|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Keeping your Kubernetes cluster up to date is crucial for security, stability, and access to the latest features.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk through upgrading a kubeadm-managed Kubernetes cluster from v1.32.0 to v1.33.0, following official best practices and real-world operational insights.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Why Upgrade?
Each Kubernetes release introduces performance improvements, API enhancements, and critical security fixes.
The 1.33 release includes:
- Native Sidecar Containers (Stable), official support for true sidecar lifecycle management
- In-place Pod Resource Resizing (Beta)
- API Deprecations & Cleanup, Endpoints API deprecated in favor of EndpointSlices
- Improved Security Controls and RBAC refinements
Before upgrading production clusters, always test the upgrade in a staging environment, and ensure you have etcd snapshots and deployment manifests backed up.
Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you meet these requirements:
- Existing Cluster: Running Kubernetes v1.32.0 using kubeadm
- SSH Access: Root or sudo privileges on all nodes
- Internet Access: Nodes can reach Kubernetes package repositories
- Backups Taken:
|
1 2 |
# Take etcd snapshot ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot save /root/etcd-snapshot.db |
5. Cluster Health:
|
1 2 |
kubectl get nodes kubectl get pods -A |
All nodes and core system pods should be in the Ready state.
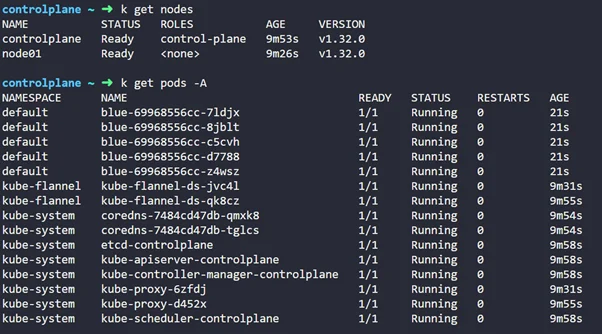
Step-by-Step Guide
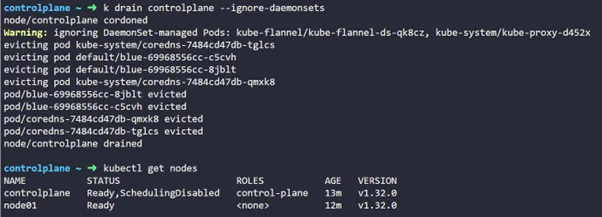
Step 1: Make the controlplane UnSchedulable
|
1 |
kubectl drain controlplane --ignore-daemonsets |
Step 2: Verify the package repository
|
1 |
pager /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list |
![]()
Modify the version 1.32 to 1.33 so that you can upgrade
Step 3: Find the latest patch release for 1.33 using os package manager
|
1 2 |
sudo apt update sudo apt-cache madison kubeadm |
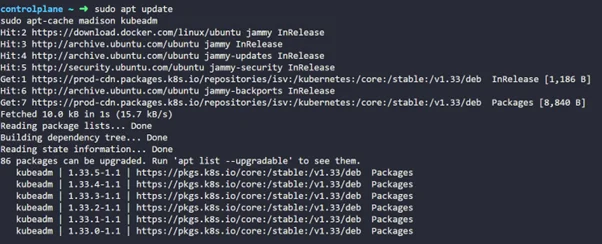
So you can see we can upgrade to all these possible versions, but I will move ahead with the 1.33.0-1.1 version for this demo
Make sure you copy that
Step 4: Now, let’s upgrade the control plane
|
1 2 3 |
sudo apt-mark unhold kubeadm && \ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y kubeadm='1.33.0-1.1' && \ sudo apt-mark hold kubedam |
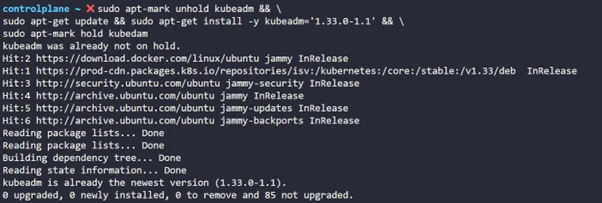
So now kubedam is updated to the new version.
![]()
Step 5: Let’s plan the upgrade
|
1 |
sudo kubeadm upgrade plan |
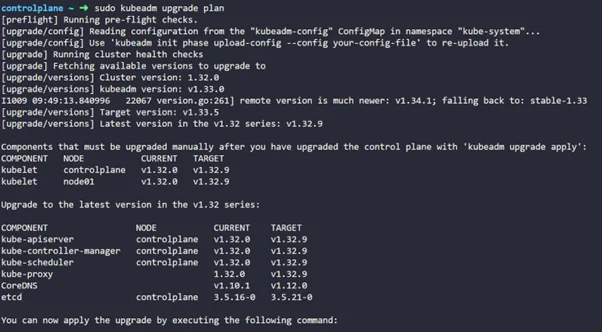
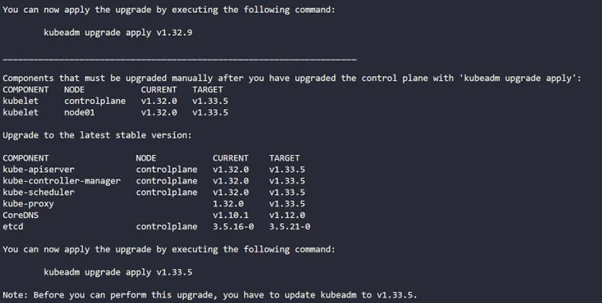
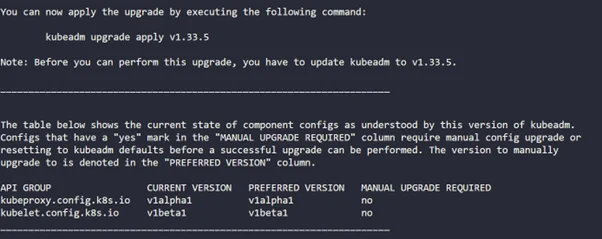
Step 6: Now upgrade to your desired version ( 1.33.0)
|
1 |
kubeadm upgrade apply v1.33.0 |
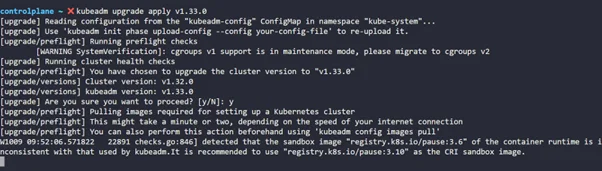
Note that this step usually takes 5-10 minutes.
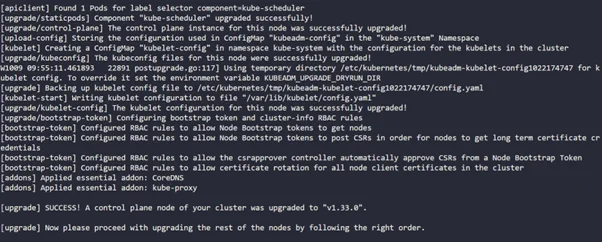
Step 7: Now let’s upgrade kubectl and kubelet as well
|
1 2 3 |
sudo apt-mark unhold kubelet kubectl && \ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y kubelet='1.33.0-1.1' kubectl='1.33.0-1.1' && \ sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubectl |
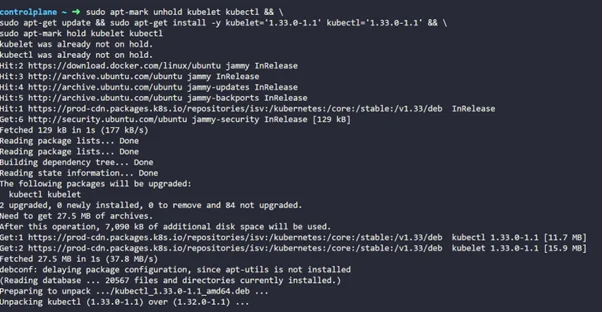
Step 8: Once that’s done, make sure you restart the kubelet
|
1 2 |
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart kubelet |
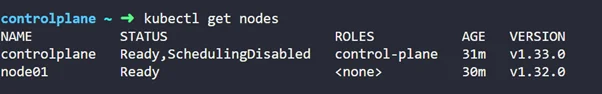
Now, let’s make the node uncordon ( so they can schedule pods)
kubectl uncordon controlplane
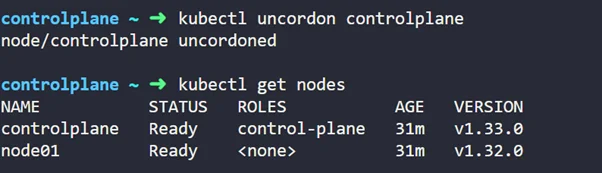
Step 9: Now, let’s jump into upgrading worker nodes (node01)
Let’s make them first unscheduled
|
1 |
kubectl drain node01 --ignore-daemonsets |
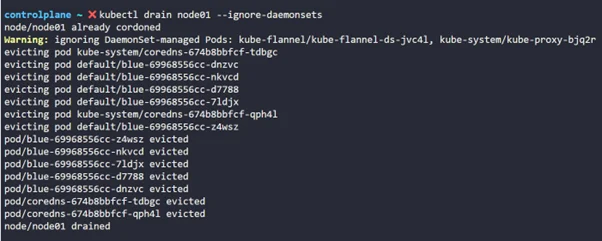
Step 10: Let’s SSH into node01 to perform upgradation
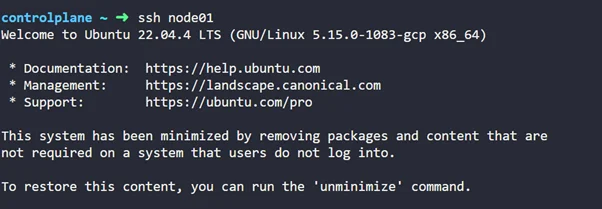
Step 11: Let’s update the Kubernetes package repository list.
|
1 |
pager /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list |

Step 12: Now let’s upgrade kubelet & kubectl.
|
1 2 3 |
sudo apt-mark unhold kubelet kubectl && \ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y kubelet='1.33.0-1.1' kubectl='1.33.0-1.1' && \ sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubectl |
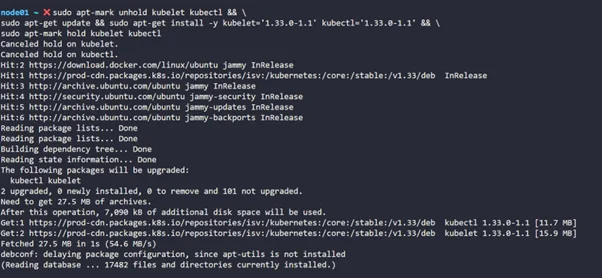
Step 13: Once that’s done, let’s restart kubelet
|
1 2 |
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart kubelet |
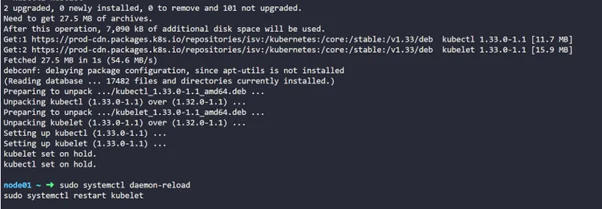
Now, exit or log out from node01 (worker node)
Step 14: Now let’s uncordon this node so pods can be scheduled and verify the upgradation
|
1 |
Kubectl uncordon node01 |
Step 15: Check all system components
|
1 |
kubectl get pods -n kube-system |
Rollback Plan (Optional but Important)
If something goes wrong:
- Restore your etcd snapshot:
|
1 |
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot restore /root/etcd-snapshot.db |
- Revert node packages to v1.32.0:
|
1 |
sudo apt-get install kubeadm=1.32.0-00 kubelet=1.32.0-00 kubectl=1.32.0-00 |
Final Checklist
- Etcd Backup Taken
- Control Plane Upgraded
- Worker Nodes Upgraded
- Kubelet Restarted
- Cluster Verified
Conclusion
Upgrading a Kubernetes cluster might seem daunting, but with kubeadm, it’s a clean, predictable, and reversible process.
By upgrading from v1.32.0 to v1.33.0, you ensure that your environment benefits from the latest security patches, improved performance, and new stable features, such as sidecar containers and pod resizing.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Kubernetes and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY Akshay Ramnani
Akshay Ramnani works as a DevOps Engineer with over 3 years of hands-on experience in architecting CI/CD pipelines, Kubernetes-based deployments, and multi-cloud automation across AWS, GCP, and Azure. He has a proven track record in scaling microservices on Amazon EKS, streamlining observability platforms, and driving infrastructure as code using Terraform, Helm, and ArgoCD.


 Login
Login


 November 26, 2025
November 26, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments