|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
When we run a self-managed Kubernetes cluster, the control plane is the single biggest operational risk. Nodes can be replaced, workloads can be redeployed, and manifests can be re-applied, but if the control plane goes down. We don’t have a proven recovery path, we are effectively blind, with no scheduling, no scaling, no API access, and no safe way to manage the cluster.
In self-managed setups (kubeadm/on-prem/EC2 VMs), etcd is the source of truth. It stores almost everything that makes up a cluster, including namespaces, deployments, services, RBAC, CRDs, secrets, and configuration. That’s why a real Kubernetes disaster recovery plan starts with one thing taking consistent etcd snapshots and knowing how to restore them.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Solution Overview
We take a consistent snapshot of the etcd datastore and securely store it. During disaster recovery, we will restore the etcd snapshot on the control-plane nodes, bring up the Kubernetes control-plane components (etcd, kube-apiserver, controller-manager, scheduler), and validate that the cluster state and workloads are recovered.
Prerequisite
- Self-managed Kubernetes control plane (e.g., kubeadm / on-prem / EC2 VMs) where you can access the control-plane node(s).Necessary permissions to access the cluster and take the backup.
- Access to the control-plane node(s) (SSH or console) with sudo/root access, because etcd data and certs live on the node.
- Permissions to run cluster validation commands after restore (access to admin.conf or kubeconfig)
- Etcdctl API needs to be installed on the cluster that matches the etcd major version.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Verify ETCD Version
Run the below command to verify the etcd version.
|
1 |
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl version |
- Static Pod manifests backup
Move the static pod folder otherwise, the kubelet keeps restarting api server and other static pods.
|
1 2 |
mkdir -p /root/k8s-manifests-backup mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/*.yaml /root/k8s-manifests-backup/ |
- Check the Data directory path
Check the etcd data directory. In kubeadm, it uses /var/lib/etcd. Verify once from YAML or if etcd is running as a service, check –data-dir path.
|
1 |
cat /root/k8s-manifests-backup/etcd.yaml | grep -E 'data-dir|/var/lib/etcd' |
![]()
- Backup of existing etcd data
Take a backup of existing data. Run the command to take the backup.
|
1 |
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot save /opt/snapshot-pre-boot.db --cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 --key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key --cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt |
The flags shown above are required to take a backup and restore it. We can get the details of these flags from the manifests file of the etcd server.
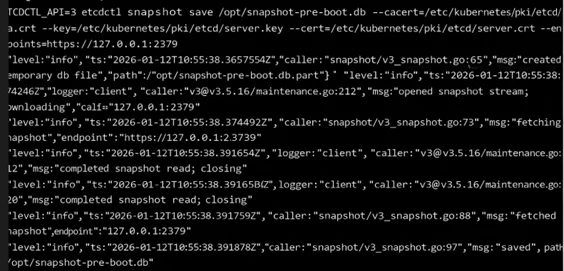
- Cleaning the older etcd database
Wipe the old data dir to avoid mixing old state, or else restore the backup to a new directory and update the volume path in the yaml.
|
1 2 |
sudo systemctl stop kubelet || true sudo rm -rf /var/lib/etcd/* |
Stop the kubelet, then remove the data from the etcd data directory
- Restoring the snapshot
Restore snapshots in /var/lib/etcd. This creates the etcd data dir from the snapshot.
|
1 |
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot restore /opt/snapshot-pre-boot.db --data-dir /var/lib/etcd --cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 --key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key --cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt |
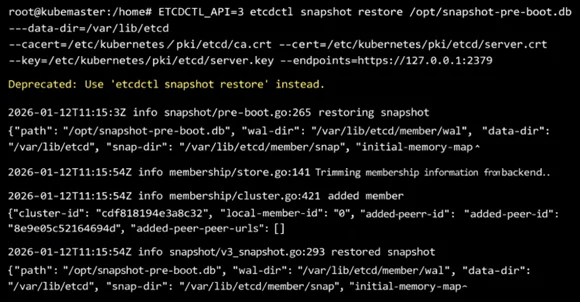
Note: If, for some reason, restoring in /var/lib/etcd is not working, restore the backup to a different directory and update the etcd yaml volume path to point to the backup location.
- Restoring the static manifests file
Copy api server and other manifests from the backup to the manifests location
|
1 2 3 |
mv /root/k8s-manifests-backup/kube-apiserver.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/ mv /root/k8s-manifests-backup/kube-controller-manager.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/ mv /root/k8s-manifests-backup/kube-scheduler.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/ |
- Verification of services
Verify that the deployments and services are running again after restoring the backup.
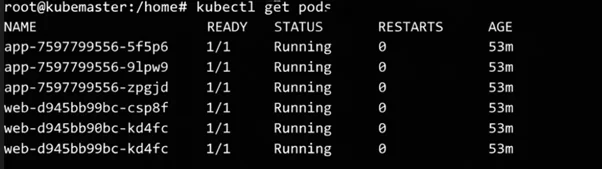
Key Benefits
- Provides a step-by-step, incident-ready procedure to rebuild the Kubernetes control plane from an etcd snapshot.
- Helps us restore API access and cluster operations faster during control-plane failures.
- Shows how to validate snapshots and verify recovery.
- Helps you define and meet RPO/RTO targets with repeatable processes and checks.
Conclusion
In a self-managed Kubernetes setup, losing the control plane doesn’t have to mean losing the cluster. Since etcd is the source of truth, a reliable snapshot and a proven restore process are the fastest way to recover our Kubernetes state, including namespaces, workloads, RBAC, CRDs, and configuration, after a major failure. Make etcd snapshotting automatic, store backups off the control-plane node, and run periodic restore game days to measure your RPO/RTO. With that in place, control-plane recovery becomes a repeatable operational task.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Kubernetes and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Can I do an etcd restore on managed Kubernetes, such as EKS/GKE/AKS?
ANS: – No. Managed services handle etcd/control plane internally and don’t expose restore workflows. This blog applies to self-managed control planes (kubeadm/on-prem/VM-based clusters).
2. Does restoring an etcd snapshot recover my application data (databases/files)?
ANS: – Not usually. etcd restores Kubernetes objects (manifests/state), not persistent data stored in PVs or external databases

WRITTEN BY Suryansh Srivastava
Suryansh is an experienced DevOps Consultant with a strong background in DevOps, Linux, Ansible, and AWS. He is passionate about optimizing software development processes, ensuring continuous improvement, and enhancing the scalability and security of cloud-based production systems. With a proven ability to bridge the gap between IT and development teams, Surayansh specializes in creating efficient CI/CD pipelines that drive process automation and enable seamless, reliable software delivery.


 Login
Login


 February 10, 2026
February 10, 2026 PREV
PREV











Comments