|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
🧭 Introduction
In the cloud-native world, Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications. Whether you’re a developer, system admin, or DevOps engineer, learning Kubernetes is a must-have skill.
In this blog, we will cover:
- What is Kubernetes and AKS?
- How to create your first Kubernetes cluster on Azure
- The core building block: Pods
- Hands-on labs: Namespaces, Pod creation, YAML, labels, and interactive access
Let’s break this down with theory + practical labs to give you a full-circle understanding! 🔄
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
🌩️ What is Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)?
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a managed Kubernetes service offered by Microsoft Azure. It simplifies the deployment, management, and operations of Kubernetes clusters by:
- Handling control plane management
- Integrating with Azure AD, monitoring, and logging
- Providing automatic updates and scaling
- Reducing operational overhead for teams
💡 With AKS, you don’t need to worry about manually setting up the Kubernetes master components—it’s managed for you!
⚙️ Step-by-Step: Creating Your First AKS Cluster
🚀 Step 1: Launch Azure Cloud Shell
Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based terminal that comes preconfigured with the Azure CLI.
- Open Azure Portal.
- Click on the Cloud Shell icon in the top-right corner.
- Choose Bash, wait for initialization.
🔧 Step 2: Set Environment Variables
RESOURCE_GROUP=”K8S-RG”
CLUSTER_NAME=”aks-cluster”
|
1 |
LOCATION="centralus" |
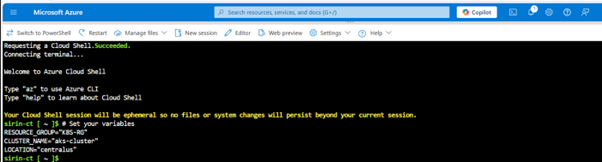
✅ These variables help in reusability and better scripting practices.
📌 Make sure Resource Group already exists
☸️ Step 3: Create the AKS Cluster
|
1 |
az aks create --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER_NAME --node-count 2 --node-vm-size Standard_DS2_v2 --generate-ssh-keys |
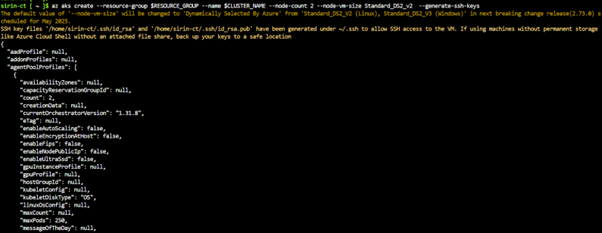
This command does the following:
- Creates a managed Kubernetes cluster with 2 worker nodes
- Uses VM size Standard_DS2_v2 (2 vCPUs, 7GB RAM)
- Generates SSH keys for secure access
⏳ Takes a few minutes. After completion, you’ll get details like fqdn, kubeConfig path, and more.
🔗 Step 4: Connect to Your AKS Cluster
Get a list of Kubernetes Clusters
|
1 |
az aks list -o table |
![]()
|
1 |
az aks get-credentials -n aks-cluster -g K8S-RG |
![]()
📌 This downloads the kubeconfig and merges it with your local Kubernetes config, allowing you to use kubectl commands.
✅ Step 5: Verify the Cluster Nodes
|
1 |
kubectl get nodes |
📌 This confirms the cluster is active and nodes are ready.
📦 Understanding Kubernetes Pods
🔍 What is a Pod?
A Pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. It wraps one or more containers, networking, storage, and metadata into a single logical unit.
Think of a Pod as a single virtual machine, but designed for containers.
🧱 Pod Architecture
- Containers: One or more (most often one)
- Shared IP: Containers share the same IP and port space
- Volumes: Shared storage volumes across containers in a Pod
📊 Pod Types
| Type | Use Case |
| Single-container | Most applications (e.g., NGINX, Node.js apps) |
| Multi-container | Sidecar patterns like log collectors, proxies |
🔁 Pod Lifecycle
| Phase | Description |
| Pending | Pod created but containers not started |
| Running | Containers running normally |
| Succeeded | Containers completed successfully |
| Failed | Containers terminated with errors |
| Unknown | State could not be determined |
⚡ Init Containers
Init containers run before app containers start. Used for:
- Pre-loading configs
- Waiting for a database to be ready
- Running setup tasks
📌 They run sequentially and must complete before the main app starts.
🧪 Lab : Kubernetes Pods
⚙️ Task 1: Create Pod via Command Line
|
1 |
kubectl run nginx-pod --image=nginx --port=80 |
![]()
|
1 |
kubectl get pod |
![]()
|
1 |
kubectl describe pod nginx-pod |
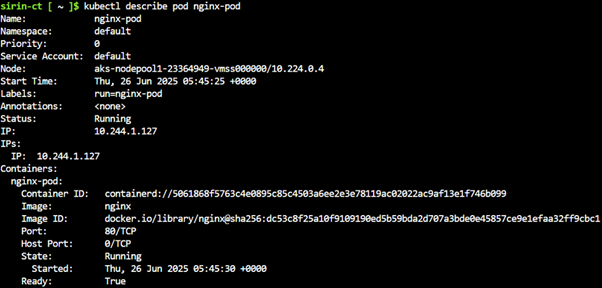
You’ve created a pod running the NGINX web server.
📝 Task 2: Create Pod via YAML
Why YAML?
YAML provides declarative configuration, making it reusable, version-controlled, and infrastructure-as-code (IaC) friendly.
Create the file:
|
1 |
vi httpd-pod.yaml |
Paste this config:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: httpd-pod labels: env: prod type: front-end app: httpd-ws spec: containers: - name: httpd-container image: httpd ports: - containerPort: 80 |
Apply it:
|
1 |
kubectl apply -f httpd-pod.yaml |
![]()
|
1 |
kubectl get pods |
|
1 |
kubectl get pods -o wide |
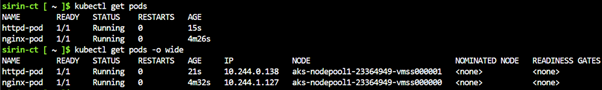
|
1 |
kubectl describe pod httpd-pod |
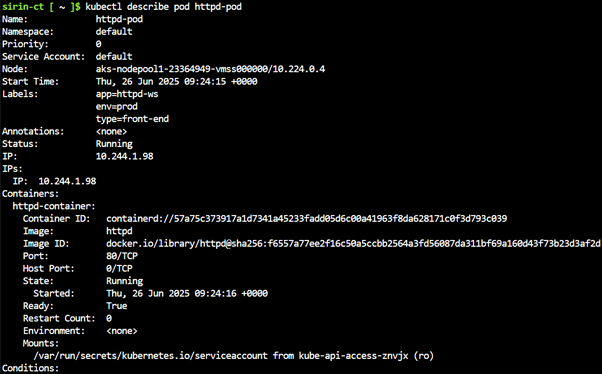
🔧 Task 3: Exec into Pod
🚪 Why Use kubectl exec?
You may need to:
- Debug issues inside a pod
- Install utilities for testing
- Inspect config files or logs
|
1 |
kubectl exec -it httpd-pod -- /bin/bash |
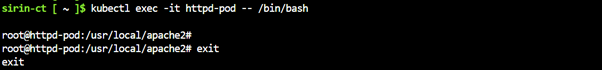
Type exit to return.
🧠 Conclusion
You’ve now completed a foundational journey in Kubernetes using AKS, learning how to provision clusters, manage pods, and interact with workloads using both commands and YAML. This forms the base for running production-grade containerized applications on Azure.
To advance your career and solidify your expertise, consider these next steps:
- Build a strong foundation in Azure resource management with the AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator Associate certification.
- Take your DevOps skills further by mastering CI/CD pipelines, containerized deployments, and cloud-native practices with the AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions certification.
🚀 With these certifications, you’ll be fully prepared to design, implement, and scale enterprise-grade cloud-native DevOps solutions powered by Kubernetes and Azure AKS.
📚 Further Reading & Official Reference
For more information, best practices, and advanced use cases, visit the official Kubernetes documentation:
For Azure-specific Kubernetes documentation (AKS):
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY Sirin Kausar Isak Ali
Sirin Ali is a seasoned corporate trainer and Subject Matter Expert with 11+ years of experience in cloud infrastructure, DevOps automation and Kubernetes. She has extensive real-time project experience in designing enterprise-grade CI/CD pipelines, automating containerized microservices deployments and implementing GitOps practices with advanced observability solutions. Skilled across diverse Kubernetes distributions, she brings hands-on expertise in transforming infrastructure and applications using industry best practices. Sirin has trained over 1500+ professionals worldwide and holds multiple certifications including CKA, Terraform Associate, Azure AI Engineer, GCP ACE, MCP, CCNA and MCT. Her practical, real-world approach simplifies complex DevOps concepts, empowering learners to confidently build production-ready solutions.


 Login
Login


 September 17, 2025
September 17, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments