|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
Although generating AI is revolutionizing enterprise applications, it remains challenging to produce reliable, high-quality results for complex tasks consistently. Monolithic, multi-part instructions are frequently problematic for large language models (LLMs). Here’s where Amazon Bedrock’s Prompt Chaining comes in handy.
A sophisticated prompt engineering method called “Prompt Chaining” divides a difficult task into a series of more manageable, clearly defined subtasks. A structured, multi-step workflow is created by automatically feeding the output from one LLM invocation as the input to the subsequent one. Strong and scalable prompt chaining solutions can be implemented by utilizing orchestration tools such as AWS Step Functions or Bedrock Flows, as well as Amazon Bedrock. This fully managed service provides a selection of high-performing Foundation Models (FMs).
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Objective
This blog post aims to define prompt chaining, explain its primary advantages, and demonstrate how the Amazon Bedrock ecosystem utilizes it architecturally. Developers can create more dependable, transparent, and advanced generative AI applications that can manage complex, enterprise-level tasks by comprehending this pattern.
Prompt Chaining
The process of breaking down a more complex task into a sequence of prompt steps and feeding the results of one step into the subsequent prompt, often with extra context or transformation, is known as prompt chaining.
For example:
- Examine the raw material (such as a lengthy document) and identify any important facts or entities.
- Summarize those entities/facts into a more manageable format.
- Create a final, business-ready output (report, brief, or decision) using the summary.
You structure several linked prompts instead of asking the LLM to complete everything in a single, monolithic prompt. Prompt chaining “allows you to break down complex tasks and questions into subtopics, each as a different input prompt to a model,” according to AWS.
Why is this helpful?
- The model increases reliability, as it can handle smaller prompts with a more focused scope more easily.
- Debugging and iteration are made easier because you can test and improve each sub-step separately.
- Enables workflow logic by allowing you to create loops, decision points, and result reuse.
- Allows for modularity and maintainability: Prompt templates for frequently performed subtasks can be reused.
Why Use Amazon Bedrock's Prompt Chaining?
The following explains how prompt Amazon Bedrock in particular supports chaining and why you might use it:
- Integrated orchestration assistance
With features like Amazon Bedrock Flows and AWS Step Functions integration, Bedrock facilitates deep workflows. The AWS documentation, for instance, provides an example project in which Step Functions coordinate prompt chaining with Bedrock. Flows and Step Functions are perfect for complex chains because they let you define loops, parallel branches, sequences, and decision logic.
- Timely versioning and Management
Prompt Management is a feature of Amazon Bedrock that allows you to save, test, and version prompt templates (with variables) for later use. This promotes reuse, speeds up development, and guarantees uniformity throughout workflow stages.
- Integration of advanced patterns
Prompt chaining can be combined with other strategies, such as conditional branching (routing), retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), human-in-the-loop, and others. AWS explains human error in a prompt-chaining process, for instance. - Production readiness and scalability
You can scale these workflows in production with branching, error handling, and monitoring by utilizing managed LLM endpoints and serverless orchestration (Step Functions, Lambdas). This is demonstrated in the “amazon-bedrock-serverless-prompt-chaining” GitHub repository.
Architectural Flow of Prompt Chaining in Amazon Bedrock
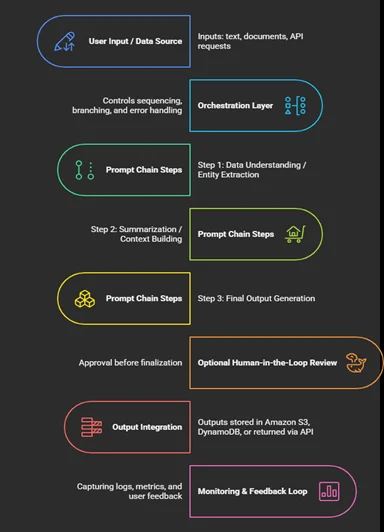
Obstacles and How to Get Past Them
Even though prompt chaining is effective, there are a few things to think about:
- Context propagation: Ensuring that each step receives the right context; If the chain gets too long, you run the risk of memory/context overflow or losing track of previous inputs. In between steps, provide concise summaries.
- Error accumulation: If an early step yields a subpar result, the error may spread to later steps. Use human review, validations, checks, or backup procedures to mitigate.
- Cost and latency: Several model calls result in higher expenses and longer reaction times. Chaining granularity and overhead should be balanced.
- Model consistency and drift: As models change over time, you may notice variations in the behavior of the output. Create a version of your prompts and track any modifications made.
- Governance and compliance: Every step’s output may require auditability, traceability, and human oversight, particularly in regulated industries.
- Complex branching logic: Maintaining orchestration logic (flows, conditions) may become more difficult as chains get longer. Utilize visual flow builders and modular design.
- Quick maintenance: You will need to handle versioning, documentation, and reusable catalogs, as you will have a large number of prompt templates. Amazon Bedrock’s Prompt Management can help with this.
Real World Applications
- Automation of Customer Support:
Using Step Functions in Bedrock, prompt chaining can categorize customer tickets, compile complaints, produce answers, and start escalation processes.
- Document Intelligence
Chaining can extract facts, summarize findings, and create summaries that are ready for compliance in the legal, financial, or healthcare sectors.
- Creation of Product Descriptions
E-commerce businesses can utilize chain prompts to examine features, create descriptions optimized for search engines, and tailor tone to their audience or location.
- Management of Knowledge
Large document repositories can be cleaned, condensed, and arranged into searchable knowledge bases by organizations using chain prompts.
- QA and Code Generation
Code snippets can be generated, tested, and improved across iterations by developers using chained prompts, which increases safety and dependability.
- Pipelines for Marketing Content
Campaign creation, including ideation, draft writing, tone assessment, and final ad copy generation, can be automated with prompt chains.
Conclusion
Builders can transform foundation models into reliable, production-grade systems with the help of prompt chaining. This method works well with Amazon Bedrock’s managed services, which provide flexibility, scalability, and dependability.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Amazon Bedrock and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Is it possible to combine various foundation models in a chain?
ANS: – Indeed. Depending on the task, you can direct prompts to various models (such as Titan Text for summarization and Claude for reasoning).
2. How can we make sure multi-step workflows are reliable?
ANS: – Apply human-in-the-loop reviews when needed, include guardrails, and use validation at every stage.
3. Is it economical to use prompt chaining?
ANS: – Yes, provided it is properly designed. Token usage and total model calls can be decreased by maintaining the focus of each prompt and eliminating superfluous context.

WRITTEN BY Balaji M
Balaji works as a Research Associate in Data and AIoT at CloudThat, specializing in cloud computing and artificial intelligence–driven solutions. He is committed to utilizing advanced technologies to address complex challenges and drive innovation in the field.


 Login
Login


 October 30, 2025
October 30, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments