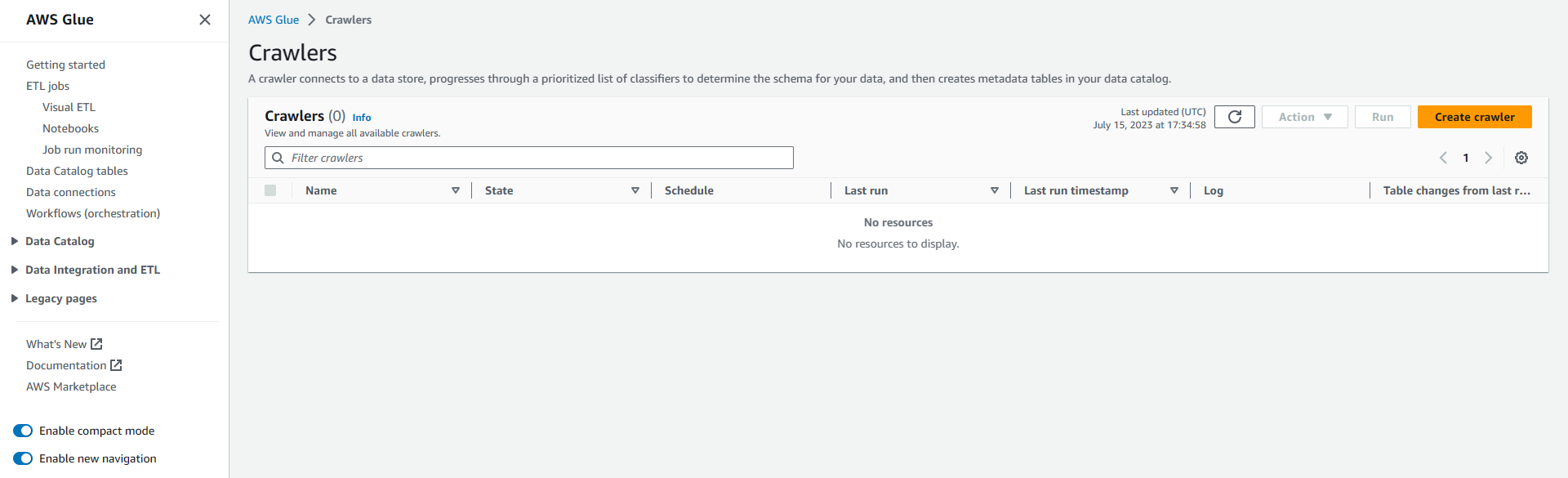

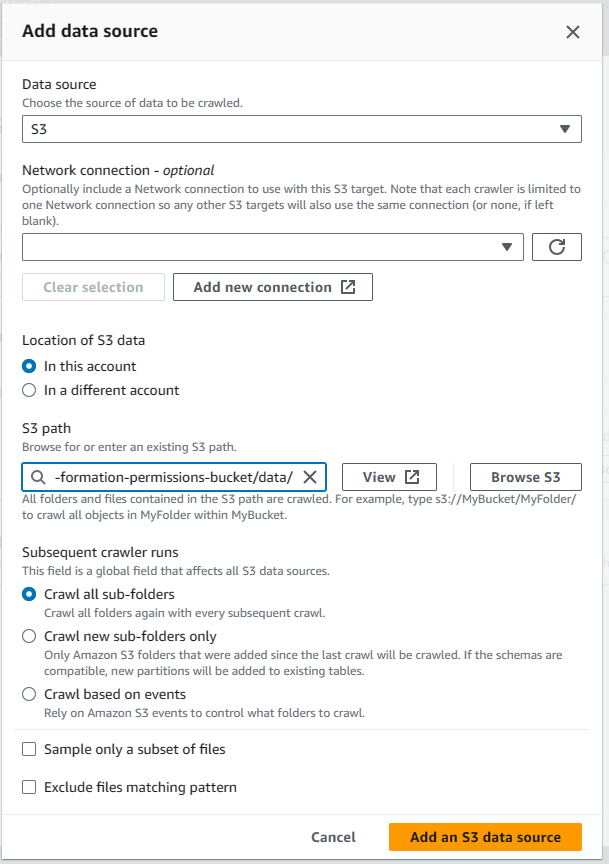




Step 8: Create a Glue Crawler and run it

Step 9: The Glue Crawler runs and takes some mins to populate the tables inside our database created

Step 10: You can check out the schema populated in the database in AWS LakeFormation

Step 11: Now jump onto the Amazon Athena to query the data. Since Nehal is the administrator User, so once she fires a SQL query using Amazon Athena, she can see all the data.


Step 12: Now, let’s grant permission to Tina IAM User, who is a consumer user on a selected column



Step 13: Validate the results by jumping onto the Amazon Athena with the Tina User login in


Summary
The fine-grained permission model in AWS Lake Formation provides organizations with granular control over data access and security in their data lakes. By defining precise permissions at different levels, organizations can protect sensitive data, enforce data governance policies, and ensure compliance with regulations. The scalability and flexibility of the permission model, combined with integration with other AWS services, make AWS Lake Formation a powerful solution for managing and securing data lakes in the cloud.
References
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/athena/latest/ug/lf-athena-access.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/athena/latest/ug/what-is.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lake-formation/latest/dg/what-is-lake-formation.html
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY Nehal Verma
Nehal is a seasoned Cloud Technology Expert and Subject Matter Expert at CloudThat, specializing in AWS with a proven track record across Generative AI, Machine Learning, Data Analytics, DevOps, Developer Tools, Databases and Solutions Architecture. With over 12 years of industry experience, she has established herself as a trusted advisor and trainer in the cloud ecosystem. As a Champion AWS Authorized Instructor (AAI) and Microsoft Certified Trainer (MCT), Nehal has empowered more than 15,000 professionals worldwide to adopt and excel in cloud technologies. She holds premium certifications across AWS, Azure, and Databricks, showcasing her breadth and depth of technical expertise. Her ability to simplify complex cloud concepts into practical, hands-on learning experiences has consistently earned her praise from learners and organizations alike. Nehal’s engaging training style bridges the gap between theory and real-world application, enabling professionals to gain skills they can immediately apply. Beyond training, Nehal actively contributes to CloudThat’s consulting practice, designing, implementing and optimizing cutting-edge cloud solutions for enterprise clients. She also leads experiential learning initiatives and capstone programs, ensuring clients achieve measurable business outcomes through project-based, real-world engagements. Driven by her passion for cloud education and innovation, Nehal continues to champion technical excellence and empower the next generation of cloud professionals across the globe.


 Login
Login


 September 12, 2023
September 12, 2023 PREV
PREV











Comments