|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
In the evolving landscape of modern applications, responsiveness and scalability are no longer optional, they are essential. As organizations shift towards building highly decoupled, scalable, and real-time systems, event-driven architecture (EDA) emerges as a practical and efficient solution.
This guide introduces beginners to the fundamentals of EDA, explains how AWS services support event-driven systems, and shares industry best practices to help you get started with confidence.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Event-driven Architecture
Event-driven architecture is a software design pattern where components of a system communicate through events. An event is a significant change in system state, such as a user uploading a file or a payment being completed. The architecture is built around the principle of producing, routing, and consuming these events asynchronously.
Core Components of EDA:
- Event Producer: The source that emits the event (e.g., Amazon S3, user actions).
- Event Router: The intermediary that receives and forwards events (e.g., Amazon EventBridge, Amazon SNS).
- Event Consumer: A service that listens to the event and reacts accordingly (e.g., AWS Lambda, AWS Step Functions).
This architecture promotes loose coupling between services, which improves system flexibility, scalability, and resilience.
Why Choose an Event-driven Architecture?
- Scalability: Handle varying workloads without manual intervention.
- Resilience: Failures in one component don’t crash the whole system.
- Real-time Processing: React to events as they occur.
- Improved Modularity: Decoupled services are easier to maintain, test, and deploy.
Key AWS Services for Event-driven Architecture
AWS provides a robust suite of services to build, manage, and scale event-driven systems efficiently:
- Amazon EventBridge
EventBridge is a serverless event bus that simplifies event routing between AWS services, your applications, and external SaaS providers. It enables schema-based event handling and supports complex event filtering and transformation.
Use case: Route events from multiple microservices to trigger specific workflows in Step Functions.
- Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service)
Amazon SNS is a managed publish-subscribe service that allows one-to-many message delivery. It supports multiple subscribers like Lambda functions, HTTP endpoints, email, and SMS.
Use case: Notify multiple downstream services when a customer places an order.
- Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service)
Amazon SQS is a message queue that temporarily stores messages for processing, ensuring reliable and decoupled communication between services.
Use case: Buffer order-processing tasks to ensure smooth handling during peak traffic.
- AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that automatically runs your code in response to triggers such as file uploads, API calls, or event notifications.
Use case: Resize an uploaded image, store it in Amazon S3, and log metadata in Amazon DynamoDB.
- Amazon S3
While Amazon S3 is primarily used for storage, it can generate event notifications (e.g., object created) to trigger downstream actions.
Use case: A file uploaded to Amazon S3 triggers an AWS Lambda function for processing.
Building an Example Workflow
Scenario: Image Processing System
- A user uploads an image to an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Amazon S3 triggers an event notification to Amazon EventBridge.
- Amazon EventBridge routes the event to an AWS Lambda function.
- AWS Lambda resizes the image and stores the new version in another Amazon S3 bucket.
- The processed image metadata is saved in Amazon DynamoDB.
- A notification is sent to the user via Amazon SNS.
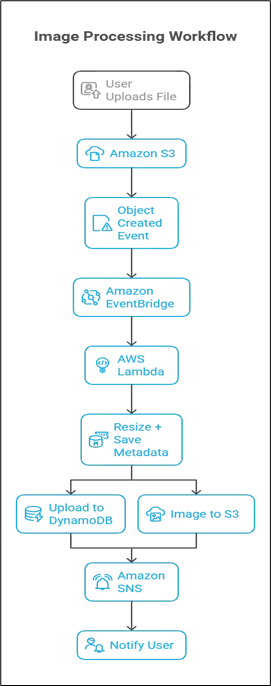
This system is modular, highly scalable, and responds in real-time.
Best Practices for Implementing Event-driven Architecture
Based on AWS’s architectural guidelines, here are key practices to follow:
- Design for Loose Coupling
Ensure event producers and consumers operate independently. Use Amazon EventBridge or Amazon SNS to decouple services.
- Ensure Event Immutability
Events should be immutable and self-contained. Avoid changing event structure or data after publishing.
- Implement Idempotency
Consumers should be idempotent, processing the same event more than once should not cause errors or duplicates.
- Use Event Schema Registries
Maintain consistent and validated schemas using Amazon EventBridge Schema Registry to avoid integration issues.
- Monitor and Trace Events
Enable observability using Amazon CloudWatch and AWS X-Ray to monitor and trace event flows.
- Handle Failures Gracefully
Use Dead Letter Queues (DLQs) and retries for failed event processing, particularly in Amazon SQS and AWS Lambda.
- Design for Scalability and Throughput
Utilize scalable consumers, such as AWS Lambda, and avoid tight coupling with downstream databases or synchronous dependencies.
Challenges and Considerations
- Event Ordering: Amazon SQS standard queues do not guarantee message order. Use FIFO queues where order matters.
- Event Duplication: Consumers must handle potential duplication due to retries or system issues.
- Data Contracts: Changes to event structure must be backward compatible to prevent consumer breakage.
Conclusion
Event-driven architecture is a powerful approach to building scalable, decoupled, and responsive applications.
By following best practices and starting with small use cases, you can unlock the full potential of event-driven systems in your cloud journey.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Event-driven architecture and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Amazon SNS and Amazon EventBridge?
ANS: – Amazon SNS is a pub-sub messaging service suitable for simple broadcast use cases. Amazon EventBridge is more flexible, supporting filtering, routing, and integrations with SaaS platforms.
2. Can Amazon S3 trigger an AWS Lambda function directly?
ANS: – Yes. Amazon S3 supports native event notifications that can invoke AWS Lambda, Amazon SNS, or Amazon SQS when specific object actions occur.
3. How do I monitor event-driven applications on AWS?
ANS: – Use Amazon CloudWatch for logs and metrics, and AWS X-Ray for tracing and debugging the event flow.

WRITTEN BY Kajal Modhvadiya
Kajal Modhvadiya works as a Research Associate with a keen interest in cloud computing and modern software technologies. She possesses foundational skills in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and is continually exploring cloud platforms such as AWS. Kajal is passionate about learning and simplifying complex tech concepts for beginners. In her free time, she enjoys experimenting with new tools and technologies.


 Login
Login


 December 8, 2025
December 8, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments