|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
Automation is the backbone of modern software delivery in today’s fast-paced cloud environment. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines ensure applications are delivered faster, with fewer errors, and minimal downtime.
When it comes to serverless applications, AWS Lambda allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. But how do you continuously update your AWS Lambda functions with new code changes seamlessly?
This is where AWS CodePipeline comes in. It’s a fully managed CI/CD service that automates the build, test, and deployment phases.
In this blog, we will walk through how AWS CodePipeline can deploy changes automatically to an AWS Lambda function, ensuring fast, reliable, and repeatable delivery.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Why Use AWS CodePipeline with AWS Lambda?
- End-to-end automation: From code commit to deployment.
- Serverless focus: No servers to manage during the deployment.
- Integration with AWS services: Works seamlessly with AWS CodeCommit, AWS CodeBuild, Amazon S3, Amazon CloudWatch, and AWS IAM.
- Faster innovation: Reduce manual steps and push new features quickly.
AWS CodePipeline with AWS Lambda
AWS CodePipeline is a CI/CD orchestration service that allows you to model your release process as a series of stages. With AWS Lambda as the target, AWS CodePipeline automates packaging, testing, and deploying your serverless code.
A typical AWS Lambda pipeline involves:
- Source Stage – Tracks code changes from repositories like AWS CodeCommit, GitHub, or Amazon S3.
- Build Stage – This stage uses AWS CodeBuild to package dependencies and prepare deployment artifacts.
- Deploy Stage – Automatically updates the AWS Lambda function with the new build.
This integration provides a serverless-first approach to CI/CD where you don’t need to manage servers at any stage of the delivery lifecycle.
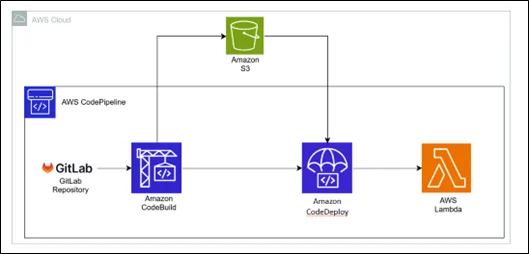
Architecture Overview
Here’s a simple flow of how the pipeline works:
- Source Stage: Code is pushed to a repository (AWS CodeCommit, GitHub, GitLab, or Amazon S3).
- Build Stage: AWS CodeBuild packages the AWS Lambda code and dependencies into a deployment package (ZIP).
- Deploy Stage: AWS CodeDeploy (with AWS CodePipeline) updates the AWS Lambda function with the new package.
Architecture Diagram:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Prerequisites
- An existing AWS Lambda function with an alias was created. (This is referred to at the deploy stage of the AWS CodePipeline).
- AWS CLI or Management Console access.
- An Amazon S3 bucket for storing artifacts.
- AWS IAM roles for AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS Lambda.
- Create the Source Stage
- If using AWS CodeCommit:
- Push your AWS Lambda source code into an AWS CodeCommit repo.
- If using Amazon S3/GitHub:
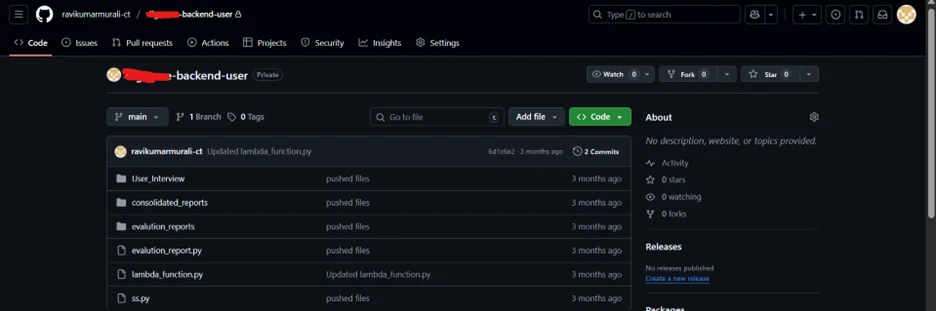
- Configure as the pipeline source. Let’s have the code in GitHub and connect this repository to the AWS CodePipeline as a source.
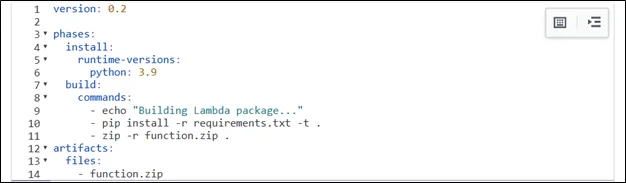
- Build Stage with AWS CodeBuild
- Create a buildspec.yml file:

- This ensures dependencies are moved as expected with the files and folder structure. It needs to be packaged as a zip, and deploy the below buildspec.yaml
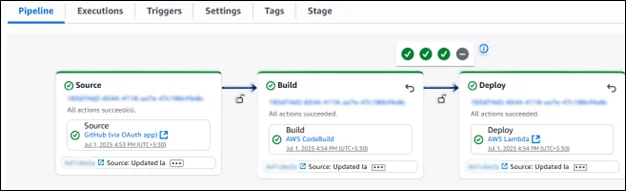
- Deploy Stage with AWS CodePipeline
- Use AWS CodeDeploy for AWS Lambda or directly configure AWS CodePipeline Deploy Action.
Your code pipeline will look as follows, with three stages added:
- Define the AWS Lambda function name in the deployment stage.
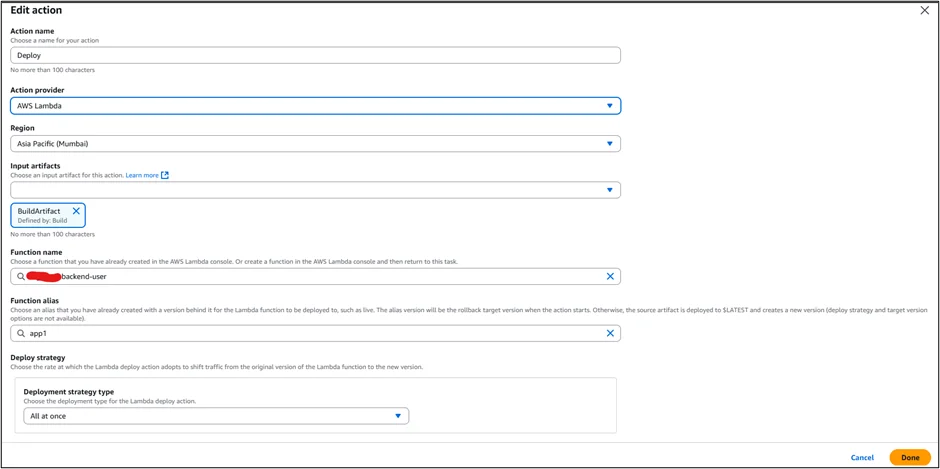
- Each successful build automatically updates the function.
Best Practices
- Use separate stages (dev, stage, prod) with manual approvals before production.
- Store sensitive credentials in AWS Secrets Manager.
- Enable Amazon CloudWatch Alarms to roll back failed deployments.
- Version your AWS Lambda functions for rollback safety.
Conclusion
Integrating AWS CodePipeline with AWS Lambda allows you to achieve a fully automated CI/CD workflow tailored for serverless applications. This accelerates feature delivery and ensures consistency, reliability, and minimal downtime.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding AWS CodePipeline or AWS Lambda and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Can I deploy multiple AWS Lambda functions in one AWS CodePipeline?
ANS: – Yes. Depending on your architecture, you can define multiple deploy stages in a single pipeline or create separate pipelines for each AWS Lambda function.
2. Do I always need AWS CodeBuild to deploy to AWS Lambda?
ANS: – Not necessarily. If your AWS Lambda code is small and doesn’t require dependencies, you can directly store the ZIP file in Amazon S3 and let AWS CodePipeline deploy it. CodeBuild is useful when packaging dependencies or running tests.

WRITTEN BY Saurabh Jain
Saurabh Kumar Jain is the CSA – Projects Head for DevOps and Kubernetes at CloudThat. An innovative Solutions Architect and technical leader, he is passionate about driving digital transformation across diverse industries. He specializes in designing enterprise-grade, cloud-native solutions, with deep expertise in multi-cloud platforms, Kubernetes orchestration, and AI-powered automation. Saurabh has extensive experience in architecting secure, scalable systems for sectors including oil & petroleum, financial services, e-commerce, and government organizations. He is recognized for his thought leadership in modernization strategies, GitOps workflows, and comprehensive observability implementations. In his free time, he explores emerging technologies in AI and GenAI, contributes to open-source projects, and shares knowledge through technical content and industry speaking engagements.


 Login
Login


 September 17, 2025
September 17, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments