|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
In the modern era of software development, delivering applications rapidly and reliably is vital to maintaining business competitiveness. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines enable development teams to automate their build, test, and deployment processes, allowing faster iterations and consistent releases with higher confidence in quality.
This guide explains architecting a production-grade, highly available, and secure Jenkins environment on AWS using Terraform for Infrastructure as Code (IaC). This architecture leverages AWS services such as Amazon EC2, Amazon Elastic File System (EFS), Application Load Balancer (ALB), AWS Certificate Manager (ACM), AWS SSO, and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to deliver performance and operational excellence.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
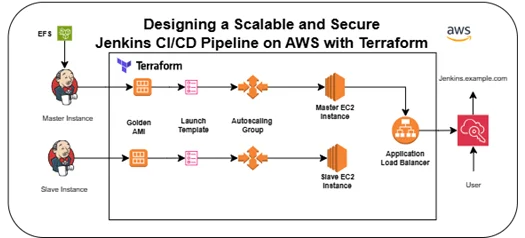
Architecture Diagram
Prerequisites
- AWS Account with access keys for an AWS IAM user or role that has permission to create Amazon EC2, Amazon VPC, Amazon EFS, ALB, AWS IAM roles/policies, ACM certificates, and related networking resources.
- Terraform is installed (ideally the latest stable) on your local machine.
- AWS CLI was installed and configured for validation and manual tasks outside Terraform. Configure it with aws configure.
- Jenkins Configuration Artifacts
- Jenkins installation scripts
- Jenkinsfile (pipeline as code) for your projects
- Any Groovy init scripts if you’re automating plugin installation and security configuration
5. Knowledge of Git to store your Terraform configurations and Jenkinsfiles in version control for traceability.
6. AWS IAM Permissions for Terraform need permissions to create and manage AWS resources you’ll define in your infrastructure.
7. Optional but Recommended:
-
- Domain name registered (e.g., via Amazon Route53) if you plan to expose Jenkins at ci.example.com
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) certificate for HTTPS
- AWS SSO or AWS IAM roles for Jenkins users to integrate with AWS services securely
What Terraform makes simple in this setup?
- Build the Golden AMI for Jenkins master/slave with pre-installed software/plugins
- Define Launch Templates and Auto Scaling Groups for horizontal scalability
- Provision Amazon EFS for persistent Jenkins data, so master node rebuilds don’t lose job configs
- Configure an ALB to balance traffic across Jenkins instances
- Wire up security groups, AWS IAM roles/policies, Amazon VPC networking, all through code
- Automate certificate creation and HTTPS setup with ACM
- Maintain everything in a single source of truth
Jenkins Master Setup
- Java Runtime: Jenkins runs on Java, so the master needs a compatible JDK installed (Java 11 is the current recommended version).
- Jenkins Software: Install the Jenkins server package to run the web UI, manage jobs, handle plugins, and coordinate builds.
- Persistent Storage: For resilience, the Jenkins home directory (/var/lib/jenkins) should be placed on persistent storage like Amazon EFS. This way, your Jenkins data (jobs, configs, plugins, credentials) survives even if the Amazon EC2 master node is terminated or replaced.
- Service Configuration: Jenkins should run as a system service, so it starts automatically on boot, restarts on failure, and integrates with system logs.
- Initial Admin Setup: First login to Jenkins requires unlocking it with an initial admin password from the file Jenkins generates; after that, configure plugins, credentials, and global settings.
Jenkins Slave (Agent) Setup
- Java Runtime: Like the master, each slave needs Java installed because the Jenkins agent runs as a Java process.
- Connectivity to Master: The slave must reach the Jenkins master’s URL. Inbound agent: Master connects to the agent.
- Scaling Considerations: Slaves are designed to scale horizontally and spin up more when needed for faster parallel builds or multiple jobs running simultaneously.
Persistent Jenkins Storage with Amazon EFS
- Persistence Across Master Amazon EC2 instance dies, is replaced by Auto Scaling, or needs to scale up/down, you don’t lose your Jenkins data. Because your job configs, plugins, credentials, and build history live on Amazon EFS, not the local disk.
- Shared Access runs Jenkins in a high availability setup with multiple masters, they can all read/write the same Jenkins home on Amazon EFS.
- Scalability for Amazon EFS automatically grows as your Jenkins data grows, there’s no need to manually resize or worry about running out of disk space like with EBS volumes.
- Durability & Availability of Amazon EFS data is stored redundantly across multiple AZs in your AWS region, so it’s far more reliable than storing data on a single Amazon EC2 disk or even a single EBS volume.
- Simplifies Backups snapshot Amazon EFS filesystem, letting you easily restore Jenkins to a previous state if something breaks or you accidentally delete important configs.
- No Need for Manual Syncing mess with rsync, NFS servers, or hacky data copying between servers. Amazon EFS handles shared, consistent storage out of the box.
Reliability
To ensure consistent, reliable deployment of Jenkins in production, the architecture separates machine image creation from infrastructure provisioning:
- Immutable Golden AMI – Jenkins Master and Slave instances are built from preconfigured Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) that are manually baked with all necessary packages, plugins, and configurations.
- Launch Templates via Terraform – Terraform provisions separate Launch Templates for Jenkins Master and Slave nodes using the prebuilt AMIs. This ensures every instance launched is consistent with the intended runtime environment.
- Auto Scaling Groups (ASG) – Terraform-managed Auto Scaling Groups ensure that if a Jenkins node (master or slave) fails, a new one is automatically launched from the Launch Template using the same AMI, preserving availability without manual intervention.
- Application Load Balancer (ALB) – An ALB sits before Jenkins Master instances and distributes incoming traffic. Combined with Auto Scaling, this setup enables zero-downtime restarts and ensures Jenkins remains accessible even during instance replacements or failures.
Security
- Centralized Access AWS SSO manages Jenkins user identities and roles in one place, so you don’t have to juggle separate Jenkins accounts for every user.
- Stronger Security enforces organization-wide policies like multi-factor authentication and centrally logs all access, which is critical for securing a system that can deploy your code.
- Seamless User Experience users log in once with their corporate credentials and get direct access to Jenkins without multiple passwords.
Conclusion
Designing Jenkins on AWS with Terraform, Amazon EFS, and Autoscaling isn’t just about automation, it’s about building a reliable, scalable, and secure CI/CD foundation that the team can trust. By offloading persistent storage to Amazon EFS, you ensure Jenkins data survives instance replacements. Using Autoscaling and Golden AMIs gives you resilience and consistency. Layering AWS SSO on top simplifies access management and locks down your environment with enterprise-grade security.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Jenkins and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Why use Terraform with AWS for Jenkins deployment?
ANS: – Terraform enables infrastructure as code, making your AWS environment fully repeatable, version-controlled, and easy to maintain. It automates the creation of everything Jenkins needs, Amazon EC2 instances, security groups, Amazon EFS, load balancers, and more, while ensuring consistency across environments. You get faster provisioning, safer rollbacks, and full visibility into infrastructure changes.
2. Why integrate Jenkins with AWS SSO?
ANS: – AWS SSO centralizes user access control and integrates with your organization’s identity provider (like Okta or Azure AD). This eliminates local user management in Jenkins, enforces MFA and audit trails, and gives users one-click access using their existing credentials. It boosts security and simplifies access without compromising control.

WRITTEN BY Saurabh Jain
Saurabh Kumar Jain is the CSA – Projects Head for DevOps and Kubernetes at CloudThat. An innovative Solutions Architect and technical leader, he is passionate about driving digital transformation across diverse industries. He specializes in designing enterprise-grade, cloud-native solutions, with deep expertise in multi-cloud platforms, Kubernetes orchestration, and AI-powered automation. Saurabh has extensive experience in architecting secure, scalable systems for sectors including oil & petroleum, financial services, e-commerce, and government organizations. He is recognized for his thought leadership in modernization strategies, GitOps workflows, and comprehensive observability implementations. In his free time, he explores emerging technologies in AI and GenAI, contributes to open-source projects, and shares knowledge through technical content and industry speaking engagements.


 Login
Login


 August 26, 2025
August 26, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments