|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
A New Era of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is undergoing a dramatic transformation. The early days of rule-based systems and single-purpose models are behind us. Today’s AI is evolving into a network of intelligent agents that can think, remember and collaborate.
This transformation is powered by what experts are calling the new AI stack – an architecture built around Large Language Models (LLMs), Memory and Multi-Agent Collaboration.
This new stack marks the shift from reactive AI (which only responds to prompts) to proactive AI (which reasons, plans and acts). It enables systems that continuously learn, coordinate and perform complex multi-step tasks – much like a team of humans.
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
The Foundation of the New AI Stack: Large Language Models (LLMs)
At the heart of the new AI stack are Large Language Models (LLMs) – massive neural networks trained on trillions of tokens of text. These models, such as GPT, Claude, Llama and Amazon Titan, have become the “brains” of modern AI systems.
They can reason, analyze, generate content, write code and perform creative problem-solving across domains. Yet, despite their intelligence, LLMs have a key limitation – they are stateless.
Every time an LLM receives a prompt, it treats it as an isolated event, with no memory of past interactions. This makes it difficult for such models to sustain context, recall previous experiences or adapt over time – all essential qualities for enterprise-scale and human-like intelligence.
This is where the memory layer comes in.
Memory: Giving AI Context, Continuity and Learning
Memory is the context engine of the new AI stack. It gives LLMs the ability to remember previous interactions, decisions and learned facts – effectively transforming them from chatbots into thinking, evolving systems.
AI memory can be broken down into three core types:
- Short-Term Context Memory
This type of memory exists inside the LLM’s context window – the space where it processes recent input. Modern models like GPT-4 Turbo and Claude 3.5 can handle context windows exceeding 200,000 tokens, allowing them to analyze books, codebases or complex business workflows in one go. However, this context disappears once the conversation ends.
- Long-Term Memory (Vector Memory)
To provide persistent recall, AI systems utilize vector databases such as Pinecone, Weaviate or Amazon S3 Vectors. These store information as numerical embeddings that represent meaning. When queried, the AI retrieves semantically relevant content – not just keyword matches – enabling Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
RAG is widely used in enterprise chatbots, knowledge assistants and AI copilots to access internal data without retraining the model.
- Episodic and Knowledge Memory
This is the “experience layer.” It allows agents to record events, actions and outcomes over time, building an evolving understanding of the world. Episodic memory is vital for autonomous agents – enabling them to learn from mistakes and improve with each iteration.
Multi-Agent Collaboration: When AIs Work Together
The next breakthrough layer in the new AI stack is multi-agent collaboration – the ability for multiple AI agents, each with specialized roles, to coordinate toward a common goal.
Imagine a system where:
- One agent plans the strategy
- Another gathers data
- A third analyzes insights
- And a fourth writes a final report
Each agent is powered by an LLM but has distinct capabilities and access to tools. Through communication protocols, they negotiate, verify and refine outputs – similar to human teamwork.
This architecture is made possible by open frameworks such as:
- LangGraph and CrewAI (for building multi-agent systems)
- AutoGen (Microsoft) for conversational collaboration
- AWS Step Functions and EventBridge for enterprise orchestration
The Architecture of the New AI Stack
The modern AI architecture can be visualized as a layered stack:
Each layer has a defined role:
- LLMs handle reasoning and natural language understanding.
- Memory systems provide continuity and long-term knowledge.
- Agents collaborate to execute multi-step tasks.
- Integration layers connect AI to real-world data and APIs.
This modular structure is what allows enterprises to scale AI solutions efficiently and safely.
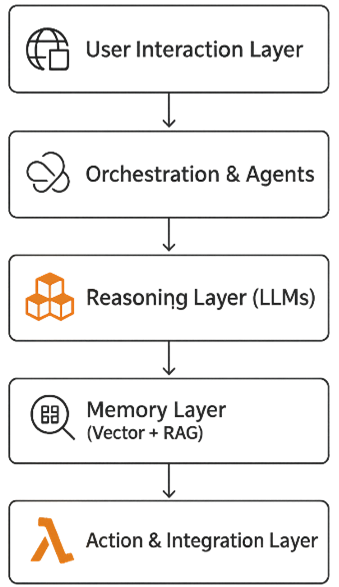
Fig 1: Architecture of the New AI Stack
How AWS Powers the New AI Stack
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides one of the most comprehensive toolsets for building this stack end-to-end:
- Reasoning Layer: Use Amazon Bedrock to access leading foundation models like Titan, Claude and Llama 3 through a managed interface.
- Memory Layer: With Amazon S3 Vectors, developers can store and search semantic embeddings natively in S3, integrating seamlessly with Bedrock RAG workflows.
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: Orchestrate AI agents using AWS Step Functions for workflow management and EventBridge for real-time communication between services.
- Execution Layer: Agents can invoke AWS Lambda, DynamoDB or SageMaker for data retrieval, processing and analytics.
From Automation to Autonomy: The Rise of Agentic AI
Traditional automation follows predefined rules – it doesn’t adapt or reason. The new AI stack, however, gives rise to Agentic AI – systems that dynamically decide how to achieve objectives.
Agentic AI doesn’t just execute commands; it plans, learns and collaborates.
Example Applications
- Data Engineering: AI agents can monitor data pipelines, detect anomalies, and restart failed workflows.
- Customer Support: Agents can combine chat interactions, database lookups, and documentation retrieval to deliver accurate answers.
- Business Analysis: AI teams can collaborate to generate insights, forecast trends and prepare reports automatically.
This level of autonomy marks a major leap toward self-managing enterprise systems.
Challenges and Governance
While promising, the new AI stack brings challenges that organizations must address:
- Data Privacy & Governance: Persistent memory and agent coordination require strong access control.
- Cost Optimization: Multi-agent operations and LLM inference can be resource intensive.
- Quality Control: Multi-agent interactions can introduce bias or inconsistencies.
- Security & Compliance: Each AI interaction must be monitored and auditable to prevent data leaks or unauthorized access.
The Future of Autonomous AI
The new AI stack – integrating LLMs for reasoning, memory for persistence and multi-agent collaboration for teamwork – is paving the way for a new era of autonomous, context-aware and continuously learning AI systems.
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY Nitin Kamble
Nitin Kamble is a Subject Matter Expert and Champion AAI at CloudThat, specializing in Cloud Computing, AI/ML, and Data Engineering. With over 21 years of experience in the Tech Industry, he has trained more than 10,000 professionals and students to upskill in cutting-edge technologies like AWS, Azure and Databricks. Known for simplifying complex concepts, delivering hands-on labs, and sharing real-world industry use cases, Nitin brings deep technical expertise and practical insight to every learning experience. His passion for bike riding and road trips fuels his dynamic and adventurous approach to learning and development, making every session both engaging and impactful.


 Login
Login


 December 16, 2025
December 16, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments