|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Modern cloud infrastructures produce massive amounts of logs, metrics, and alerts. In the event of an incident, engineers need to correlate data across multiple systems rapidly to identify the root cause and restore service. This post describes how agentic AI systems will automate incident analytics in the cloud by orchestrating the work of multiple intelligent agents that investigate, reason, and recommend actions to reduce response time and operational overhead.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Introduction
Traditional rule-based monitoring and alerting systems break down and provide less actionable insight as cloud architectures continue to grow in complexity. Engineers often manually scan dashboards, logs, and runbooks for clues during every outage, which is very valuable time.
Agentic AI works differently. Rather than a single model that responds to prompts, many specialized agents work together as powerful components called knowledge workers that handle tasks such as log analysis, metric evaluation, or remediation guidance.
Benefits of Agentic AI in Incident Analysis
- Rapid Root Cause Identification
Every agent focuses on a particular data source, enabling multiple agents to analyze data in parallel and resulting in faster diagnosis.
- Reduced Operational Load
It helps in optimizing the tasks of the engineers, thus eliminating the need to physically assess the alerts automatically.
- Consistent and Explainable Responses
Agentic workflows entail a predetermined sequence of reasoning steps, which deliver structure, repeatability, and auditable outcomes.
Use Cases
Cloud Production Outages
Analysing monitoring notifications, recent deployment activity, and error logs helps agents identify issues in services such as Kubernetes pods and serverless functions.
Configuration Drift Detection
This is when an “agent” identifies deviations in predicted cloud patterns and provides explanations for the drift that occurred in what way and when it happened.”
Security Incident Triage
In this technique, agents use unusual patterns of access and network activity to detect potential threats to the system’s security.
Solution Explanation
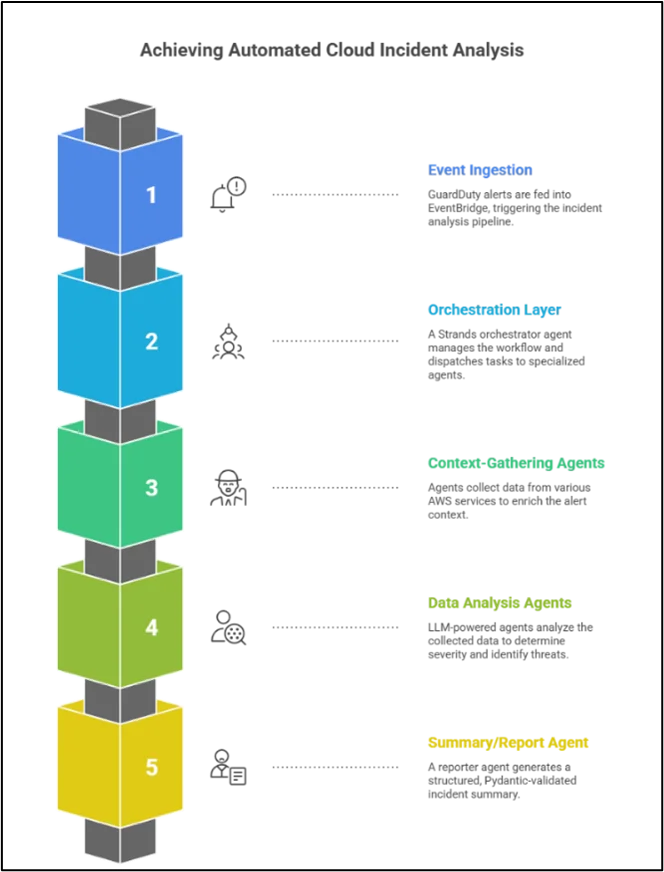
The response uses Strands Agents to manage a multi-step, multi-agent incident triage pipeline on AWS. An Amazon GuardDuty finding (via EventBridge) triggers a pipeline that activates the Strands-based orchestrator (e.g., Strands running in an AWS Lambda function), which controls the work of specialized sub-agents. Each agent tackles a dedicated task, such as EvidenceCollector agents for extracting data from/around AWS, Analysis agents for threat analysis, and a dedicated Reporter agent for presenting the outcome. The data source/toolset is provided via the involved AWS services. Amazon GuardDuty is the initial finding, which is forwarded via the Amazon GuardDuty rule trigger in Amazon EventBridge to our agent pipeline. An example architecture would then be as follows:
Event Ingestion: The results are fed to Amazon EventBridge, which triggers an AWS Lambda or Step Function, which in turn triggers the Strands orchestrator.
Orchestration Layer: A Strands “orchestrator” agent is the main agent that receives the alert JSON and dispatches tasks to child agents. Following Strands’ “agents-as-tools” pattern, specialized agents are exposed as callable tools. One tool-agent might handle log retrieval, another threat classification, and another summary generation.
Context-Gathering Agents: Agents call AWS APIs to enrich the alert. As such, a LogRetrieval agent will query CloudTrail for related API events, or for inventories of Amazon EC2/Amazon VPCs, or for Amazon S3 logs, based on the Amazon GuardDuty finding. Similarly, a ConfigEnrichment agent could get AWS Config data or tags from Amazon S3 or Amazon DynamoDB in order to understand the context of the resource. All these tools are using boto3 under the hood, so every single API call, be that GetTrailEvents or DescribeInstances, is tracked by CloudTrail, thus fully auditable.
Data Analysis and Triage Agents: Once data is collected, an Analysis agent analyzes the evidence. They can determine the type of case, severity, or suspect attacker activity. As Strands is model-driven, the LLM will instruct which tools to invoke.
Summary/Report Agent: Finally, a Reporter agent generates a structured incident summary. With a Pydantic schema, it produces a JSON report (incidents_id, severity, description, action_items). The structured-output capability of Strands assures that this report is in our schema. If not, Pydantic will detect the difference, thus preventing wrong outputs. The summary can be persisted to Amazon S3 or sent to a ticketing service. All key findings (timeline, impact, mitigation actions) are summarized here.
For example, our Python pseudo-code could look like:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
from strands import Agent, tool import boto3 @tool def get_cloudtrail_logs(guardduty_finding: str) -> str: # Query CloudTrail for events related to this finding trail = boto3.client('cloudtrail') events = trail.lookup_events(LookupAttributes=[{'AttributeKey':'ResourceName','AttributeValue':guardduty_finding}]) return json.dumps(events['Events']) @tool def analyze_incident(logs_json: str) -> str: # Use a Bedrock LLM (e.g. nova-premier) to analyze logs and classify threat prompt = f"Analyze these CloudTrail logs and classify the severity (low/med/high)." response = bedrock_client.invoke_model(modelId='us.amazon.nova-premier-v1', text=logs_json, prompt=prompt) return response @tool def summarize_report(findings_json: str) -> str: # Generate structured incident report following Pydantic schema prompt = "Generate a JSON report with fields: incident_id, severity, description, recommended_actions." response = bedrock_client.invoke_model(modelId='us.amazon.nova-premier-v1', text=findings_json, prompt=prompt) return response agent = Agent( model="amazon.bedrock:us.amazon.nova-premier-v1", tools=[get_cloudtrail_logs, analyze_incident, summarize_report] ) result = agent("GuardDuty Finding ID 12345: Possible EC2 threat. Triage and report.") print(result) # JSON summary (validated by Pydantic schema) |
In this chain, agents decide actions through @tool calls, with linked steps that mirror a human incident-response workflow. While Strands flow APIs can orchestrate complex or parallel actions, even simple tool chaining enables a clear path from alert to final report.
All outputs are well-structured and auditable. A Pydantic-enforced JSON schema ensures that required fields, such as severity and timeline, are consistently present. AWS actions are automatically logged in AWS CloudTrail, providing a complete audit trail. Combined with Strands’ tracing and metrics, this delivers a high-fidelity, traceable report to SecOps within minutes, fully integrated into the custom Strands agent pipeline.
Key Takeaways: A Strands-based multi-agent system ingests GuardDuty alerts via Amazon EventBridge, invokes specialized AWS-integrated tools (Lambda/boto3) to gather evidence, and uses an Amazon Bedrock LLM to triage and summarize. Agents output Pydantic-validated JSON reports, and all AWS calls are recorded by AWS CloudTrail, delivering an end-to-end, auditable incident triage pipeline.
Conclusion
Agentic AI represents the next big leap for cloud operations. Teaming multiple intelligent agents with cloud-native tooling transforms incidents from reactive handling to proactive, automated analytics.
For teams operating at scale on platforms like AWS, Agentic AI enables faster recovery, greater reliability, and more efficient use of engineering time. As cloud systems continue to grow in complexity, agent-based architectures will become a foundational component of modern DevOps and SRE practices.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Agentic AI and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. What is Security Incident Triage in this solution?
ANS: – Security Incident Triage is the automated process of collecting, analyzing, and prioritizing security alerts to determine their severity, root cause, and recommended actions. In this solution, agentic AI coordinates multiple specialized agents to investigate alerts end-to-end, rather than relying on manual analysis.
2. How does agentic AI differ from a traditional LLM-based chatbot?
ANS: – A traditional LLM responds to a single prompt.
An agentic AI system:
- Breaks the problem into tasks
- Assigns tasks to specialized agents (log analysis, threat analysis, reporting)
- Calls tools and AWS APIs
- Produces structured, auditable outputs
3. What AWS services are used in this solution?
ANS: – The solution integrates tightly with AWS-native services, including:
- Amazon Web Services for infrastructure
- Amazon GuardDuty for threat detection
- AWS CloudTrail for audit logs
- Amazon EventBridge for event-driven triggers
- AWS Lambda for orchestration and tool execution
- Amazon Bedrock for LLM inference

WRITTEN BY Akanksha Choudhary
Akanksha works as a Research Associate at CloudThat, specializing in data analysis and cloud-native solutions. She designs scalable data pipelines leveraging AWS services such as AWS Lambda, Amazon API Gateway, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon S3. She is skilled in Python and frontend technologies including React, HTML, CSS, and Tailwind CSS.


 Login
Login


 January 29, 2026
January 29, 2026 PREV
PREV










Comments