|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
The data architectures of today are highly reliant on Amazon S3 as a repository for analytics, logs, and machine learning data. With data sets consisting of millions of objects, dealing with massive-scale processing across those files becomes that much more complicated. AWS Lambda loops, AWS Glue jobs, or manifest-based pipeline scenarios require custom logic for listing Amazon S3 objects, concurrency management, and failure recovery. AWS Step Functions Distributed Map with Amazon S3 Prefix is a turnkey and scalable solution. It enables an AWS Step Functions state machine to automatically find, read, and process all objects in an Amazon S3 prefix in parallel, without requiring manual looping or manifest management. It supports data-intensive workloads, such as log aggregation, data transformation, and ETL, at scale with minimal operational overhead.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
AWS Step Functions Distributed Map: What it is and how it works
AWS Step Functions is a serverless workflow service used to coordinate various AWS building blocks as workflows. Distributed Map state is designed for data-parallel workloads and can perform thousands or millions of iterations in parallel, each as a standalone item from a dataset. The developers previously had to list Amazon S3 objects explicitly and invoke AWS Lambda functions or AWS Step Functions runs on a batch basis. The Amazon S3 Prefix feature eliminates all that. The state machine makes an internal call to ListObjectsV2 and converts each object found into a Distributed Map iteration. This method provides a declarative, fully managed mechanism for orchestrating large-scale Amazon S3 data processing without additional code.
The LOAD_AND_FLATTEN Transformation
The LOAD_AND_FLATTEN transformation introduces this feature, supporting processing at the record level. AWS Step Functions not only traverse Amazon S3 objects but also read the data in each file, process structured data, and output individual records as separate workflow items. This transformation makes AWS Step Functions a lightweight, high-speed data-processing machine for structured Amazon S3 datasets.
Supported input file formats are:
- CSV – Each row is processed as a separate record.
- JSON / JSONL – Line-delimited and array-based JSON formats are supported.
- Parquet – Tabular data is read and flattened out into single records.
By defining parameters such as InputType and Transformation, a workflow can natively read Amazon S3 data without requiring middle AWS Lambda parsing or AWS Glue transformations. If InputType is JSONL and Transformation is LOAD_AND_FLATTEN, each individual JSON line is processed as a single item for downstream processing. Fine-grained parallelization is supported for both analytical and operational workloads.
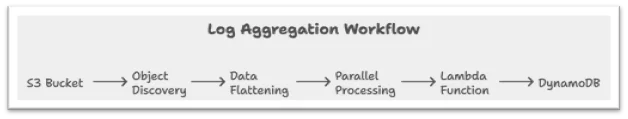
Example: Log Aggregation Workflow
Use the example of an application writing logs daily as JSONL files into an Amazon S3 bucket named logs/2025-10-25/. Each log record has fields timestamp, log level, and message. The goal is to produce hourly INFO, WARNING, and ERROR counts and output to Amazon DynamoDB. AWS Step Functions Distributed Map with Amazon S3 Prefix support workflow design process consists of the following steps:
- Object Discovery
The state machine is fed the Amazon S3 prefix (logs/2025-10-25/). AWS Step Functions will automatically list all objects within this prefix, eliminating the need for a single listing job.
- Data Flattening
All files are converted with the LOAD_AND_FLATTEN transformation. Every JSON line is flattened into a single input record, containing the necessary log information for aggregation.
- Parallel Processing
Distributed Map handles all records in parallel. Each execution invokes a Lambda function that processes the log record, maintains counters for log levels, and writes aggregated metrics to Amazon DynamoDB.
The outcome is an end-to-end, serverless, parallelized data pipeline that can consume millions of log records with minimal configuration. The same operation can be reused for multiple time partitions by dynamically changing the prefix input to facilitate low-latency daily or hourly data aggregation.
Considerations
- Uniform Data Format
All files in the given prefix must share the same schema and format. When InputType is set to JSONL, all files must be in this format. Mixing formats leads to parsing errors during execution.
2. Prefix Granularity
Prefixes must be reasonable partitions, for example, daily or hourly directories, to enable efficient listing and reasonable execution sizes. More broken-up prefixes enable faster runs and quicker retries.
- Concurrency Control
While Distributed Map accommodates scale-out parallelism, concurrency settings must be compatible with the capacity of downstream services, such as Amazon DynamoDB or AWS Lambda. The MaxConcurrency setting regulates concurrent iterations and prevents throttling or service ceilings.
- AWS IAM Permissions
AWS IAM permissions for s3:ListObjectsV2 and s3:GetObject in the AWS Step Functions execution role need to be included, along with other services called within the workflow. Correct permissions enable safe access and correct functioning.
- Handling Large Files
Very large files can cause latency or memory overload during flattening. Partitioning data into smaller chunks or utilizing optimized services such as AWS Glue for heavy transformations enhances efficiency and stability.
These factors deliver reliable performance, cost-effective price, and dependability while workloads scale.
Conclusion
Mixing Amazon S3 Prefix and LOAD_AND_FLATTEN in AWS Step Functions Distributed Map provides a fault-tolerant, serverless way of elastic data processing. Workflows that previously required complex AWS Lambda orchestration or specialized manifest logic can now be defined declaratively as a single state machine. Step Functions takes care of Amazon S3 object discovery, record extraction, and concurrent execution behind your back.
This architecture is especially fit for massive-scale analytics, log processing, and ETL jobs. It eschews manual coordination, reduces operational overhead, and leverages the elasticity of AWS’s serverless architecture. Organizations can develop highly scalable and cost-effective pipelines for structured data processing directly from Amazon S3 using AWS Step Functions, AWS Lambda, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon CloudWatch.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Amazon S3 Prefix and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is the main benefit of a Distributed Map with Amazon S3 Prefix?
ANS: – The feature automatically detects and traverses Amazon S3 objects within a given prefix, eliminating the need for custom file-listing code or manifest management.
2. Can AWS Step Functions handle individual records instead of whole files?
ANS: – Yes. Using the LOAD_AND_FLATTEN transformation, AWS Step Functions can handle structured files, such as CSV, JSONL, or Parquet, and handle each record individually.
3. How does concurrency work in the Distributed Map?
ANS: – Concurrency is controlled by configuration options such as MaxConcurrency. Step Functions scales within boundaries to maintain performance and avoid saturating downstream service capacity.

WRITTEN BY Daniya Muzammil
Daniya works as a Research Associate at CloudThat, specializing in backend development and cloud-native architectures. She designs scalable solutions leveraging AWS services with expertise in Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring and AWS CloudFormation for automation. Skilled in Python, React, HTML, and CSS, Daniya also experiments with IoT and Raspberry Pi projects, integrating edge devices with modern cloud systems.


 Login
Login


 November 6, 2025
November 6, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments