|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
Cloud storage services have become the backbone of modern IT infrastructure. Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are the three major players offering comprehensive storage solutions for various needs. This blog post provides a detailed comparison of storage services across these platforms, covering their types, use cases, performance, pricing, and management capabilities.
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
Overview of Storage Services
| Storage Type | Azure | Google Cloud | Amazon Web Services |
| Object Storage | Azure Blob Storage | Cloud Storage | Amazon S3 |
| File Storage | Azure Files | Filestore | Amazon EFS |
| Block Storage | Azure Managed Disks | Persistent Disks | Amazon EBS |
| Archive Storage | Azure Archive Storage | Nearline/Coldline | Amazon Glacier |
| Hybrid Storage | Azure Stack | Transfer Appliance | Snowball/Outposts |
Architecture Diagrams
Below is a high-level comparison of cloud storage architecture across providers.
Diagram: GCP Storage
Diagram: AWS Storage
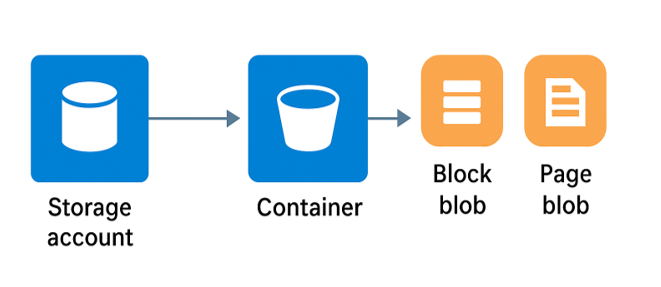
Diagram: Azure Storage
Features Comparison
Each provider offers unique features within their storage services. Here is a comparison:
| Feature | Azure | Google Cloud | AWS |
| Versioning | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lifecycle Management | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data Encryption | At rest & in transit | At rest & in transit | At rest & in transit |
| Redundancy Options | LRS, GRS, ZRS | Standard, Nearline, Coldline, Archive | S3 Standard, IA, One Zone, Glacier |
| Data Transfer Tools | AzCopy, Data Box | Storage Transfer Service | AWS Snowball, Transfer Acceleration |
Compute and Network Integration
Cloud storage services are rarely used in isolation. Their value multiplies when integrated seamlessly with compute resources and network configurations. Here, we explore how Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) integrate storage with compute and networking components, along with practical examples and diagrams.
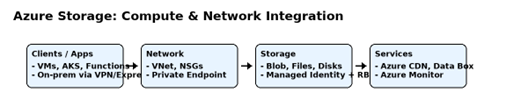
Azure: Compute and Network Integration
Azure provides multiple compute services such as Virtual Machines (VMs), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Azure Functions that can directly interface with its storage services. For instance, Azure Blob Storage is commonly accessed from AKS pods through managed identities, ensuring secure, keyless authentication.
From a networking perspective, Azure uses Virtual Networks (VNets), Network Security Groups (NSGs), and Private Endpoints to enable secure access to storage accounts. Private Endpoints route traffic through Microsoft’s backbone network, bypassing public internet exposure. This setup is ideal for enterprise scenarios where sensitive data must remain within a private boundary.
An example is hosting a web application on Azure App Service that stores images in Blob Storage. The app can be integrated into the same VNet as the storage account, secured by NSGs, and granted RBAC permissions through Azure AD. This ensures only the app’s managed identity has access.
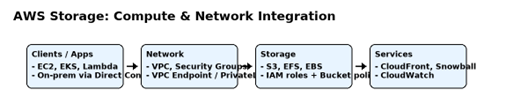
AWS: Compute and Network Integration
AWS integrates its storage services—such as Amazon S3, Elastic File System (EFS), and Elastic Block Store (EBS)—closely with compute services like EC2, Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), and AWS Lambda. IAM roles and policies are used for fine-grained access control, removing the need for static credentials.
Networking in AWS revolves around Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and Security Groups. Private connectivity to S3 can be established using VPC Endpoints or AWS PrivateLink, which allows services to be accessed privately without traversing the public internet. Direct Connect enables low-latency connections from on-premises data centers to AWS.
For example, a machine learning pipeline running on EC2 can retrieve large datasets from S3 via a VPC Endpoint, ensuring data never leaves the AWS internal network. This is both faster and more secure than public access.
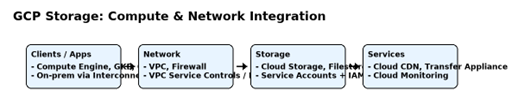
GCP: Compute and Network Integration
Google Cloud integrates Cloud Storage, Filestore, and Persistent Disks with compute offerings like Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and Cloud Functions. Service Accounts provide secure access without embedding keys in code, and IAM policies control permissions.
Networking features include Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks, firewall rules, and Private Google Access, which allows VM instances without external IP addresses to access Google APIs and services privately. VPC Service Controls can be used to create security perimeters around storage buckets to prevent data exfiltration.
For instance, a GKE-hosted analytics platform can pull raw data from Cloud Storage buckets via Private Google Access, process it, and push results to BigQuery—without exposing the traffic to the public internet.
Side-by-side comparison (compute & network features)
| Concern | Azure | AWS | GCP |
| Block storage | Managed Disks (VM-attached) | EBS (VM-attached) | Persistent Disk / Local SSD |
| Shared files | Azure Files (SMB/NFS) | EFS (NFS) | Filestore (NFS) |
| Object storage | Blob Storage | S3 | Cloud Storage |
| Private-network access | Private Endpoint (NIC in VNet) | VPC Gateway / Interface Endpoints, PrivateLink | Private Google Access, VPC Service Controls, Private Service Connect |
| On-prem private link | ExpressRoute | Direct Connect | Cloud Interconnect |
| Transfer appliances | Data Box | Snowball | Transfer Appliance |
| Auth model | Managed Identity, RBAC, SAS | IAM Roles, Bucket Policies, Pre-signed URLs | Service accounts, IAM |
| Common use cases | Microsoft stacks, AD integration | Mature ecosystem, 3rd-party integrations | Data/AI pipelines, global buckets |
Pricing Summary
Pricing can vary significantly depending on the storage class, region, and access frequency. Here is a generalized summary for standard object storage (as of mid-2025):
| Provider | Standard Storage (Per GB/Month) | Retrieval Cost | Data Transfer Out |
| Azure | $0.0184 | Low | $0.087/GB |
| Google Cloud | $0.020 | Low | $0.12/GB |
| AWS | $0.023 | Low | $0.09/GB |
Conclusion
Choosing the right cloud storage provider depends on your specific needs, such as use case, budget, geographical reach, and existing cloud infrastructure. Azure, GCP, and AWS all offer reliable, scalable, and secure storage solutions. Azure may appeal to organizations already in the Microsoft ecosystem, Google Cloud is favored for analytics and AI-driven storage solutions, and AWS provides a mature, feature-rich storage portfolio.
Course URLs
https://www.cloudthat.com/training/aws/
https://www.cloudthat.com/training/azure/
https://www.cloudthat.com/training/google-cloud-certification
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY Pankaj P Waghralkar
Pankaj Waghralkar is a Subject Matter Expert and Microsoft Certified Trainer at CloudThat. He has total of 15+ years of professional experience in various fields like Cloud Computing, Web Development, Digital Marketing and training experience in IT & Computer Engineering streams. He has trained more than 2500 students, working & corporate professionals. He published two national patents on biometric technologies and also published more than 10+ international research articles on different trends in technologies. His expertise includes designing secure hybrid cloud infrastructures and enhancing online visibility through strategic web development and marketing initiatives. Proficient in leveraging advanced cloud technologies, effective networking solutions and comprehensive software engineering practices to drive business growth, Pankaj has trained professionals across industries, helping them master Azure services such as Virtual Networks, Azure Active Directory, Security, Networking and more. Known for his clear teaching style and deep technical knowledge, Pankaj is dedicated to shaping the next generation of cloud experts.


 Login
Login


 September 16, 2025
September 16, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments