|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Running mutually exclusive table operations in Amazon Redshift using Apache Airflow requires thoughtful orchestration to prevent locking issues and maximize both cluster throughput and ETL reliability. This in-depth blog will walk through the architectural principles, Airflow DAG design patterns, Amazon Redshift locking behavior, and best practices you need to build scalable pipelines. Visuals are described within each section to guide your implementation.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Introduction
Data engineering workloads often require updating, transforming, or inserting data into multiple Amazon Redshift tables. When multiple concurrent tasks access the same table, especially with heavy DDL or batch inserts, locks can stall pipelines, delay reporting, and impact user queries. Apache Airflow, as a workflow orchestrator, can mitigate this by enforcing mutually exclusive task patterns.
Understanding Amazon Redshift Table Locks
Amazon Redshift uses a version of PostgreSQL’s table-level locking. Key lock modes include:
- ACCESS SHARE: Allows concurrent SELECT, but blocks DDL.
- ACCESS EXCLUSIVE: Blocks all other table operations, triggered by commands like ALTER, DROP, and TRUNCATE.
Illustration: Visualize an Amazon Redshift cluster with multiple sessions, each trying to ALTER or INSERT into the same table, resulting in a queue of waiting operations.
Long-running transactions, uncommitted changes, and simultaneous DDL can all force exclusive locks, stalling other tasks until the lock is released.
DAG Design for Mutual Exclusivity
Task Isolation Strategy
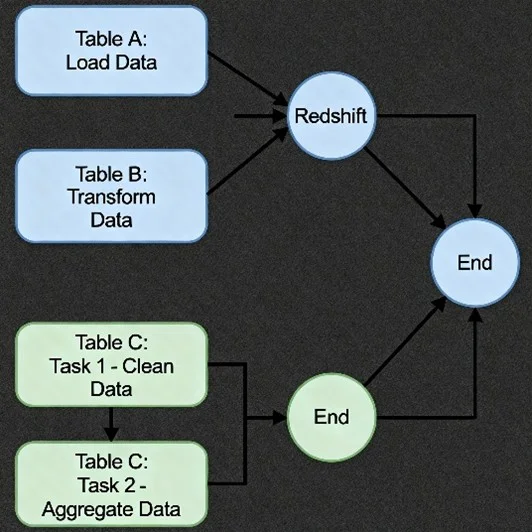
Imagine a directed graph (DAG) with distinct branches for each table. Each Airflow task targets only one table at a time. Downstream tasks for table B cannot run until upstream tasks for table A are finished if they touch the same table.
- Code Example:

Task Grouping and Dependencies
By grouping tasks in Airflow and defining dependencies, you can serialize table operations to avoid concurrent access. For example, group all table A modifications together and use Airflow’s native dependencies (task_A1 >> task_A2) to sequence them.
Orchestrating Multiple Tables
Parallel vs Serial Execution
- Safe Parallelism: Operations on different tables (e.g., table A and table B) can run in parallel, leveraging Airflow’s concurrency features, as long as they do not interfere with each other.
- Serial Execution: When two operations touch the same table, serialize them using explicit Airflow dependencies.
Handling Locks and Preventing Conflicts
Monitor and Release Locks
Use system views or queries to monitor lock states:

In Airflow, you could trigger a PythonOperator to poll for locks before proceeding with heavy operations.
Short Transactions & Autocommit
Keep transactions short; avoid open transactions spanning multiple steps. Use Amazon Redshift’s AUTOCOMMIT setting to quickly free locks:
Python

Amazon Redshift Operator Best Practices
Use Airflow Amazon Redshift Operators
- RedshiftSQLOperator for individual SQL commands.
- Set up connections via Airflow UI or AWS Secrets Manager to avoid embedding credentials directly in DAGs.
Sensor Implementation
Use Airflow Sensors to check table availability or lock status, pausing the DAG until the table is free.
Amazon Redshift Configuration Tips
- Tune Workload Management: Configure WLM queues to isolate ETL jobs from reporting queries, reducing lock contention.
- Concurrency Scaling: Amazon Redshift can auto-scale queries, enable this for larger workloads to prevent user queries from being queued.
- Sort and Distribution Keys: Design tables to minimize concurrent access hot spots by choosing optimal sort and distribution keys.
Data Quality and Cleanup
Include cleanup tasks in your DAGs to eliminate orphaned temp data and ensure all transactions are finalized (committed or rolled back). This is crucial to avoid lingering locks after failed workflows.
Example End-to-End DAG
A full DAG might involve:
- Staging data from Amazon S3
- Transforming with isolated table operators (RedshiftSQLOperator)
- Quality checks (PythonOperator or custom Sensor)
- Serializing table operations when needed
- Cleanup steps to finalize transactions and unlock resources
Conclusion
By designing Airflow DAGs with explicit, mutually exclusive task patterns, monitoring Amazon Redshift locks, tuning cluster configuration, and using short transactions, you can build scalable, high-performance data pipelines while avoiding costly table locks and workflow failures.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Amazon Redshift and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. How can Airflow DAGs prevent table locks in Amazon Redshift?
ANS: – By sequencing tasks that access the same table and running operations on different tables in parallel, Airflow DAGs avoid simultaneous locks on Amazon Redshift tables.
2. What is the main cause of table locks in Amazon Redshift during ETL?
ANS: – Locks mainly occur due to concurrent DDL operations or long-running, uncommitted transactions on the same table.
3. What Airflow feature helps detect or avoid lock conflicts?
ANS: – Airflow Sensors and explicit task dependencies let you check lock status and serialize table modifications, minimizing lock conflicts.

WRITTEN BY Bineet Singh Kushwah
Bineet Singh Kushwah works as an Associate Architect at CloudThat. His work revolves around data engineering, analytics, and machine learning projects. He is passionate about providing analytical solutions for business problems and deriving insights to enhance productivity. In his quest to learn and work with recent technologies, he spends most of his time exploring upcoming data science trends and cloud platform services, staying up to date with the latest advancements.


 Login
Login


 December 2, 2025
December 2, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments