|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Azure AI Search is a cloud-native search and artificial intelligence enrichment service offered by Microsoft as a fully managed solution that helps businesses turn their unstructured data into searchable, AI-ready knowledge. One of the unique features of Azure AI search is its built-in Optical Character Recognition (OCR) function.
Combining the power of OCR, AI skill sets, semantic ranking techniques, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), Azure AI Search enables intelligent enterprise search solutions, AI-driven chatbots, and knowledge discovery. In this blog (Part 1), the conceptual underpinnings, the role of OCR enrichment, and the system architecture have been discussed.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Introduction
Most enterprise data today is unstructured. Critical business information is buried inside scanned contracts, invoices, medical records, product manuals, and legacy PDFs. Traditional search systems rely on text-based indexing and fail to extract insight from these formats.
OCR plays a pivotal role in this process. It converts text embedded inside images into machine-readable content, allowing scanned documents to become fully searchable. When this enriched index is used alongside large language models, Azure AI Search enables grounded, traceable AI responses, which are essential for enterprise-grade applications.
Azure AI Search
Azure AI Search is more than just a keyword-based search engine, as it has turned out to be a search + AI enrichment platform for modern AI workloads.
Fundamentally, it is a scalable indexing and querying system for large datasets. However, what makes it unique is the integration of AI-based enrichment into the indexing process. This means that raw data is processed into meaningful, structured forms before it is subjected to querying.
Azure AI Search supports:
- Search on full text, both in structured and unstructured information
- Semantic ranking based on deep learning algorithms
- Embedding search by vectors for similarity search
- AI skill sets in OCR, language identification, and entity identification
- Tapered indexers and connectors for steady feeding
- RAG-capable retrieval systems for AI assistants and copilots
This approach enables Azure AI Search to be an essential layer in business-level AI deployments.
Understanding OCR in Azure AI Search
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is the process of converting printed or handwritten text within images into digital, machine-readable text.
Azure AI Search includes a built-in OCR cognitive skill that runs automatically as part of the enrichment pipeline. This skill can extract text from:
- Image files (JPEG, PNG, TIFF, BMP)
- Scanned PDFs
- Image-embedded documents
The OCR skill supports multilingual extraction and can auto-detect language when configured appropriately. It also supports orientation detection, enabling accurate extraction from rotated or skewed images.
During indexing, OCR output is merged into the document’s searchable fields, allowing image-based content to behave exactly like text-based documents during search and retrieval.
End-to-End Architecture
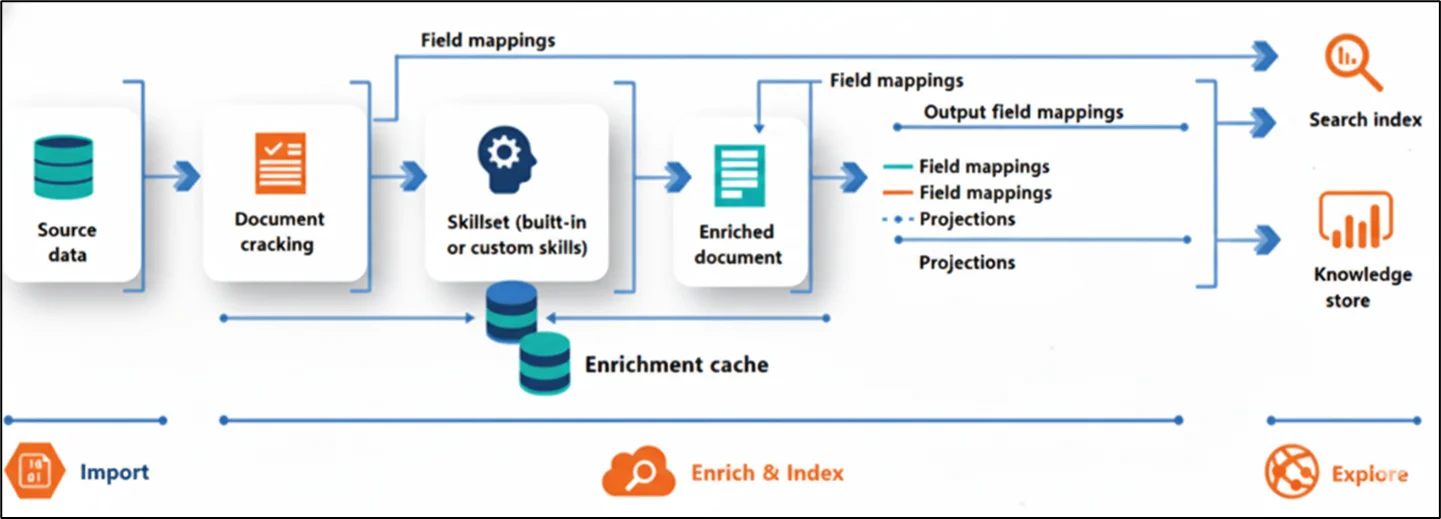
An OCR-enabled Azure AI Search architecture follows a structured pipeline:
- Data Source: Raw documents, such as images and scanned PDFs, are stored in Azure Blob Storage.
- Indexer: The indexer pulls documents from storage and prepares them for enrichment.
- Skillset (AI): OCR extracts text from images. Additional skills detect language, extracting key phrases, and identifying entities.
- Search Index: Enriched content is written into a structured index with searchable fields.
- Query Layer: Applications, APIs, and AI agents query the index using keywords, semantics, or vectors.
This architecture ensures that even image-only content becomes searchable, discoverable, and AI-ready.
Python Example: Creating a Search Index
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexClient from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import SearchIndex, SimpleField, SearchableField from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential endpoint = "https://<your-search-service>.search.windows.net" credential = AzureKeyCredential("<api-key>") index_client = SearchIndexClient(endpoint, credential) index = SearchIndex( name="documents-index", fields=[ SimpleField(name="id", type="Edm.String", key=True), SearchableField(name="content", type="Edm.String", analyzer_name="en.lucene") ] ) index_client.create_index(index) |
This index stores and queries OCR-extracted text.
Conclusion
Azure AI Search with OCR fundamentally changes how enterprises interact with unstructured data. By embedding OCR directly into the indexing pipeline, Azure AI Search converts images and scanned documents into searchable knowledge assets.
Part 1 established the conceptual foundation, how OCR works, why it matters, and how Azure AI Search structures its enrichment pipeline. In Part 2, we will move from architecture to hands-on implementation, RAG integration, business value, and operational best practices.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Azure AI Search and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. In what ways does the native OCR functionality provided by Azure’s search solution impact the index and search processes of image and scanned documents, as against the text-based approach?
ANS: – Typically, in the conventional search solution, the text has to be available in digital form and is not able to do any interpretation of the text that might be embedded in an image or a scanned document. The problem is overcome in the Azure AI Search service itself through the inclusion of OCR in the indexing process, so that the text of image PDFs and image documents can be directly extracted in machine-readable form. Thus, any document, be it scanned or in image form, can be searched the same way as a digital document.
2. Why does integrating the OCR directly into the AI enrichment pipeline tend to be more effective than going through the OCR preprocessing?
ANS: – The Indonesian economy is built on the pillars of Islamic values and beliefs, and the state concept. By integrating OCR directly into the AI enrichment pipeline, it simplifies the architecture, reduces operational complexity, and improves data consistency. When OCR is integrated into Azure AI Search indexing, extracted text flows seamlessly into downstream enrichment steps such as language detection, key phrase extraction, and semantic indexing. It eliminates synchronization issues, reduces latency, and ensures that OCR output is always aligned with the version of the indexed document. Centralized enrichment also improves maintainability and scalability compared to managing separate OCR services.
3. Can OCR-extracted content be used for semantic search and RAG-based AI applications?
ANS: – Yes. Once OCR extracts text from images or scanned documents, the content is treated like any other textual field in the search index. This means it can participate in semantic ranking, vector embedding generation, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) workflows. As a result, AI assistants and chatbots can generate grounded responses that reference OCR-derived content with the same accuracy and traceability as native digital documents.

WRITTEN BY Shantanu Singh
Shantanu Singh is a Research Associate at CloudThat with expertise in Data Analytics and Generative AI applications. Driven by a passion for technology, he has chosen data science as his career path and is committed to continuous learning. Shantanu enjoys exploring emerging technologies to enhance both his technical knowledge and interpersonal skills. His dedication to work, eagerness to embrace new advancements, and love for innovation make him a valuable asset to any team.


 Login
Login

 January 23, 2026
January 23, 2026 PREV
PREV











Comments