|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
In the dynamic world of cloud computing, ensuring the high availability, scalability, and performance of your applications is paramount. Azure offers a comprehensive suite of load balancing services, each designed to address specific needs across different layers of the network stack. Understanding their distinctions is crucial for architecting robust and efficient cloud solutions.
Let’s dive into the various Azure load balancers and when to deploy them.
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
1. Azure Load Balancer: The Foundation (Layer 4)
Azure Load Balancer is the workhorse of regional load balancing, operating at Layer 4 (Transport Layer – TCP/UDP) of the OSI model. It helps in distributing the incoming traffic to the backend VMs.
When to use it:
Internal Load Balancing: For distributing traffic between different tiers of an application within the same virtual network (e.g., web servers to application servers, or application servers to databases). This enhances internal application availability and scalability.
External Load Balancing for Non-HTTP(S) Traffic: When you need to expose services to the internet that don’t rely on HTTP or HTTPS, such as gaming servers (UDP) or custom TCP protocols.
Simple, High-Performance Regional Load Balancing: For applications requiring ultra-low latency and high throughput where advanced application-layer features are not a priority.
Outbound Connections: A public Azure Load Balancer can also provide outbound connections for VMs within your virtual network by translating their private IP addresses to public ones.
Key Features: Health probes (TCP, HTTP), session persistence (sticky sessions), automatic failover, zone redundancy, and cross-region load balancing (with Standard SKU).
2. Azure Application Gateway: The Web Traffic Specialist (Layer 7)
It is a Layer 7 load balancer which uses HTTP/HTTPS protocols. It offers advanced routing capabilities and specialized features for web applications.
When to use it:
Web Application Load Balancing: Ideal for managing traffic to web applications, including those hosted on Azure App Services, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), or VMs running web servers.
SSL/TLS Offloading: To offload the CPU-intensive task of SSL/TLS encryption/decryption from your backend servers, improving their performance.
Web Application Firewall (WAF): Integrates with a WAF to protect your web applications from common web vulnerabilities and exploits like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
URL-based Routing (Path-based routing): For directing traffic to different backend pools based on the URL path (e.g., /images to an image server pool, /videos to a video server pool).
Multi-site Hosting: To host multiple web applications on the same Application Gateway using host headers.
Session Affinity (Cookie-based): To ensure a user’s requests are consistently routed to the same backend server, crucial for applications that maintain session state.
3. Azure Front Door: The Global Accelerator (Layer 7 CDN + WAF)
Azure Front Door is a global, scalable entry point that uses Microsoft’s global edge network to accelerate, secure, and globally load balance web applications. It’s effectively a global Application Gateway with CDN capabilities.
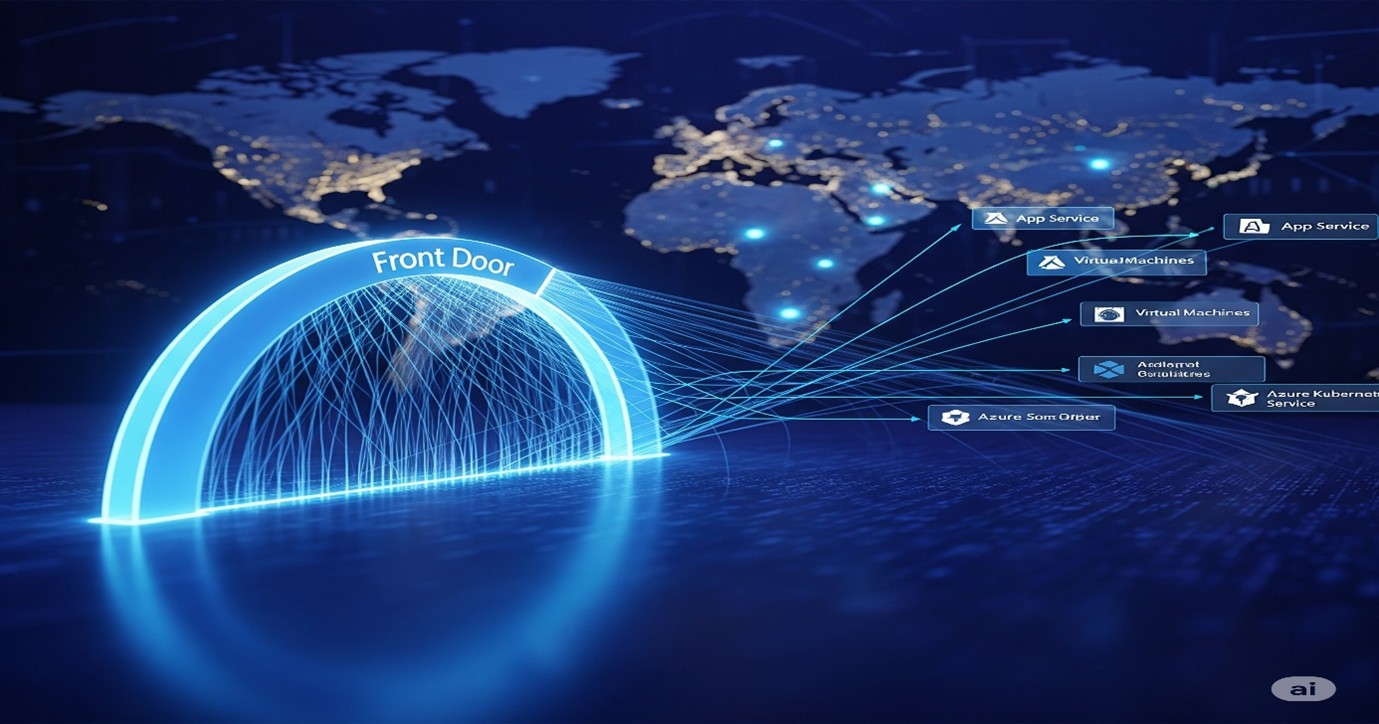
When to use it:
Global Web Application Delivery: When you need to deliver web applications and content globally with optimal performance and high availability. It uses anycast routing to direct users to the closest point of presence (PoP).
Dynamic Site Acceleration (DSA): To significantly improve the performance of dynamic web content by optimizing network paths.
Global WAF Protection: For centralized web application firewall protection at the edge, closer to your users.
Multi-region Architectures with Active-Active or Active-Passive: For seamless failover across different Azure regions in case of a regional outage.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Capabilities: While not a dedicated CDN, it offers caching capabilities for static content at the edge.
4. Azure Traffic Manager: The DNS-based Global Director (DNS Layer)
This is a DNS-based load balancer which distribute the traffic across the global regions to different public facing applications. Unlike the other services, Traffic Manager doesn’t proxy traffic; it simply returns the IP address of the chosen endpoint in response to a DNS query.

When to use it:
Global DNS-based Traffic Distribution: When you need to direct users to the most appropriate service endpoint based on various routing methods (e.g., performance, priority, geographic, weighted).
Disaster Recovery (Failover): For quickly rerouting traffic to a healthy endpoint in another region if the primary region experiences an outage.
Hybrid Cloud Deployments: To distribute traffic between Azure-hosted applications and on-premises datacenters.
Service Maintenance without Downtime: To seamlessly shift traffic away from an endpoint undergoing maintenance.
Any Protocol (not just HTTP/S): Since it operates at the DNS level, it’s suitable for load balancing any internet-facing service, regardless of the application protocol.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right Azure load balancing solution is not a one-size-fits-all decision; it’s a strategic choice that depends on the specific needs of your application. Azure Load Balancer provides a solid, high-performance foundation for regional, Layer 4 traffic distribution. For web applications, Application Gateway offers advanced Layer 7 features like SSL offloading and WAF. When your reach extends globally, Azure Front Door and Traffic Manager become essential tools. Front Door accelerates and secures web traffic at the edge, while Traffic Manager provides DNS-based global traffic routing for a wide range of services. By carefully considering your application’s architecture, traffic patterns, and performance requirements, you can select the optimal combination of these powerful services to build highly available, scalable, and resilient cloud solutions on Azure.
For a good understanding of networking and choose the right Load Balancer for your business requirements, referring to these courses would be helpful:
https://www.cloudthat.com/training/azure/az-305-designing-microsoft-azure-infrastructure-solution
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY Naved Ahmed Khan
Naved Ahmed Khan is a Research Associate with over 5+ years of experience in Cloud. He is an MCT and also the winner of Top 100 MCT Quality Awards Winner for 2024-25. Naved is known for adding humor into his training making it engaging and fun. He has a passion for IoT services because of his roots in Electrical & Electronics Engineering and his habit of reading fictional novels add an imaginative punch into his training method. With 12 certifications in Azure, he has trained over 1000+ individuals across different verticals like Infra & Architect, Security, Data and AI. His core skillset lies in Networking, Security, Python and Powershell.


 Login
Login


 September 17, 2025
September 17, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments