|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
Managing database credentials is one of the biggest security challenges in modern applications. Hardcoded usernames and passwords can easily be leaked in logs, source code, or misconfigured tools. Even when handled carefully, rotating and managing these static credentials across teams is tedious and often overlooked.
In this blog, we will explore why AWS IAM DB Authentication is a better approach, walk step-by-step through setting it up for an Amazon RDS PostgreSQL instance, and highlight best practices and common pitfalls from real-world implementations.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Why Use AWS IAM DB Authentication?
Traditional Amazon RDS connections require a username and password. This method introduces multiple challenges:
- Credential risk: Hardcoding credentials in applications, scripts, or configuration files creates security exposure.
- Complex management: Rotating passwords across distributed teams or services is cumbersome.
- Compliance concerns: Storing and reusing static credentials violates the principle of least privilege.
By contrast, AWS IAM DB Authentication provides several advantages:
- Temporary access: Tokens are valid for 15 minutes, reducing the attack surface if compromised.
- No stored credentials: Applications need not keep passwords in source code or environment variables.
- AWS IAM integration: Permissions can be tightly scoped with AWS IAM roles and policies, ensuring only approved users or services gain access.
- Scalability: Works seamlessly with serverless services like AWS Lambda, where traditional credential storage is problematic.
Step-by-Step Setup for AWS IAM DB Authentication
Step 1: Create or Modify Your Amazon RDS PostgreSQL Instance
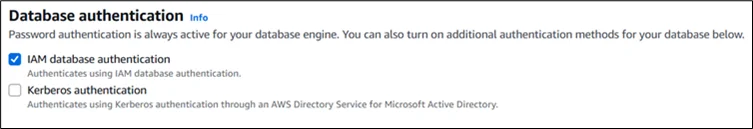
Enable AWS IAM DB Authentication in the configuration settings when launching an Amazon RDS PostgreSQL instance. If your instance already exists, you can enable it later:
- Open the Amazon RDS Console.
- Navigate to your DB instance settings.
- Under Connectivity & security, enable AWS IAM DB Authentication.
- Save and apply changes (note: the DB may restart briefly).
Ensure your Amazon RDS instance resides in a private subnet and that its security group allows inbound connections (e.g., from Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, or your client machine if using a VPN).
Step 2: Create a Database User for AWS IAM
Log in using your Amazon RDS master user and create a new AWS IAM-enabled user. For example:
![]()
The rds_iam role is critical because it links the PostgreSQL user to AWS IAM-based authentication instead of traditional passwords.
Step 3: Attach an IAM Role to Your AWS Lambda (or Application)
Applications like AWS Lambda or Amazon EC2 need an AWS IAM role to connect to the database. The policy should look like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "rds-db:connect", "Resource": "arn:aws:rds-db:region:account-id:dbuser:db-cluster-id/fcc_iam" } |
Key points:
- Replace region, account-id, and db-cluster-id with your actual values.
- The dbuser portion must match the PostgreSQL user you created (fcc_iam).
- Attach this policy to the IAM role associated with your AWS Lambda or Amazon EC2 instance.
Ensure the AWS IAM role includes the correct DB user and resource ARN.
Step 4: Generate an Authentication Token for Clients (e.g., DBeaver)
If you want to connect manually from a client such as DBeaver or psql, you can generate a token using the AWS CLI:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
aws rds generate-db-auth-token \ --hostname your-db-host.rds.amazonaws.com \ --port 5432 \ --region your-region \ --username fcc_iam \ --profile your-aws-profile |
Copy the generated token and paste it into the Password field of your database client.
Keep in mind:
- Tokens are valid for 15 minutes only.
- If the connection attempt is delayed beyond that, you must generate a new one.
- For longer sessions, consider automation scripts to regenerate tokens on demand.
Best Practices
- Automate token generation: Instead of manually creating tokens, integrate token generation into your application using the AWS SDK.
- Use AWS IAM roles, not users: Whenever possible, attach IAM roles to AWS services (AWS Lambda, Amazon ECS, Amazon EC2) instead of issuing IAM access keys.
- Limit privileges: Scope IAM policies narrowly to the required DB user and resources.
- Combine with SSL: Use IAM authentication and SSL/TLS to secure connections fully.
- Monitor with Amazon CloudWatch: Track database connection attempts and AWS IAM usage to detect suspicious activity.
Common Pitfalls
- Expired tokens: Tokens last 15 minutes. If connections fail unexpectedly, ensure the token is still valid.
- Incorrect ARNs in policies: A mismatched DB cluster ID or DB user in the AWS IAM policy will block access.
- Networking issues: Ensure the Amazon RDS security group allows traffic from the AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2, or your client environment.
- Forgotten GRANT statement: The PostgreSQL user must be explicitly granted the rds_iam role.
Conclusion
AWS IAM DB Authentication offers a secure, scalable, and modern approach to accessing Amazon RDS databases. By eliminating the risks of static passwords and shifting to short-lived AWS IAM tokens, you significantly reduce credential exposure and improve compliance with security best practices.
When properly configured with AWS IAM roles, precise policies, and awareness of token expiration, AWS IAM DB Authentication integrates seamlessly with serverless services, developer tools, and cloud-native architectures. This feature is a strong step forward for organizations aiming to improve database security without adding complexity.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding AWS IAM DB Authentication and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. Is IAM DB Authentication supported for MySQL and Aurora?
ANS: – Yes. AWS IAM DB Authentication is available for both PostgreSQL and MySQL engines on Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora.
2. How long does the AWS IAM token remain valid?
ANS: – Tokens are valid for 15 minutes. After that, a new token must be generated.
3. Can DBeaver remember or refresh the AWS IAM token automatically?
ANS: – No. DBeaver cannot refresh AWS IAM tokens on its own. You must generate a new token manually or use a script each session.

WRITTEN BY Esther Jelinal J
Esther Jelinal J is a Research Associate at CloudThat, working as a Full Stack Developer with a strong focus on backend development. She is skilled in technologies such as React.js, Node.js, JavaScript, Python, PostgreSQL, and AWS. With a strong passion for cloud technologies, Esther is growing her expertise as a cloud-native developer. She is enthusiastic about exploring emerging technologies and has the potential to build innovative, scalable solutions.


 Login
Login


 September 18, 2025
September 18, 2025 PREV
PREV











Comments