|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
In today’s sustainability‑driven world, organisations are increasingly focused on understanding and reducing their carbon impact. Cloud usage and digital infrastructure are significant contributors to corporate emissions, and visibility into those emissions is essential. In response, Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool (CCFT) in March 2022 to enable customers to measure the estimated carbon emissions associated with their AWS workloads.
Recently, AWS announced a major expansion of the CCFT to include additional emissions categories, most notably, Scope 3 emissions, such as fuel & energy‑related activities (FERA), embodied emissions of hardware and buildings, and upstream transportation. This blog explores the enhancements, key features, implementation architecture, real‑world use cases, and FAQs.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Expanded Emissions Coverage: What’s New?
The latest release of the Customer Carbon Footprint Tool expands coverage across all emission categories, refining the existing Scope 1 and Scope 2 methodologies and introducing new Scope 3 categories.
- Scope 1 and 2: Refined models for accurate energy and operational emissions attribution.
- Scope 3: Includes upstream fuel and energy‑related activities (FERA), embodied emissions of data centre hardware and buildings, and transportation within the AWS supply chain.
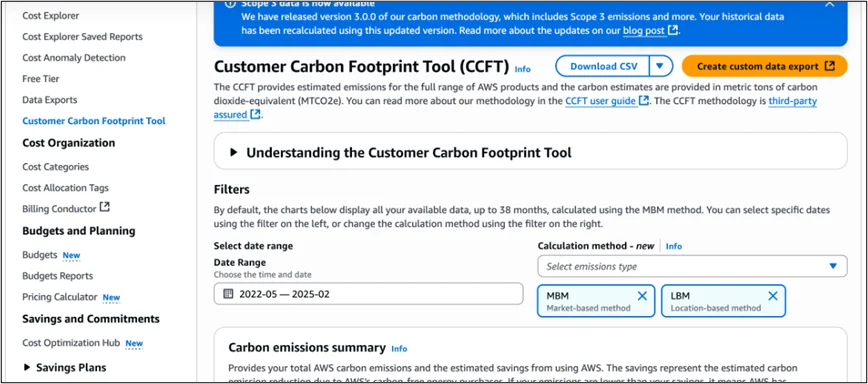
- Granular exports: Enables customers to export monthly emissions data via the AWS Billing and Cost Management console.
- Regional breakdown: Emissions can be viewed per AWS Region for workload placement analysis.
- Location‑based and Market‑based accounting: Customers can view emissions under both methods, depending on grid intensity preferences.
Architecture & Implementation Steps
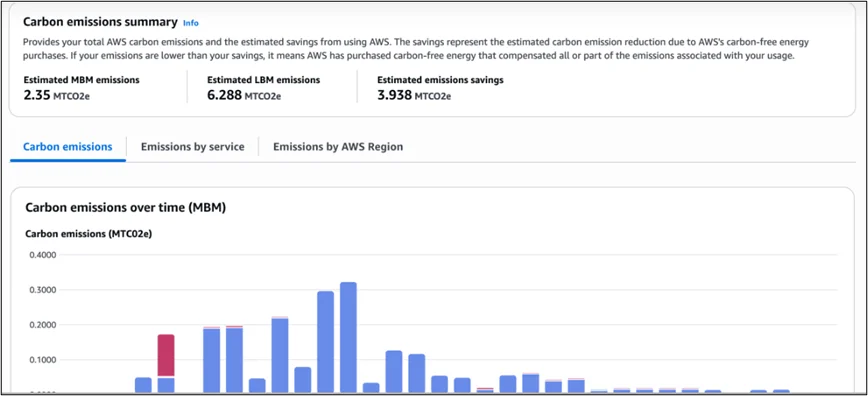
The architecture of the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool integrates with AWS Billing and Cost Management, as well as AWS Data Exports. It allows users to automate emissions data collection, store results in Amazon S3, and visualize insights via Amazon Athena or Amazon QuickSight.
Implementation steps:
- Enable the Customer Carbon Footprint Tool in the AWS Billing Console.
- Configure Carbon Emissions Data Export in the Data Exports section and select or create an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Use AWS Glue to catalogue the emissions data and query it via Amazon Athena.
- Build a dashboard in Amazon QuickSight for emissions trends and Scope 3 insights.
- Analyse and act on findings, optimise workloads, migrate to cleaner regions, or right‑size infrastructure.
Use Cases
The expansion of the CCFT has opened new possibilities for organizations aiming to integrate sustainability into their digital operations. Here are several detailed use cases demonstrating how enterprises can leverage these enhancements:
- Enterprise‑Wide Carbon Tracking – Large organizations often operate multiple AWS accounts across regions and business units. By consolidating CCFT exports, sustainability teams can create centralized dashboards that aggregate emissions data for all workloads. This unified visibility enables enterprises to benchmark emissions intensity across regions and services, identify high-impact workloads, and drive carbon-aware migration strategies. For example, a multinational bank might use CCFT data to compare the carbon efficiency of compute workloads in Frankfurt versus those in Singapore, thereby aligning its cloud strategy with internal sustainability goals.
- Workload Placement Optimization – The regional breakdown feature in CCFT provides insights into the carbon intensity of specific AWS Regions. By correlating emissions data with renewable energy mix and regional grid intensity, customers can make informed decisions about workload placement. For instance, a SaaS provider can reduce emissions by relocating compute-intensive workloads to regions powered by higher proportions of renewable energy, such as AWS Europe (Stockholm) or US West (Oregon). This allows sustainability and DevOps teams to collaborate on balancing performance, latency, and carbon efficiency.
- Hardware Lifecycle and Procurement Planning – Scope 3 coverage now includes embodied emissions of IT hardware and data center infrastructure. This helps procurement and infrastructure teams understand the upstream carbon cost of new hardware deployments. Organizations can evaluate whether to extend hardware lifecycles, adopt refurbished equipment, or transition to serverless architectures that reduce hardware demand. Enterprises in manufacturing and logistics can integrate these insights into supply chain sustainability models to track embodied emissions from cradle to grave.
- Sustainability Reporting and Compliance – Many companies must comply with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) regulations that require transparent reporting of GHG emissions. By utilizing CCFT data exports and integrating them with ESG reporting platforms, organizations can automate carbon disclosure aligned with frameworks such as the GHG Protocol, CDP, and the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive). This not only reduces manual data handling but also enhances the accuracy of sustainability reports submitted to investors and regulators.
- Cost‑Carbon Optimization (FinOps + GreenOps) – The integration of emissions and financial data enables teams to assess both the cost and environmental impact of workloads. Cloud financial operations (FinOps) teams can now extend their analysis to include carbon efficiency metrics, creating a new discipline often referred to as ‘GreenOps’. For instance, organizations can identify services that have high carbon intensity but low utilization and target them for consolidation or migration to energy‑efficient instance types. This dual optimization approach ensures that cost savings align with sustainability objectives.
Conclusion
The expansion of the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool to include Scope 3 emissions marks a significant milestone in cloud sustainability.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool?
ANS: – It’s a dashboard and reporting utility that estimates carbon emissions (in CO₂e) associated with AWS usage by service, region, and account.
2. What emission scopes are now included?
ANS: – CCFT now includes Scope 1, Scope 2, and selected Scope 3 categories such as FERA, embodied emissions, and transportation.
3. How do I access the emissions data?
ANS: – You can export monthly carbon emissions data through the AWS Billing & Cost Management Data Exports feature to Amazon S3.

WRITTEN BY Neetika Gupta
Neetika Gupta works as a Subject Matter Expert at CloudThat with experience deploying multiple data science projects across various cloud platforms. She has successfully delivered end-to-end AI applications tailored to business requirements on cloud frameworks such as AWS, Azure, and GCP. Neetika also specializes in deploying scalable applications using CI/CD pipelines.


 Login
Login


 November 6, 2025
November 6, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments