|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) is a cost-effective, flexible, and scalable cloud-based email service that enables businesses to send and receive email using their domain. While sending email is a common use case, many organizations also need to receive and process incoming email for various applications like support tickets, email-based automation, or routing messages.
This blog will guide you through the essentials of setting up email receiving in Amazon SES, focusing on domain and email identity verification, DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) setup, Custom MAIL FROM Domain configuration, and updating the required Mail Exchanger (MX) and TXT DNS (Domain Name System) records provided by Amazon SES for that specific identity.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Introduction
Amazon SES (Simple Email Service) offers more than email sending, it also supports email receiving, enabling users to build automated workflows using AWS services like AWS Lambda, Amazon S3, and Amazon SNS. You must create and verify your domain identity and configure MX records to receive emails. These steps allow Amazon SES to accept and process incoming messages for your domain. This makes Amazon SES a powerful tool for building scalable, event-driven email applications in the cloud.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication standard that ensures the domain owner genuinely authorizes an email claiming to originate from a specific domain.
MX (Mail Exchange) Records are DNS entries that direct email traffic for a domain to the correct mail server. When someone sends an email to your domain, MX records determine which server should receive and handle that email. Configuring MX records properly ensures emails are routed to Amazon SES for processing.
TXT Records are DNS entries that allow domain owners to store text-based information in their DNS. They are commonly used for email authentication mechanisms like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. In the case of Amazon SES, TXT records are used to prove domain ownership and publish the DKIM public key to verify signed emails.
To start receiving emails using Amazon SES, three main steps are involved:
- Verifying your domain and creating an email identity to be used as the sender (From address)
- Enabling DKIM and configuring a custom MAIL FROM domain for the identity
- Updating the domain’s MX and TXT DNS records to route and authenticate email properly
Step-by-Step Configuration
- Domain Verification for Receiving Emails
You must prove domain ownership before Amazon SES can process incoming mail for your domain. This verification is separate from the verification required to send an email.
Steps:
- Open the Amazon SES Console.
- Navigate to Email Receiving → Domains.
- Click “Verify a New Domain”.
- AWS will generate the MX and TXT DNS records. Copy this.
- Add the MX and TXT records to your domain’s DNS using your DNS provider (Amazon Route 53, GoDaddy, Cloudflare, etc.).
- Wait for AWS to validate the domain.
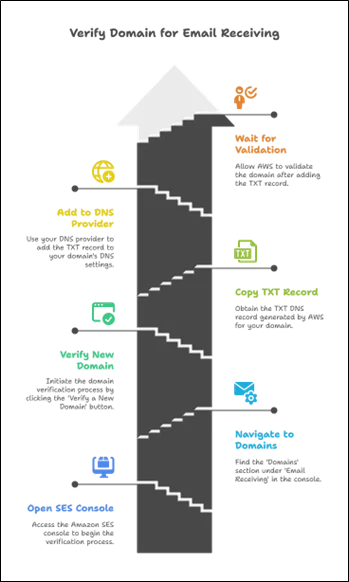
Once the record is detected, the domain is marked as verified, and Amazon SES is ready to accept mail, provided other steps are completed.
Tip: DNS changes can take a few minutes to a few hours to propagate globally. You can use tools like dig or online DNS checkers to verify propagation status.
- Creating a Sender Identity and Enabling DKIM
Once the domain is verified, the next step (especially for email sending) is to create an identity, typically an email address like noreply@yourdomain.com, that will be used as the “From” address.
- Navigate to Amazon SES → Verified Identities.
- Choose “Create Identity” → Email address, and enter an email like info@yourdomain.com.
- If the email address domain matches the already-verified domain, Amazon SES will automatically verify DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) for that identity.
- DKIM helps ensure the email is not tampered with in transit and improves email deliverability by authenticating the source.
- Setting Up a Custom MAIL FROM Domain
To further improve email reputation and ensure bounce handling and SPF alignment, it’s recommended that a custom MAIL FROM domain be configured.
Steps to configure:
- Go to Amazon SES → Verified Identities and click the identity you created.
- Scroll to the “MAIL FROM Domain” section and click Edit.
- Check “Use a custom MAIL FROM domain”.
- Enter a subdomain (e.g., mail.yourdomain.com) that will be used as the MAIL FROM address.
- Under Behavior on MX failure, choose “Use default MAIL FROM domain” to provide fallback safety.
- Click Save.
Amazon SES will now generate two DNS records that need to be published at your domain’s DNS level:
- An MX record pointing to Amazon SES’s inbound mail endpoint.
- A TXT record used for SPF verification (v=spf1 include:amazonses.com -all).
These records ensure that mail sent using your domain complies with sender authentication frameworks like SPF and that bounce messages are properly routed.
Note: These DNS records must be added correctly to your domain’s DNS settings. Failure to do so may result in email delivery issues, SPF failures, or the inability to track bounces.
Conclusion
Setting up email receiving in Amazon SES involves more than just domain verification, it requires configuring a complete sender identity with DKIM, setting up a custom MAIL FROM domain, and publishing the necessary DNS records (MX and TXT) to ensure proper email routing and authentication. These steps help improve email deliverability, align with SPF and DKIM standards, and enable advanced workflows through integration with other AWS services like AWS Lambda, Amazon S3, and Amazon SNS. With Amazon SES, organizations can build reliable, scalable, and fully managed inbound email pipelines within a secure and compliant AWS environment.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Amazon SES and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Do I need to verify the domain and email identity in Amazon SES?
ANS: – Yes. The domain must be verified for email receiving and for enabling DKIM. Additionally, the sender’s identity (e.g., noreply@yourdomain.com) should also be verified to see if it will be used in the “From” address.
2. Why should I configure a custom MAIL FROM domain?
ANS: – Using a custom MAIL FROM domain improves your email reputation, ensures SPF alignment, and provides more control over bounce messages. It’s especially recommended for production use cases or customer-facing communication.
3. Does Amazon SES automatically enable DKIM for verified identities?
ANS: – Yes. If your email identity matches a domain already verified in Amazon SES, DKIM will be automatically enabled. You can check and manage DKIM settings under each verified identity in the Amazon SES console.

WRITTEN BY Sridhar Andavarapu
Sridhar Andavarapu is a Senior Research Associate at CloudThat, specializing in AWS, Python, SQL, data analytics, and Generative AI. He has extensive experience in building scalable data pipelines, interactive dashboards, and AI-driven analytics solutions that help businesses transform complex datasets into actionable insights. Passionate about emerging technologies, Sridhar actively researches and shares knowledge on AI, cloud analytics, and business intelligence. Through his work, he strives to bridge the gap between data and strategy, enabling enterprises to unlock the full potential of their analytics infrastructure.


 Login
Login


 September 1, 2025
September 1, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments