|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
In today’s cloud-native world, organizations often demand not only scalable data storage and processing but also disaster recovery and high availability across regions. To address these needs, building a multi-region data lakehouse architecture has become a popular and effective solution.
In this blog, we explore how to build a resilient and secure multi-region data lakehouse using AWS Lake Formation and Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication (CRR). This approach ensures high availability, compliance, data governance, and analytical scalability, all while minimizing complexity.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Data Lakehouse
A data lakehouse unifies the flexibility of data lakes with the performance of data warehouses. It enables organizations to store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in a central repository (such as Amazon S3), while providing schema enforcement, ACID transactions, and query performance comparable to that of data warehouses.
By integrating services such as AWS Lake Formation, AWS Glue, Amazon Athena, and Amazon Redshift Spectrum, AWS enables a seamless data lakehouse solution that is both scalable and cost-effective.
Why Multi-Region?
Operating in a single AWS region comes with risks like service disruptions, outages, or compliance violations (especially in finance, healthcare, or government sectors). A multi-region architecture offers the following benefits:
- Disaster Recovery: Data remains available if one region fails.
- Low Latency Access: Serve users from the region closest to them.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet country-specific data residency laws.
- High Availability: Keep analytics workloads running smoothly.
Core Components of the Architecture
To build a resilient multi-region lakehouse, we combine the following AWS services:
- Amazon S3 – Storage backbone of the lakehouse.
- AWS Lake Formation – Fine-grained access control and catalog management.
- Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication (CRR) – Ensures data redundancy in another region.
- AWS Glue – For ETL and metadata synchronization.
- Amazon Athena / Amazon Redshift Spectrum – To query lake data.
- AWS CloudTrail + CloudWatch – For auditing and monitoring.
Step-by-Step: Building the Multi-Region Lakehouse
Let’s break down the process into the following steps:
Step 1: Set Up the Primary Data Lake in Amazon S3
- Create an Amazon S3 bucket in the primary region (e.g., us-east-1) to serve as the source of truth for raw, curated, and transformed data.
- Use folder structures or prefixes to organize data (e.g., /raw/, /curated/, /analytics/).
Step 2: Enable Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
- Create a replica bucket in the secondary region (e.g., ap-south-1).
- Enable CRR on the primary bucket:
- Go to S3 console → Management → Replication.
- Set replication rules based on prefixes, tags, or the entire bucket.
- Ensure both buckets have versioning enabled.
- Assign appropriate AWS IAM roles for replication permissions.
Tip: Use SSE-KMS encryption and replicate KMS keys securely in both regions.
Step 3: Set Up AWS Lake Formation in Both Regions
Lake Formation centralizes access control, table registration, and metadata governance.
- In both regions, register the corresponding Amazon S3 buckets in Lake Formation.
- Define Lake Formation administrators and assign permissions.
- Catalog your data using Glue Crawlers and register the tables.
Note: AWS Glue crawlers need to be run independently in both regions unless metadata synchronization is automated.
Step 4: Sync Metadata Across Regions
While Amazon S3 replicates data, metadata doesn’t sync automatically.
You can:
- Export the AWS Glue Data Catalog using the get_table API, and re-import into the secondary region using create_table.
- Or, use custom scripts/Lambda functions to automate periodic metadata synchronization.
For example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# Pseudocode: Copy metadata from Region A to Region B source_client = boto3.client('glue', region_name='us-east-1') target_client = boto3.client('glue', region_name='ap-south-1') table = source_client.get_table(DatabaseName='analytics', Name='sales_data') target_client.create_table(DatabaseName='analytics', TableInput=table['Table']) |
Step 5: Enforce Security and Fine-Grained Access Control
Lake Formation allows you to:
- Grant table-level, column-level, or row-level permissions.
- Manage access using AWS IAM, SSO, or Active Directory
Ensure that identical security policies are enforced in both regions. Automate this using AWS CLI or CloudFormation for repeatable deployments.
Step 6: Query Data with Amazon Athena or Amazon Redshift Spectrum
In both regions:
- Set up Amazon Athena or Amazon Redshift Spectrum to query data stored in Amazon S3.
- Connect Amazon Athena to the regional AWS Glue Catalog.
- For Amazon Redshift Spectrum, create external schemas mapped to the Lake Formation catalog.
You now have a mirrored analytical environment in both regions.
Auditing and Monitoring
- Use AWS CloudTrail to track Lake Formation access and AWS Glue events.
- Set up Amazon CloudWatch Alarms to monitor replication delays, failed jobs, and unauthorized access.
- Integrate with Amazon SNS for proactive alerts.
Disaster Recovery Scenario
If the primary region fails:
- Analysts can immediately switch to Amazon Athena/Amazon Redshift in the secondary region.
- Since Amazon S3 data is already replicated and metadata is in sync, there is minimal downtime.
- Automation scripts can update DNS, endpoint configurations, or dashboard links to redirect traffic.
Cost Considerations
- Amazon S3 CRR incurs additional charges for data transfer and storage.
- Glue metadata syncing may require custom automation.
- However, these costs are justified by the availability, fault tolerance, and compliance
Conclusion
Building a multi-region data lakehouse using AWS Lake Formation and Amazon S3 replication is a powerful approach to ensure resilience, security, and availability in your data platform. Whether you’re preparing for disaster recovery or ensuring low-latency access across geographies, this architecture can scale to meet your evolving data and business needs.
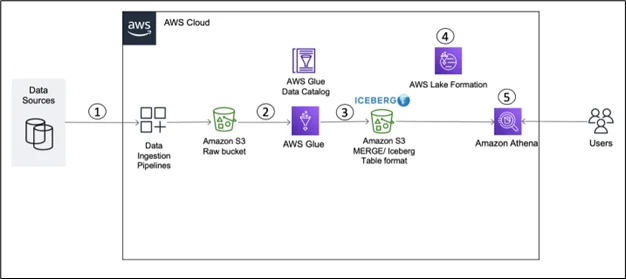
Image source: Link
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding AWS Lake Formation or Amazon S3 and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a data lake and a data lakehouse?
ANS: – A data lake stores raw data in its native format, while a data lakehouse combines the storage scalability of a data lake with data management and querying capabilities typically found in a data warehouse, enabling both structured and unstructured analytics.
2. Why should I consider a multi-region architecture for my data lakehouse?
ANS: – A multi-region architecture enhances disaster recovery, ensures high availability, delivers improved performance for globally distributed users, and facilitates compliance with data residency and regulatory requirements.
3. Does Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication replicate metadata like AWS Glue Data Catalog or Lake Formation permissions?
ANS: – No, Amazon S3 CRR only replicates data objects. Metadata, such as AWS Glue tables or AWS Lake Formation permissions, must be synchronized manually or through custom scripts.

WRITTEN BY Khushi Munjal
Khushi Munjal works as a Research Associate at CloudThat, specializing in Tech Consulting. With hands-on experience in services like Redshift, EMR, Glue, Athena, and more, she is passionate about designing scalable cloud solutions. Her dedication to continuous learning and staying aligned with evolving AWS technologies drives her to deliver impactful results and support clients in optimizing their cloud infrastructure.


 Login
Login


 November 28, 2025
November 28, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments