|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
This blog explains how to deploy MLflow, an open-source machine learning lifecycle platform, on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) using Terraform for infrastructure automation. The deployment includes persistent storage, external access to the MLflow UI, and integration with core AWS services, all automated using Terraform.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Introduction
In modern machine learning workflows, it’s not enough to train a model, teams must also track experiments, manage model versions, and reproduce results. MLflow is a tool designed to help with exactly that. While MLflow can run locally for development, deploying it on the cloud is essential for production use cases.
Amazon EKS, AWS’s managed Kubernetes service, provides a scalable and resilient environment for running containerized workloads like MLflow. Pairing this with Terraform, a widely adopted Infrastructure-as-Code tool, allows you to automate the entire setup, from network infrastructure to Kubernetes deployments.
In this blog, we will explore how these three technologies, MLflow, Amazon EKS, and Terraform, come together to create a reliable and repeatable platform for managing your machine learning experiments in the cloud.
MLFlow
MLflow is a platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning lifecycle. It helps with:
- Tracking experiments and metrics
- Packaging and saving models
- Deploying models into production
- Organizing runs and results in a UI
Data scientists and ML engineers widely use it to streamline model development and reproducibility.
Why Deploy MLflow on Amazon EKS?
While MLflow can run locally or on a VM, deploying it on Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) provides several advantages:
- Scalability: Amazon EKS automatically scales resources to handle large ML workloads.
- High Availability: Amazon EKS runs across multiple Availability Zones, improving reliability.
- Isolation & Security: Each workload runs in a containerized environment, improving separation and control.
- Integration with AWS services: You can use Amazon S3 for artifact storage, Amazon CloudWatch for logs, and AWS IAM for access control.
Why Use Terraform?
Terraform is an open-source tool that lets you define and provision cloud infrastructure using code. With Terraform, you can:
- Automate the creation of Amazon EKS clusters, networks, and storage.
- Reuse infrastructure modules for consistency.
- Track changes to your cloud environment using version control.
- Re-deploy environments quickly and reliably.
Steps Involved in Deploying MLflow on Amazon EKS with Terraform
Step 1: Set Up Terraform Project Structure
Start by organizing your Terraform files and modules. This typically includes:
- A root configuration (main.tf, variables.tf, outputs.tf)
- Modules for Amazon VPC, Amazon EKS, EBS, and optionally AWS IAM roles
- A directory for Kubernetes manifests (MLflow deployment, service, PVC, etc.)
This structure makes your infrastructure modular and reusable.
Step 2: Provision VPC and Networking
Use Terraform to create:
- A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Public and private subnets across multiple Availability Zones
- Internet gateway, NAT gateway, and routing tables
This network setup is the foundation for your Amazon EKS cluster and other resources.
Step 3: Deploy Amazon EKS Cluster
Next, create an Amazon EKS cluster using Terraform:
- Define the cluster name, version, and networking settings
- Create a node group using Amazon EC2 instances (e.g., t3.large)
- Assign AWS IAM roles to allow the nodes and Amazon EKS to interact with AWS services
After the cluster is ready, configure kubectl to connect with it.
Step 4: Create an EBS Volume for Persistent Storage
To store MLflow experiment logs (mlruns), provision an EBS volume in the same Availability Zone as your EKS nodes. This volume will be attached to the MLflow pod using a PersistentVolume (PV) and PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC).
Step 5: Apply Kubernetes Manifests
Once the infrastructure is up:
- Create a PersistentVolume and PersistentVolumeClaim to mount the EBS volume
- Deploy the MLflow application using a Kubernetes Deployment
- Expose the MLflow UI through a LoadBalancer Service
These resources run on your Amazon EKS cluster, making MLflow accessible via a public URL.
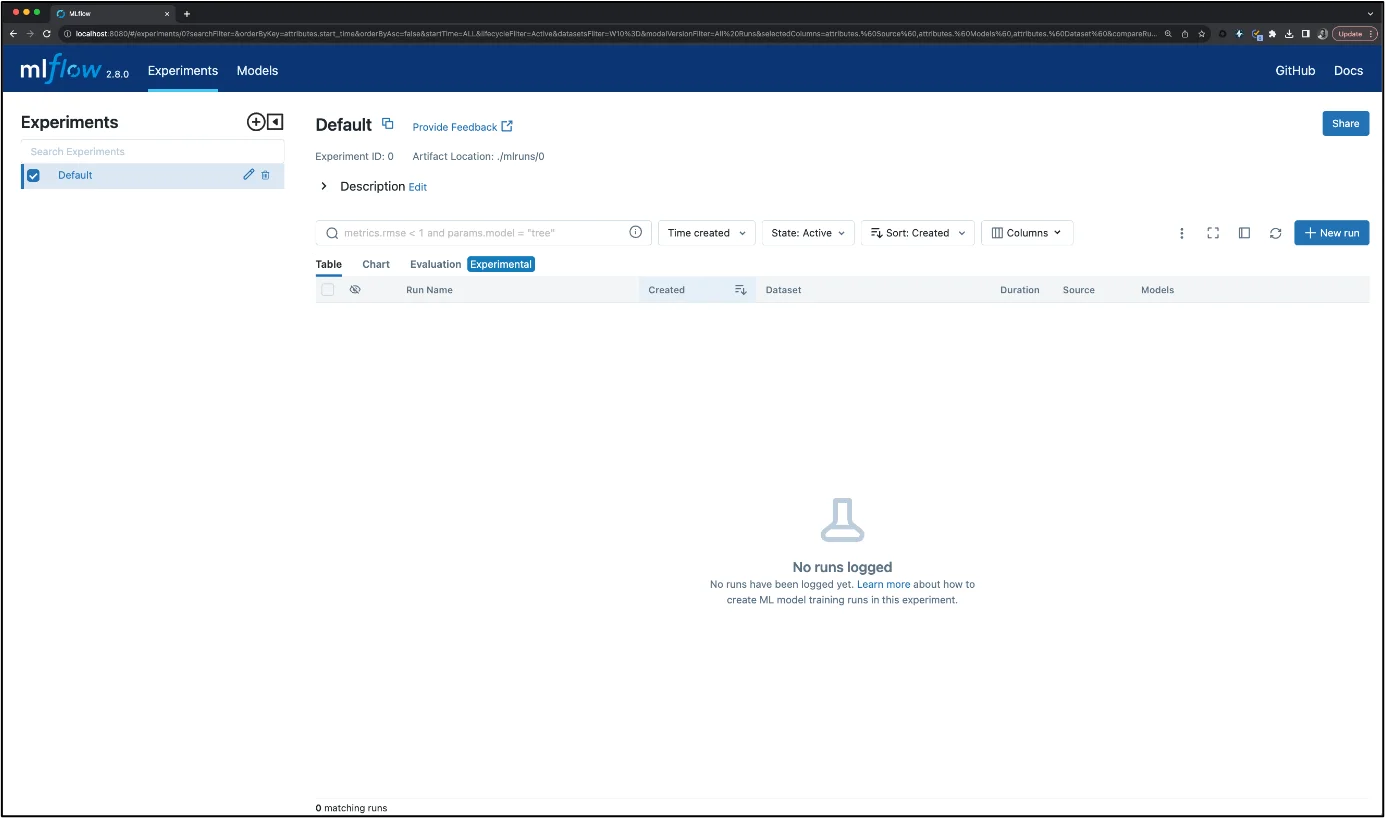
Step 6: Access MLflow UI
After deployment, get the external IP of the MLflow service. You can open this in a browser to access the MLflow tracking server and start logging experiments.
MLFlow UI
Conclusion
Terraform simplifies infrastructure setup and makes deployments repeatable. This setup is ideal for teams aiming for a reliable, cloud-native MLOps platform.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding MLflow and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. How does Terraform handle state management when deploying MLflow on Amazon EKS?
ANS: – Terraform uses a state file to track resource configurations, which should ideally be stored remotely (e.g., in an Amazon S3 bucket) for collaboration.
2. How do you ensure the EBS volume is provisioned in the correct Availability Zone for Amazon EKS nodes?
ANS: – You must create the EBS volume in the same Availability Zone as the worker node where the MLflow pod is scheduled.

WRITTEN BY Keerthana N
Keerthana N works as a Research Intern at CloudThat. She holds a master's degree in Computer Applications and a strong passion for cloud technologies. Her keen interest in cloud computing has motivated her to pursue a career in AWS consulting. She is dedicated to learning and consistently works to keep pace with the latest advancements in AWS services and industry standards. With a clear focus on innovation and excellence, Keerthana aims to make a meaningful contribution to the cloud computing landscape by helping businesses effectively harness the power of AWS.


 Login
Login


 July 29, 2025
July 29, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments