|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
In today’s cloud-native world, applications are increasingly built using microservices that span multiple Amazon VPCs, accounts, and regions. Managing secure and scalable communication between these services can be complex, often requiring deep networking knowledge and custom configurations. Amazon VPC Lattice is a fully managed application networking service from AWS that simplifies this challenge. It enables developers to connect, secure, and monitor service-to-service communication without managing traditional networking constructs like IP addresses, load balancers, or peering connections.
Amazon VPC Lattice introduces a service-centric model for networking, allowing services to communicate using logical names and policies, rather than relying on infrastructure-level details. This makes it particularly valuable for organizations adopting microservices, serverless architectures, or multi-account setups. By abstracting the complexity of networking, VPC Lattice empowers teams to focus on building scalable and secure applications.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Key Features
Amazon VPC Lattice offers a rich set of features designed to streamline service connectivity and observability:
- Service Discovery: Services can be registered with VPC Lattice and discovered using logical names, eliminating the need for manual DNS management or IP tracking.
- Traffic Routing: Amazon VPC Lattice supports advanced routing capabilities, including path-based routing, weighted traffic distribution, and listener rules. This allows developers to control how requests are routed to different versions or components of a service.
- Security: Access control is enforced using AWS IAM policies and service-level permissions. This enables fine-grained authorization and supports zero-trust networking principles.
- Observability: VPC Lattice integrates with Amazon CloudWatch and AWS X-Ray, providing built-in metrics, logs, and distributed tracing. This helps teams monitor performance, troubleshoot issues, and optimize service interactions.
- Multi-VPC and Multi-Account Support: Services across different Amazon VPCs and AWS accounts can communicate seamlessly, reducing the need for complex peering or transit gateway setups.
Steps to Implement Amazon VPC Lattice
Implementing Amazon VPC Lattice involves a few key steps. Below is a simplified guide to get started:
Prerequisites:
- Access to AWS CLI or AWS Management Console
- At least two services (e.g., Amazon ECS, AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2) are deployed in different Amazon VPCs or accounts
- AWS IAM permissions to create and manage Amazon VPC Lattice resources
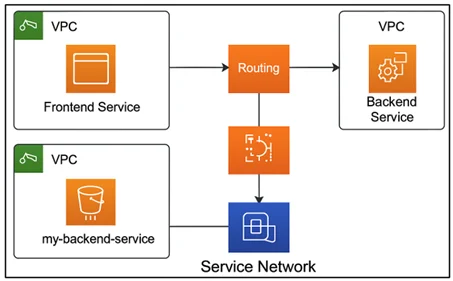
Step 1: Create a Service Network
A service network is a logical boundary that groups services and controls access.
Command:
|
1 |
aws vpc-lattice create-service-network --name my-service-network --auth-type AWS_IAM |
Step 2: Associate VPCs
Associate your VPCs with the service network to enable communication.
Command:
|
1 |
aws vpc-lattice create-service-network-vpc-association --service-network-identifier my-service-network-id --vpc-identifier vpc-xxxxxxxx |
Step 3: Register Services
Register your backend services (e.g., Amazon ECS, AWS Lambda) with Amazon VPC Lattice.
Command:
|
1 |
aws vpc-lattice create-service --name my-backend-service --auth-type AWS_IAM --custom-domain-name api.example.com |
Step 4: Configure Listeners and Routing Rules
Define how incoming traffic is handled and routed.
Commands:
|
1 2 |
aws vpc-lattice create-listener --service-identifier my-backend-service-id --protocol HTTP --port 80 aws vpc-lattice create-rule --listener-identifier my-listener-id --match '{"pathMatch":{"match":"PREFIX","value":"/api"}}' --action '{"forward":{"targetGroups":[{"targetGroupIdentifier":"my-target-group-id"}]}}' |
Step 5: Apply AWS IAM Policies
Control access to your services using AWS IAM.
Example Policy:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "vpc-lattice-svcs:Invoke", "Resource": "arn:aws:vpc-lattice:region:account-id:service/my-backend-service" } ] } |
Step 6: Monitor and Debug
Use Amazon CloudWatch and AWS X-Ray to monitor traffic, latency, and errors. These tools provide visibility into service performance and help identify bottlenecks or failures.
Handle Failures & Monitoring
Robust monitoring and failure handling are essential for production-grade systems. Amazon VPC Lattice supports several mechanisms to ensure reliability and performance:
- Retries & Backoff: Clients should implement retry logic with exponential backoff to handle transient failures.
- Health Checks: Use target group health checks to ensure traffic is only routed to healthy endpoints.
- Alerts: Set up Amazon CloudWatch alarms for latency, error rates, and request volume metrics.
- Tracing: Enable AWS X-Ray to trace requests across services and identify bottlenecks.
- Logging: Use Amazon CloudWatch Logs to capture detailed request and response data for diagnostics.
Use Cases
Amazon VPC Lattice is suitable for a wide range of scenarios:
- Microservices in Multi-Account Setup: Simplifies communication across AWS Organizations.
- Hybrid Cloud Communication: Connect on-premises services with cloud-native applications.
- Zero-Trust Networking: Enforce identity-based access without relying on IP addresses or security groups.
- Service Mesh Alternative: Offers similar capabilities to service meshes without requiring sidecar proxies.
- Simplified DevOps Pipelines: Integrate with CI/CD tools like Jenkins to automate service registration and updates.
Conclusion
Amazon VPC Lattice represents a significant shift in how developers approach service connectivity in AWS.
Its integration with AWS IAM, Amazon CloudWatch, and AWS X-Ray ensures that security and observability are built in, making it a robust solution for modern cloud architectures.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Amazon VPC Lattice and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is Amazon VPC Lattice, and how is it different from traditional networking in AWS?
ANS: – Amazon VPC Lattice is a fully managed application networking service that simplifies service-to-service communication across Amazon VPCs and accounts. Unlike traditional networking that relies on IP addresses, load balancers, and peering, Amazon VPC Lattice uses a service-centric model. Services are registered and discovered by name, and communication is governed by AWS IAM policies and routing rules, making it easier to manage and scale microservices.
2. Can Amazon VPC Lattice be used across multiple AWS accounts and regions?
ANS: – Yes. Amazon VPC Lattice supports multi-account and multi-VPC environments, making it ideal for organizations using AWS Organizations or managing services across different teams. However, while it supports multiple VPCs, cross-region support may require additional configuration depending on the service setup.
3. How does Amazon VPC Lattice handle security and access control?
ANS: – Security in Amazon VPC Lattice is managed using AWS IAM policies and service-level permissions. You can define which services or users can invoke a particular service, enabling fine-grained access control. This approach supports zero-trust networking, where access is based on identity rather than network location.

WRITTEN BY Riyazuddin
Riyazuddin works as an Associate Architect – Infra, brings over 15+ years of experience in DevOps, System Design, Networking, and Programming. Skilled in AWS, Azure, Terraform, Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, Openshift, Ansible, and Python, he designs scalable, secure systems and drives automation through cloud-native architectures and IaC. Known for his analytical mindset and leadership, he mentors teams and delivers high-impact, enterprise-ready solutions aligned with business goals.


 Login
Login


 September 1, 2025
September 1, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments