|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
In modern data engineering and analytics, integrating tools like Azure Databricks and Azure Data Factory (ADF) provides immense flexibility and power for orchestrating big data workflows. Whether you’re transforming data at scale, performing machine learning operations, or building ETL pipelines, triggering a Databricks file (notebook or script) from ADF is a critical capability for production-grade systems.
In this blog, we will walk through how to run a Databricks file using ADF, explore use cases, advantages, and best practices, and understand the underlying integration mechanism.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Why Integrate Databricks with ADF?
Here are a few reasons why the integration between ADF and Databricks is essential:
- Seamless Orchestration: Easily embed Databricks processing into broader ETL workflows managed by ADF.
- Modular Pipelines: Use Databricks notebooks for complex data transformations and manage pipeline logic with ADF.
- Automation: Schedule and trigger Databricks notebooks via ADF based on events, time, or data arrival.
- Governance and Monitoring: Use ADF’s monitoring capabilities to track the execution and health of your Databricks jobs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Run Databricks File Using ADF
Let’s break this down into simple steps.
Step 1: Create a Databricks Notebook
- Go to your Azure Databricks workspace
- Create a new notebook (e.g., MyADFNotebook)
- Write a simple code snippet for testing. For example:
|
1 |
dbutils.notebook.exit("ADF Execution Successful") |
Save your notebook.
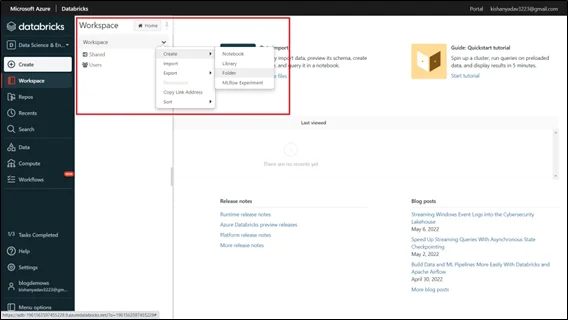
Fig 1. Azure Databricks Notebook
Step 2: Generate a Databricks Access Token
- In the Databricks workspace, go to your user profile (top-right corner) → User Settings.
- Under the Access Tokens tab, click Generate New Token
- Give it a name (e.g., ADF-Token) and copy the token. (You won’t see it again!)
Step 3: Create a Linked Service in ADF for Databricks
- Open your Azure Data Factory studio
- Navigate to Manage → Linked services
- Click + New → Choose Azure Databricks
Configure as follows:
- Name: AzureDatabricks_LinkedService
- Databricks Workspace URL: Can be found in the browser
(https://<instance>.azuredatabricks.net)
- Authentication Type: Personal Access Token
- Access Token: Paste the token from Step 2
- Choose the appropriate cluster or allow ADF to create a new job cluster
Click Create
Step 4: Create a Pipeline to Run Databricks Notebook
- Go to Author → Click + → Pipeline
- In the Activities pane, search for Databricks → Drag Notebook activity
- Configure the notebook activity:
- Name: Run_Databricks_Notebook
- Linked service: Select the one created in Step 3
- Notebook path: Browse and select your notebook
- Base Parameters: (Optional) Set input parameters if your notebook requires them
Click Debug to test the notebook execution.
Step 5: Trigger and Monitor Execution
- Publish all changes
- Create a trigger to run the pipeline on demand, on a schedule, or upon events
- Navigate to the Monitor tab in ADF to see pipeline execution details, logs, and outcomes
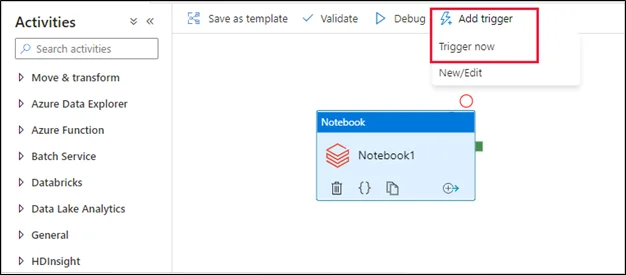
Common Use Cases
Here are real-world scenarios where running Databricks files via ADF is beneficial:
- ETL/ELT Workflows: Use Databricks for transformation logic within a broader ADF pipeline
- Machine Learning Pipelines: Schedule model training and scoring notebooks
- Data Quality Checks: Run Databricks scripts to validate and clean data before ingestion
- Batch Processing: Automate batch data pipelines using ADF triggers
Security Considerations
- Token Expiry: Regularly rotate Databricks tokens and securely store them in Azure Key Vault
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensure proper roles are assigned to restrict access to notebooks and pipelines
- Audit Logs: Enable logging in both ADF and Databricks for traceability
Logging and Monitoring
- Use ADF’s Monitor Hub to view:
- Pipeline status
- Duration
- Error messages
- In Databricks:
- Monitor job runs and cluster logs
- Use notebook.exit() to return custom status messages
- Consider writing custom logs to Azure Log Analytics or a storage account for long-term monitoring
Best Practices
- Modularize Notebooks: Keep notebooks focused on single tasks for easier maintenance.
- Use Job Clusters for ADF Runs: Helps optimize costs by spinning up only when needed.
- Parameterize Pipelines: Pass dynamic inputs like file paths, dates, or configurations via ADF.
- Integrate Key Vault: Store and retrieve tokens and secrets securely.
- Version Control: Use Git integration in Databricks for better code management.
- Monitoring Alerts: Set up alerting mechanisms in ADF for failure or performance thresholds.
Conclusion
Whether building complex data pipelines, training ML models, or just running scheduled data transformations, integrating these tools effectively can streamline your operations and increase productivity.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Azure Data Factory and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Can I run Python or Scala scripts directly from ADF, or must it be a notebook?
ANS: – ADF primarily integrates with Databricks notebooks. However, you can call Python or Scala scripts as part of a notebook. If you need to run a script directly, consider embedding it within a Databricks notebook or converting it into a notebook format.
2. Do I need to use a specific cluster type in Databricks when triggering from ADF?
ANS: – You can use either:
- An existing interactive cluster, or
- A job cluster defined in the ADF linked service

WRITTEN BY Vinay Lanjewar
Vinay specializes in designing and implementing scalable data pipelines and end-to-end data solutions on the AWS Cloud. Skilled in technologies such as Amazon EC2, S3, Athena, Glue, QuickSight, and Lambda, he also leverages Python and SQL scripting to build efficient ETL processes. Vinay has extensive experience in creating automated workflows using AWS services, transforming and organizing data, and developing insightful visualizations with Amazon QuickSight. His work ensures that data is collected efficiently, structured effectively, and made analytics-ready to drive informed decision-making.


 Login
Login


 July 29, 2025
July 29, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments