|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Generative AI large foundation models trained on massive datasets can create text, code, images, and more. PartyRock is a web-based playground that makes it easy to experiment with these models without writing production code. It lets you build small AI apps by designing input fields and writing prompts, so you can learn how model behaviour changes as you change instructions. For developers and students, PartyRock is a practical sandbox for learning prompt engineering: the craft of writing precise prompts to get useful, predictable outputs.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Why PartyRock matters for learners and builders?
PartyRock lowers the barrier to entry for working with foundation models. Instead of integrating APIs, provisioning infrastructure, or writing glue code, you define inputs, compose a prompt template, pick an output widget (text or image), and run. For testing prompt design, few-shot examples, chained workflows, and retrieval-augmented generation, this instant feedback loop is perfect. The hands-on experience helps you develop an intuition for how phrasing, context, and examples influence model outputs, a kind of digital literacy increasingly useful in both development and research.
Key takeaways for prompt engineering
- Be clear and specific. Vague prompts produce vague answers. Inform the model about the audience, the level of detail you require, and the expected outcome. Instead of “Explain cells,” say “Explain the difference between plant and animal cells to a 12th-grade student, with one short example.”
- Give background information. Describe your audience’s level of expertise, the tone you want, formatting preferences, and any edge cases the model should consider when creating expectations.
- Describe the structure and format. Tell us if you would like a step-by-step tutorial, a numbered list, or a brief synopsis. Bullet lists, labelled sections, or templates are examples of structured prompts that assist models in producing outputs that are consistent and machine-readable.
- Break tasks into steps. For multi-part problems, instruct the model to complete each part in sequence. This reduces hallucinations and makes it easier to validate intermediate outputs.
- Give a few-shot examples. The model is guided toward your preferred style and structure by displaying one or two optimal outputs. When you require specialized material or uniform formatting, examples work well.
- Iterate frequently. Prompting is often an iterative process: run, observe, refine. Small changes in wording or added constraints can produce big improvements.
A step-by-step PartyRock workflow (build a simple app)
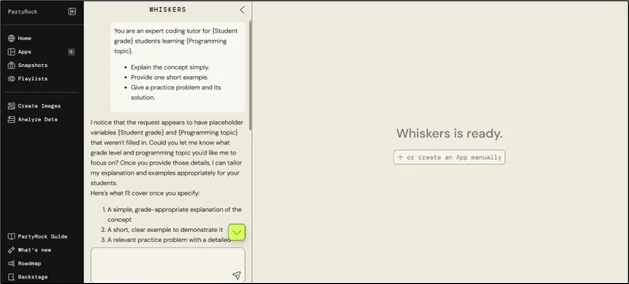
- Make a new application(app) and specify its goals. Start with a clear goal. “Build a coding tutor that explains a topic, gives one example, and provides a practice problem,” for instance.
- Specify the input fields. Select the variables that the user will enter, such as “Difficulty level,” “Student grade,” and “Programming topic.” In your prompt, these turns become template variables.
- Create the template for the prompt. Using those variables, create a concise, well-organized prompt. An example of a template.
|
1 2 3 4 |
You are an expert coding tutor for {Student grade} students learning {Programming topic}. - Explain the concept simply. - Provide one short example. - Give a practice problem and its solution. |
4. Add output widgets. Choose an AI text widget for explanations and, if useful, an image widget to generate diagrams or illustrations derived from the text.
5. Run and review results. Fill the inputs and run the app. Evaluate clarity, accuracy, and whether the output matches the requested format.
- Selecting the grade
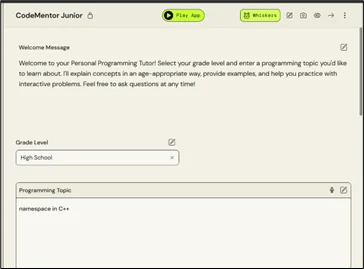
- A chatbot where students can ask questions, and topics will be explained according to grade level
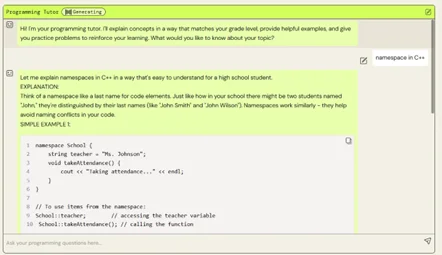
6. Make the prompt more precise. Add restrictions such as “Use simple language and keep the explanation under 150 words” if the response is overly complex or verbose. To push the style, add or modify examples.
7. Richer programs can use chain widgets. To produce visual aids, feed the text output into an image generator. For a brief takeaway part, you can also enter an explanation into a summarizer widget.
8. Examine scale and edge cases. To comprehend failure modes, experiment with different inputs and subjects. Examine how the model responds to unclear or ill-defined stimuli and make necessary adjustments. What you learn about model capabilities
Working in a playground like PartyRock teaches two complementary things: what models can do, and how to design prompts that get the most useful behaviour out of them.
- Text capabilities: Models can provide creative writing, code snippets, explanations, translations, summaries, and quizzes. Depending on how your prompt is worded and which model you select, you’ll notice differences in tone, conciseness, and technical accuracy.
- Image capabilities: Models can provide straightforward diagrams or illustrative visuals to accompany text when image production is available. Detailed visual explanations and examples are frequently beneficial for prompt image structure.
- Chaining and multi-step flows: Combining outputs as inputs for subsequent steps reveals how to set up multi-stage applications, such as generating a lesson, creating practice problems, and generating visuals, all tied together automatically.
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG): This technique demonstrates how models can eliminate hallucinations and incorporate external context by uploading documents and instructing the model to base its answers on those documents.
- Limitations and failure modes: Models can misinterpret subtle demands, overlook constraints, or generate information that appears plausible but is inaccurate. It’s critical to identify these patterns; fast methods, such as requesting the model to “show work” or provide a step-by-step response, can enhance reliability.
Effective tasks to attempt
- Personalized tutor: Create a tutor who modifies explanations according to learning preferences (textual vs. visual) and grade level.
- Quiz generator: Create multiple-choice questions with distractions and an explanation of the right response.
- Code explainer: Enter a brief code sample to receive a simplified example and an explanation in plain language.
- Study flashcards: Choose a subject and create flashcards that include definitions, examples, and brief tests.
Conclusion and recommendations
PartyRock is a friendly, low-friction space to practice prompt engineering. It provides instantaneous feedback that’s ideal for students and early-career developers trying to understand how to interact with foundation models. To get the most from it:
- Start small and iterate. Build a simple app, test, and refine the prompt.
- Always indicate audience, format, and constraints.
- Use few-shot examples to guide style and structure.
- Chain steps when the task is multi-part and test edge cases to expose weaknesses.
- Consider the playground a workshop for communication skills: good prompts are specific, structured, and purposeful.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding PartyRock and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is PartyRock?
ANS: – PartyRock is an interactive, no-code playground built by AWS for experimenting with Generative AI models. It enables users to create small AI-driven applications using simple input fields and prompt templates, with no integration with APIs or programming required.
2. Do I need to know coding to use PartyRock?
ANS: – No. PartyRock targets all categories of users: non-technical learners to seasoned developers. You can build functional AI applications using just natural language prompts, and no production code needs to be written.
3. What kind of outputs can I generate with PartyRock?
ANS: – You can generate text explanations, summaries, code, quizzes, and other content, as well as images such as illustrations and diagrams. The support for multimodal output enables richer educational and creative experiences within the platform.

WRITTEN BY Akanksha Choudhary
Akanksha works as a Research Associate at CloudThat, specializing in data analysis and cloud-native solutions. She designs scalable data pipelines leveraging AWS services such as AWS Lambda, Amazon API Gateway, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon S3. She is skilled in Python and frontend technologies including React, HTML, CSS, and Tailwind CSS.


 Login
Login


 December 2, 2025
December 2, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments