|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Generative AI has moved from experimentation to real production adoption. Enterprises are now deploying chatbots, virtual agents, document analyzers, and search assistants powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). However, once these models are integrated with real users, one problem immediately shows up: cost unpredictability.
Unlike traditional software infrastructure, where compute use is predictable and stable, Generative AI workloads fluctuate based on token volume, user prompts, and model complexity. Each prompt can trigger thousands of tokens, and when users upload large documents, the token count can explode. A single spike in token usage can result in a sudden increase in billing.
To avoid uncontrolled spending, organizations need a smart cost architecture that predicts usage and automatically optimizes compute cost. AWS enables this through three key components:
- Usage-based cost prediction
- Auto-scaling inference infrastructure
- Compute cost optimization using Inferentia clusters and Savings Plans
This blog explains how to design that architecture.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Why LLM Inference Cost Spikes?
LLMs are billed per token. Inference cost = input tokens + output tokens.
Example:
If a user uploads a long document and asks multiple questions about it, token usage increases at every step: chunking, embedding, querying, and generating an answer.
The cost problem usually arises due to:
- Uncontrolled input size (large PDF or huge prompts)
- Unbounded output generation (max tokens too high)
- Models are unnecessarily large for the task
- Always-on GPU infrastructure running even when idle
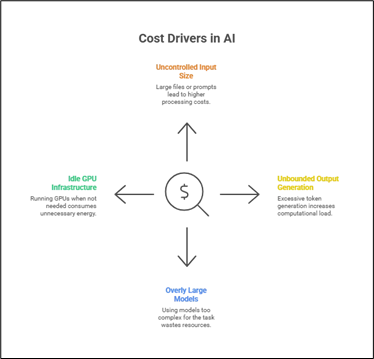
Most companies discover these problems only after receiving their monthly AWS bill. That is too late. The goal is to gain real-time visibility and optimize before costs accumulate.
AWS Solution: Cost Architecture for Predictability and Control
A scalable, cost-optimized design on AWS follows this flow:
- Incoming request enters via Amazon API Gateway or AWS AppSync.
- Lambda logs metadata, including the number of tokens, user ID, and model type.
- The cost estimation logic calculates an approximate cost per request.
- The application decides whether to route inference to:
- Bedrock (serverless, pay-per-token model inference), or
- Custom LLM deployed on Amazon SageMaker or Amazon ECS using Inferentia clusters.
- Amazon CloudWatch monitors traffic and triggers auto-scaling for compute.
- AWS Savings Plans reduce the cost of baseline compute usage.
This design gives transparency (cost tracking), elasticity (auto-scaling), and efficiency (Inferentia + Savings Plans).
Component 1: Predicting Token Cost Using AWS Lambda
The first key step is cost visibility. Every inference request logs:
- Model name used
- Input token count
- Output token count
- User/request ID
AWS Lambda function then calculates cost using a simple formula:
Estimated request cost = (Input tokens + Output tokens) × Model price per token
This helps teams track:
- Which requests are expensive
- Which users or workflows drive token usage
- Whether prompt limits need adjustment
These logs are stored in Amazon CloudWatch or Amazon S3 and visualized using Amazon QuickSight or Amazon Athena queries. Over time, the pattern becomes predictable, enabling monthly cost forecasting.
Component 2: Auto-Scaling Compute Layer Using Inferentia (Inf2)
When organizations deploy custom LLMs (e.g., Llama, Mistral, Mixtral), the compute cost becomes significant. Using GPUs (such as A10G or A100) increases costs dramatically if models run 24/7.
AWS Inferentia2 (Inf2 instances) are built specifically for inference:
- Up to 70% cost reduction compared to GPU instances
- Handles high throughput and parallel inference
AWS supports two auto-scaling deployment choices:
- Amazon SageMaker Inference Endpoint with Autoscaling
- Amazon ECS on Amazon EC2 Inferentia cluster with Application Auto Scaling
Auto-scaling triggers include:
- Queue length
- CPU / NeuronCore utilization
- Number of in-flight inference requests
When traffic increases, extra instances spin up. When requests drop, instances scale down. The business benefit is clear: only pay for compute during actual usage.
Component 3: Savings Plans to Reduce Baseline Cost
Even with auto-scaling, some base compute is always running. AWS Savings Plans help optimize the recurring cost.
Savings Plans allow you to commit to a certain amount of compute usage (e.g., $200 per month) in exchange for discounted pricing across Amazon EC2, Amazon ECS, and Amazon SageMaker.
Why Savings Plans matter here:
- Inference workloads often have predictable baseline usage
- Peak traffic is handled by auto-scaling, but baseline traffic benefits from a discounted cost
Example:
Base expected usage: 2 Inferentia instances
Peak workload: bursts to 10 instances using auto-scaling
Savings Plans apply to the base load, and auto-scaling handles the burst.
This combination gives stability + flexibility.
End-to-End Flow of the Architecture
- User sends inference request.
- Amazon API Gateway forwards it to AWS Lambda.
- AWS Lambda logs cost, estimates price, and routes to Amazon Bedrock or Inferentia.
- Amazon CloudWatch monitors token volume and instance utilization.
- Auto-scaling increases or decreases the compute fleet.
- AWS Savings Plans reduce the cost of the baseline compute that runs continuously.
The architecture strikes a balance between flexibility and cost control.
Cost Optimization Patterns
Several techniques drastically reduce cost:
- Minimize token usage through prompt compression
- Limit output tokens using the max token cap
- Dynamically choose a small vs a large model based on prompt complexity
- Cache embeddings and avoid duplicate generation
- Reuse inference compute with auto-scaling rather than always-on GPUs
Many teams overspend simply because they always opt for the largest model.
Outcome and Benefits
Companies adopting this architecture typically observe:
- 40–70% reduction in inference compute cost through Inferentia
- Predictable billing due to cost estimation and dashboards
- Zero unused compute charges thanks to auto-scaling
- Significant savings on baseline compute via Savings Plans
Instead of reacting to unexpected bills, organizations proactively manage costs.
Conclusion
Generative AI workloads introduce a new cost model, characterized by token-based pricing and elastic compute usage, which makes costs highly variable. To ensure sustainable AI adoption, enterprises need a cost architecture that predicts usage and automatically optimizes spend.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Cost for LLM Models and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. How do I estimate LLM inference cost before deployment?
ANS: – Estimate cost using:
(Input tokens + Output tokens) × model price per token.
Log token usage for every request using Lambda and store it in Amazon CloudWatch or Amazon S3.
2. Should I use Amazon Bedrock or deploy my own LLM on Amazon SageMaker/Amazon ECS?
ANS: –
- Use Amazon Bedrock when you need serverless, quick production, and managed scaling.
- Use Inferentia on Amazon SageMaker/Amazon ECS when inference volume is high, and cost optimization is a priority.
3. What makes AWS Inferentia cheaper than GPUs?
ANS: – AWS Inferentia2 is built specifically for inference, allowing higher throughput per dollar and up to 70% cost savings compared to GPU-based inference.

WRITTEN BY Sidharth Karichery
Sidharth is a Research Associate at CloudThat, working in the Data and AIoT team. He is passionate about Cloud Technology and AI/ML, with hands-on experience in related technologies and a track record of contributing to multiple projects leveraging these domains. Dedicated to continuous learning and innovation, Sidharth applies his skills to build impactful, technology-driven solutions. An ardent football fan, he spends much of his free time either watching or playing the sport.


 Login
Login


 December 2, 2025
December 2, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments