|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
Modern applications must be scalable, responsive, loosely coupled, and resilient to failure. To achieve these goals, enterprises are moving toward event-driven architectures (EDA), a design pattern where system components communicate by emitting and responding to events asynchronously.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides comprehensive tools and services that support building efficient, and scalable event-driven systems. This blog explores how to build event-driven architectures on Google Cloud, covering its core principles, components, implementation steps, use cases, best practices, and potential challenges.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
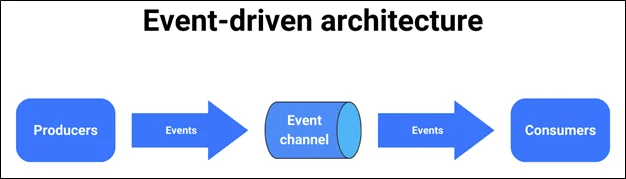
Event-Driven Architecture
Key Concepts:
- Event: A change in state (e.g., file upload, user signup, purchase made)
- Producer: Component that emits an event
- Consumer: Component that reacts to the event
- Event Bus/Queue: Middleware for transporting events between producers and consumers
Why Use GCP for Event-Driven Architectures?
Google Cloud offers native support for building event-driven systems with tools like:
- Cloud Pub/Sub: Messaging middleware for real-time, asynchronous communication
- Eventarc: Simplifies event routing across Google Cloud services
- Cloud Functions / Cloud Run: Serverless compute for handling events
- Cloud Storage and Cloud Audit Logs: Event sources for file uploads and audit trails
- Cloud Scheduler: Triggers time-based events
- Cloud Tasks: For reliable task execution with retries and deadlines
These services integrate seamlessly, providing elastic scale, managed infrastructure, and minimal operational overhead.
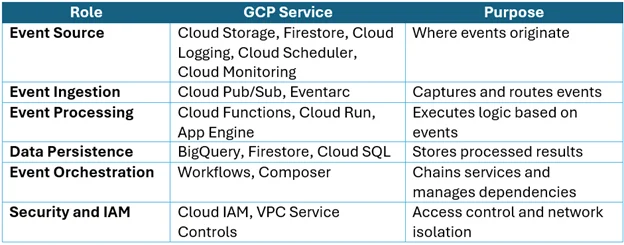
Core Components of an Event-Driven System on GCP
Here’s a breakdown of essential components in an event-driven architecture and their GCP equivalents:
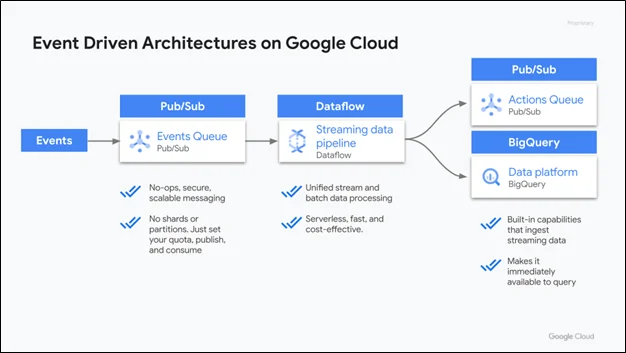
Event Flow: Example Architecture
Let’s take a closer look at a typical flow in GCP EDA:
- Event occurs: A file is uploaded to Cloud Storage
- Ingestion: The event is sent via Eventarc to a Cloud Function
- Processing: The function parses the file and stores metadata in BigQuery
- Notification: On success, another event is published to Cloud Pub/Sub, which triggers a Cloud Run service to send a Slack alert
- Persistence: Data is stored in a database or data warehouse for analysis
This architecture is scalable, decoupled, and event-driven, allowing each component to evolve independently.
Step-by-Step: Building an Event-Driven App on Google Cloud
Let’s walk through the steps to build a basic EDA where an image upload triggers a serverless function for processing.
Step 1: Set Up Cloud Storage (Event Source)
Create a Cloud Storage bucket:
|
1 |
gsutil mb gs://my-event-driven-bucket |
Enable notifications for object creation events.
Step 2: Create a Cloud Function (Event Processor)
Use Cloud Functions to respond to file uploads:
|
1 2 3 |
def process_image(data, context): file = data['name'] print(f'File uploaded: {file}') |
Deploy with an event trigger:
|
1 2 3 4 |
gcloud functions deploy process_image \ --runtime python310 \ --trigger-resource my-event-driven-bucket \ --trigger-event google.storage.object.finalize |
Step 3: Add a Cloud Pub/Sub Topic (For Decoupling)
|
1 |
gcloud pubsub topics create image-uploads |
Publish messages from the Cloud Function to the topic for further processing.
Step 4: Subscribe with Cloud Run (Optional Extension)
You can create a Cloud Run service that listens to the topic, processes metadata, sends alerts, or updates a dashboard.
Event Sources and Triggers in Google Cloud
Google Cloud supports a wide range of event sources:
Cloud Storage
- Triggers on file uploads or deletions
- Used in image processing, document workflows
Firebase / Firestore
- Real-time updates to databases
- Ideal for chat apps, IoT logs
Cloud Scheduler
- Time-based triggers (cron jobs)
- Used for periodic polling, reporting, cleanups
Cloud Audit Logs
- Logs administrative activity
- Good for security events, compliance alerts
Cloud Monitoring
- Create alerts and route them to Pub/Sub
- Enables metric-driven automation
Use Cases for Event-Driven Architectures
E-commerce
- Event: Customer places order
- Process: Inventory update, email confirmation, shipment scheduling
Media Processing
- Event: User uploads a photo
- Process: Resize, apply filters, store in different resolutions
Real-Time Analytics
- Event: Sensor emits temperature data
- Process: Stream into BigQuery, trigger alert on threshold breach
Document Workflows
- Event: Contract uploaded
- Process: OCR extraction, metadata tagging, save to Firestore
Benefits of Event-Driven Architectures
Scalability
- Services scale independently based on event load
- Ideal for microservices and distributed systems
Loose Coupling
- Producers and consumers are not tightly bound
- Increases system agility and modularity
Cost Efficiency
- Serverless compute options avoid idle costs
- Pay only for what you use
Resilience
- Failures are isolated
- Retry mechanisms like Pub/Sub dead-letter topics prevent data loss
Real-Time Responsiveness
- Enables near real-time systems
- Improves user experience and operational efficiency
Tools for Orchestration and Monitoring
Cloud Workflows
- Define workflows using YAML/JSON
- Integrate services like Cloud Run, Pub/Sub, Firestore
Cloud Composer (Airflow)
- DAG-based orchestration
- Supports data pipelines and batch-driven events
Cloud Logging + Monitoring
- Track logs, latency, and errors
- Set up alerts and dashboards
Cloud Trace + Profiler
- Visualize call stacks, latencies
- Optimize performance across services
Conclusion
Event-driven architecture on Google Cloud offers a modern way to design highly responsive, loosely coupled, and scalable systems. With services like Cloud Pub/Sub, Eventarc, Cloud Functions, and BigQuery, GCP provides everything you need to build and run production-grade, serverless, event-based applications.
Whether you’re building an e-commerce platform, a media pipeline, or a microservices system, adopting EDA with GCP will enhance your application agility, resilience, and operational efficiency.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Event-driven architecture and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is an event-driven architecture, and how does it benefit cloud-native applications?
ANS: – Event-driven architecture (EDA) is a design pattern where application components communicate by producing and responding to events. It benefits cloud-native applications by enabling asynchronous communication, loose coupling, real-time responsiveness, and horizontal scalability, making systems more resilient, agile, and easier to maintain.
2. How is Cloud Pub/Sub different from Eventarc in an event-driven architecture?
ANS: – Cloud Pub/Sub is a low-latency, global messaging service used to decouple producers and consumers through topics and subscriptions.
Eventarc, on the other hand, simplifies event routing from various Google Cloud and third-party sources to event handlers (like Cloud Run or Cloud Functions) using standardized CloudEvents. It’s ideal for automated event routing without needing to manage topic infrastructure manually.

WRITTEN BY Vinay Lanjewar
Vinay specializes in designing and implementing scalable data pipelines and end-to-end data solutions on the AWS Cloud. Skilled in technologies such as Amazon EC2, S3, Athena, Glue, QuickSight, and Lambda, he also leverages Python and SQL scripting to build efficient ETL processes. Vinay has extensive experience in creating automated workflows using AWS services, transforming and organizing data, and developing insightful visualizations with Amazon QuickSight. His work ensures that data is collected efficiently, structured effectively, and made analytics-ready to drive informed decision-making.


 Login
Login

 July 29, 2025
July 29, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments