|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction to GitHub
GitHub is a platform for online software development. It is used for software project storage, tracking, and collaboration.
Some of its significant features are as follows.
- Collaboration
- Integrated issue and bug tracking
- Track and assign tasks
- Wikisc
- Project management
- Team management
- Code hosting
- Graphical representation of branches
- Git repositories hosting
- Conversations
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
How does GitHub work?
GitHub is a platform for hosting code that allows for version control and collaboration. It allows you and others to collaborate on projects from anywhere. This tutorial will teach you the fundamentals of GitHub, such as repositories, branches, commits, and
The key benefits of GitHub are as follows.
- GitHub makes it simple to contribute to open-source projects.
- It contributes to the creation of an excellent document.
- You can impress a recruiter by displaying your work. You will have a better chance of being hired if you have a GitHub profile.
- It allows your work to be seen by the public.
- Changes in your code can be tracked across versions.
Introduction to GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions makes it simple to automate all your software workflows, and it now includes world-class CI/CD. Build, test, and deploy your code directly from GitHub. Make code reviews, branch management, and issue triaging work the way you want them to.
GitHub Actions extends beyond DevOps by allowing you to run workflows when other events occur in your repository. You can, for example, run a workflow that adds the appropriate labels whenever someone creates a new issue in your repository.
Components of GitHub Actions
Workflows
A workflow is a programmable automated process that executes one or more jobs. Workflows are defined by a YAML file that is checked into your repository and will run when triggered by an event in your repository, manually, or on a predefined schedule.
Events
An event is a specific activity in a repository that initiates the execution of a workflow. When someone creates a pull request, opens an issue, or pushes a commit to a repository, for example, activity can originate from GitHub. You can also run a workflow on a schedule,
Jobs
A job is a collection of workflow steps that run on the same runner. Each step is either a shell script to be executed or an action to be performed. Steps are carried out sequentially and are interdependent. Because each step is executed on the same runner, data can be shared from one step to the next. For example, you could have a step that builds your application followed by a step that tests the built application.
Actions
An action is a GitHub Actions platform custom application that performs a complex but frequently repeated task. Use actions to help you reduce the amount of repetitive code in your workflow files. An action can fetch your git repository from GitHub, install the necessary toolchain for your build environment, or configure your cloud provider authentication.
Runners
When your workflows are triggered, they are executed by a runner. Each runner can only run one job at a time. To run your workflows, GitHub provides Ubuntu Linux, Microsoft Windows, and macOS runners; each workflow run executes in a new, freshly provisioned virtual machine. GitHub also provides larger runners in a variety of configurations.
Steps to Perform GitHub Actions and Create a Workflow
Step 1 – Create a GitHub account and log in to it. Open the link given below:
https://github.com/skills/hello-github-actions
Click on use this template:

That will take you to create a new repository:
In the new tab, follow the prompts to create a new repository. Choose your personal account or an organization to host the repository for the owner.

Step 2 – Create a workflow file
- Open a new browser tab and navigate to this same repository. Then, work on the steps in your second tab while you read the instructions in this tab.
- Navigate to the Code tab.
- From the main branch dropdown, click on the welcome-workflow branch.
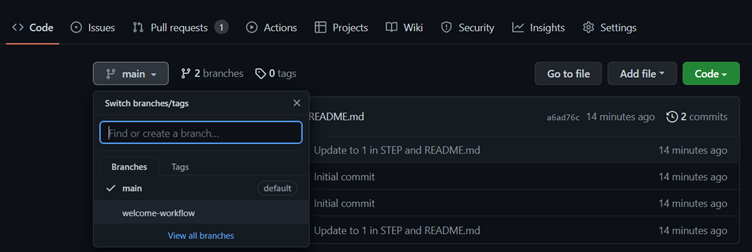
4. Navigate to the .github/workflows/ folder, then select Add file and click on Create a new file.
5. In the Name your file… field, enter welcome.yml.
6. Add the following content to the welcome.yml file:
|
1 2 3 4 |
name: Post welcome comment on: pull_request: types: [opened] |
7. To commit your changes, click Commit new file.
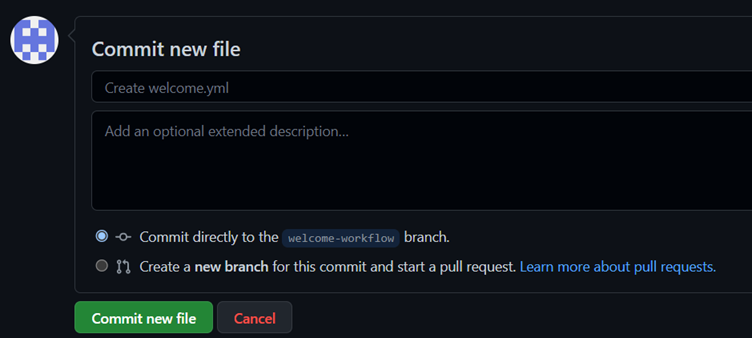
Step 3 – In this step of our exercise, we will add a “build” job. We will specify ubuntu-latest as the fastest and cheapest job runner available.
- Open the welcome.yml file and edit and paste the content
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
name: Post welcome comment on: pull_request: types: [opened] jobs: build: name: Post welcome comment runs-on: ubuntu-latest |

2. Click Start commit in the top right of the workflow editor.

3. Open the welcome.yml file and edit and paste the content
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
name: Post welcome comment on: pull_request: types: [opened] jobs: build: name: Post welcome comment runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - run: gh pr comment $PR_URL --body "Welcome to the repository!" env: GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} PR_URL: ${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url }} |

4. Click Start commit in the top right of the workflow editor.

5. In your repo, click on the Pull requests tab.
6. Click on the Post welcome comment workflow pull request.

7. Click Merge pull request, then Click Confirm merge.



Step 4 – Click on the delete branch to delete your welcome-workflow branch.

- You can see all your commits and pull requests under the actions tab

2. Create a new branch named test-workflow. Then go to README.md and add Hello from CloudThat 🙂

3. Go to your pull requests tab and click on compare & pull request

4. Click on create a pull request

5. Click on the merge pull request


6. Go to actions to see the workflow runs and pull requests

Conclusion
The GitHub interface is simple enough that even inexperienced coders can use it. Without GitHub, using Git generally necessitates a bit more technical know-how and command-line GitHub Actions integrates the automation into the software development lifecycle on GitHub through event-driven triggers. These are predefined events that can range from creating a pull request to creating a new brand in a repository. You can use GitHub Actions to automate nearly every aspect of your application development processes.
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is Git?
ANS: – Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system designed to handle projects of all sizes with speed and efficiency.
2. What is Runner?
ANS: – When your workflows are triggered, they are executed by a runner.
3. What is workflow?
ANS: – When your workflows are triggered, they are executed by a runner.

WRITTEN BY Swapnil Kumbar
Swapnil Kumbar is a Senior Research Associate at CloudThat with over 2.5 years of experience in DevOps. He specializes in AWS, Kubernetes, automation, and cloud-native technologies. Passionate about innovation and research, Swapnil focuses on building scalable infrastructure, optimizing deployments, and exploring emerging tools. In his free time, he actively contributes to knowledge sharing and community learning initiatives.


 Login
Login


 January 3, 2023
January 3, 2023 PREV
PREV











Comments