|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
AWS CloudFormation is a powerful Infrastructure as Code (IaC) service that enables developers and DevOps engineers to define, deploy, and manage cloud infrastructure consistently and efficiently. One common use case is deploying serverless AWS Lambda functions, which execute code in response to events without needing to provision or manage servers.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Solution Overview
We will write an AWS CloudFormation template and a simple AWS Lambda function with its required configuration, and will update it to test the AWS CodeDeploy traffic shifting functionality.
The Process involved.
- Creating the AWS CloudFormation template.
- Writing one basic AWS Lambda function.
- Deploying the template to create an AWS Lambda function using AWS CloudFormation
Prerequisites
AWS Account: An AWS Account with necessary permissions is needed to create and manage the AWS Lambda function and AWS CloudFormation stack.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Create the AWS CloudFormation template
We will create the AWS CloudFormation template with the necessary configuration to deploy the AWS Lambda function.
Below is the template to create the AWS Lambda function
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 |
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09' Description: 'Template to deploy lambda function' Parameters: LambdaFunctionName: Type: String Default: Lambda-Function ProvisionedConcurrency: Type: Number Default: 2 S3Version: Type: String Default: "" Resources: LambdaLogGroup: Type: AWS::Logs::LogGroup Properties: LogGroupName: !Sub /aws/lambda/${LambdaFunction} RetentionInDays: 30 LambdaRole: Type: AWS::IAM::Role Properties: RoleName: Lambda-Role AssumeRolePolicyDocument: Version: '2012-10-17' Statement: - Effect: Allow Principal: Service: - lambda.amazonaws.com Action: - sts:AssumeRole ManagedPolicyArns: - arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole LambdaFunction: Type: AWS::Lambda::Function Properties: FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFunctionName Runtime: python3.11 Handler: lambda.lambda_handler Role: !GetAtt LambdaRole.Arn Code: S3Bucket: lambda-functions-test-xy S3Key: lambda-function/lambda.zip S3ObjectVersion: !Ref S3Version Timeout: 120 Environment: Variables: LOG_LEVEL: INFO S3_BUCKET: text-bucket LambdaVersion: Type: AWS::Lambda::Version Properties: FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFunction Description: !Sub " Version from ${S3Version}" ProvisionedConcurrencyConfig: ProvisionedConcurrentExecutions: !Ref ProvisionedConcurrency DependsOn: LambdaLogGroup LambdaAlias: Type: AWS::Lambda::Alias Properties: Name: prod FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFunction FunctionVersion: !GetAtt LambdaVersion.Version UpdatePolicy: CodeDeployLambdaAliasUpdate: ApplicationName: !Ref CDApp DeploymentGroupName: !Ref CDDeploymentGroup CDApp: Type: AWS::CodeDeploy::Application Properties: ApplicationName: !Sub ${LambdaFunction}-cd ComputePlatform: Lambda CDRole: Type: AWS::IAM::Role Properties: RoleName: !Sub ${LambdaFunction}-codedeploy AssumeRolePolicyDocument: Version: '2012-10-17' Statement: - Effect: Allow Principal: Service: - codedeploy.amazonaws.com Action: sts:AssumeRole ManagedPolicyArns: - arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSCodeDeployRoleForLambda CDDeploymentGroup: Type: AWS::CodeDeploy::DeploymentGroup Properties: ApplicationName: !Ref CDApp DeploymentGroupName: !Sub ${LambdaFunction}-dg ServiceRoleArn: !GetAtt CDRole.Arn DeploymentConfigName: CodeDeployDefault.LambdaCanary10Percent5Minutes DeploymentStyle: DeploymentOption: WITH_TRAFFIC_CONTROL DeploymentType: BLUE_GREEN AlarmConfiguration: Enabled: false |
2. Explanation of the template.
- In the Resources, we have eight resources: AWS IAM role, Log Group, AWS Lambda Function, AWS Lambda Version, AWS Lambda Alias, AWS CodeDeploy Application, Code Deployment Group, and AWS CodeDeploy Role.
- In the Parameters, we have passed the AWS Lambda function name, Provisioned Concurrency, and Amazon S3 Version.
- In the AWS Lambda Function FunctionName property, we have referenced the parameter LambdaFunctionName to get the value of the AWS Lambda function name.
- In Code, we have passed the zip file of our code that is stored in an Amazon S3 Bucket. We have defined Amazon S3 Key, Amazon S3 bucket, and S3ObjectVersion that the AWS CloudFormation will use to create the lambda function.
- AWS Lambda Version creates a new AWS Lambda version every time we update the Amazon S3 object version. A new version will be created in AWS Lambda.
- We created an alias with the prod name in AWS Lambda Alias. Once we update the stack, the alias will be pointed to the latest version. Update policy helps manage traffic. “When this alias changes to point to a new function version, don’t just flip it immediately, instead, let AWS CodeDeploy manage the rollout”.
- CD App creates the application for AWS CodeDeploy.
- CD Role includes the necessary permission for the AWS CodeDeploy service.
- CD Deployment Group includes the configuration required for a canary deployment in AWS Lambda. We have used LambdaCanary10Percent5Minutes. For the first 5 minutes, 90% of the traffic will be on the older version. After 5 minutes, if there is no alarm, the remaining 90% traffic will be shifted to the newer version.
- In Deployment Style, we have used BLUE_GREEN for AWS Lambda, which means updating the alias to shift traffic from one function version (blue) to another (green). WITH_TRAFFIC_CONTROL manages the alias traffic weighting.
3. Creating the AWS Lambda function.
- Create one AWS Lambda function locally, zip it, then upload it to the Amazon S3 bucket. Below is one basic AWS Lambda function.
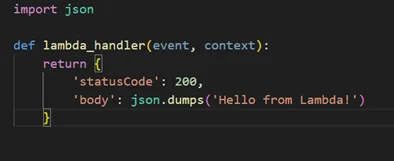
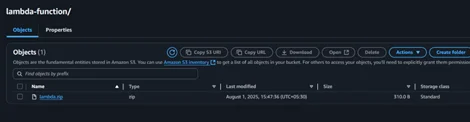
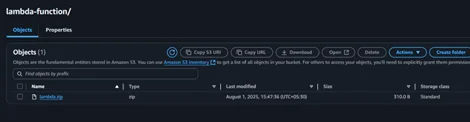
2. Uploaded as a zip in Amazon S3 bucket inside the lambda-function folder.
4. Deploying the Stack
- Upload the AWS CloudFormation template to an Amazon S3 Bucket. We have also used the same bucket to store the template.
- Inside the AWS CloudFormation Console, click Create Stack, then give the S3 URL of the template.
3. Click Next, give the stack name, click Next, again Next, and click Submit.
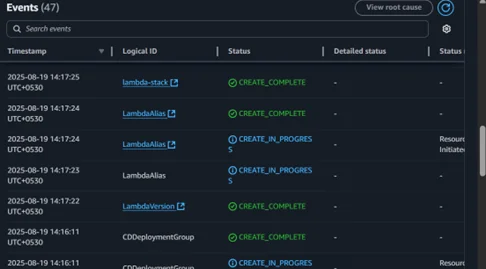
4. The stack is created, and all resources are deployed successfully.
5. AWS Lambda Function is created successfully, and all properties are also set.
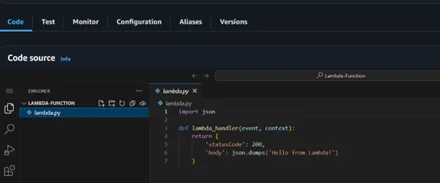
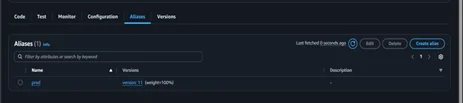
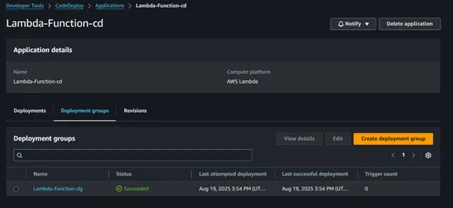
6. Update the AWS Lambda code and upload the zip file to the Amazon S3 bucket.
7. Update the Amazon S3 object version in the AWS Lambda parameter and upload a new template to the Amazon S3 bucket.
8. Create a change set and update the stack in AWS CloudFormation.
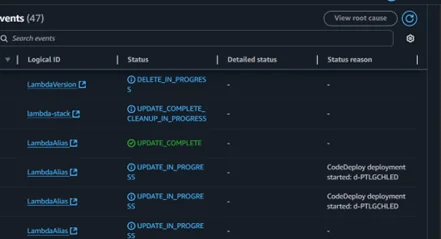
9. The above step will trigger an AWS CodeDeploy deployment.
10. While the Stack is being updated, the traffic is shifting in the AWS CodeDeploy console.
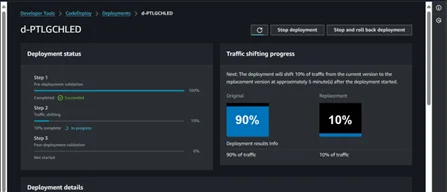
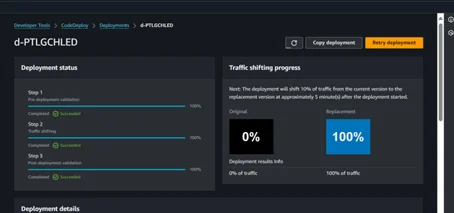
11. After 5 minutes, 100 % traffic will be shifted to the newer version.
Note: Amazon S3 Bucket Permission must be modified if cross-account stack creation is required. Add the required Amazon S3 bucket policy so the template and AWS Lambda function can be used cross-account.
Key Benefits
- AWS CloudFormation is an IaC tool limited to AWS that can create any infrastructure on AWS. We can deploy any service on AWS using AWS CloudFormation.
- AWS CloudFormation helps deploy multiple services at once, which helps orchestrate complex infrastructure setups with dependencies.
- Reduces manual effort by automating the creation, update, and deletion of AWS resources, avoiding the need to configuring each service manually.
- Using AWS CodeDeploy, we can control the traffic management in AWS Lambda and effectively manage the rollback if there is any issue in the newer version.
Conclusion
Using AWS CloudFormation to create AWS Lambda functions and AWS CodeDeploy to manage traffic shifting allows for consistent, version-controlled configuration and reduces manual overhead.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding AWS CloudFormation and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Can I attach triggers (Amazon S3, Amazon SQS, Amazon API Gateway) directly to an Alias?
ANS: – Yes. If we attach event sources to an Alias instead of $LATEST, AWS CodeDeploy can perform safe deployments by shifting traffic gradually through the Alias.
2. Can we use any CI/CD tool to manage the deployment of the AWS CloudFormation template?
ANS: – Yes, we can utilise any CI/CD tool to manage the deployment of the AWS CloudFormation template. If we use AWS CodePipeline, we can directly deploy the AWS CloudFormation template from there.

WRITTEN BY Saurabh Jain
Saurabh Kumar Jain is the CSA – Projects Head for DevOps and Kubernetes at CloudThat. An innovative Solutions Architect and technical leader, he is passionate about driving digital transformation across diverse industries. He specializes in designing enterprise-grade, cloud-native solutions, with deep expertise in multi-cloud platforms, Kubernetes orchestration, and AI-powered automation. Saurabh has extensive experience in architecting secure, scalable systems for sectors including oil & petroleum, financial services, e-commerce, and government organizations. He is recognized for his thought leadership in modernization strategies, GitOps workflows, and comprehensive observability implementations. In his free time, he explores emerging technologies in AI and GenAI, contributes to open-source projects, and shares knowledge through technical content and industry speaking engagements.


 Login
Login


 September 17, 2025
September 17, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments