|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
In a world where infrastructure and configuration need to be reliable, repeatable and quick to deliver, engineers are turning to tools that ease the burden of manual scripting. One combination that stands out is using Ansible playbooks in conjunction with GitHub Copilot, which provides code suggestions, faster drafting and fewer errors. In this article, we’ll guide you through leveraging Copilot to write Ansible playbooks more efficiently, what to watch out for and how these fit into a comprehensive automation workflow that supports DevOps training and practice.
Start Learning In-Demand Tech Skills with Expert-Led Training
- Industry-Authorized Curriculum
- Expert-led Training
Why combine Ansible playbooks with GitHub Copilot?
Working with Ansible playbooks is about describing “what” you want your machines or services to look like (packages installed, services running, configuration files templated) rather than scripting every step imperatively. It’s powerful, but writing multiple playbooks, roles and templates can still become time-intensive. That’s where GitHub Copilot enters: by offering autocomplete suggestions, module name hints and even generating full YAML blocks based on comments.

When you integrate GitHub Copilot into the development of your Ansible playbooks, you reduce boilerplate, you decrease syntax mistakes (especially in YAML) and you accelerate iteration. In the context of an automation workflow, this means you spend more time refining logic (conditions, handlers, roles) than writing repetitive scaffolding.
Setting up your environment
Before you start drafting playbooks with assistance, you’ll want a smooth setup:
- Use an editor like VS Code with the GitHub Copilot extension enabled.
- Install the Ansible extension (for YAML validation, module name hints) so your editor recognizes Ansible-specific syntax.
- Enable Copilot within YAML files and ensure it’s aware of the context (for example, you are working on an Ansible playbook).
Drafting your first assisted playbook
Imagine you need to create a playbook that installs Apache (httpd) on Red Hat-based systems and ensures the service is running. Instead of writing everything from scratch, begin with a comment describing your intent:
# Playbook to install and enable the Apache web server on RedHat hosts
As you type that, GitHub Copilot may suggest a complete playbook snippet:
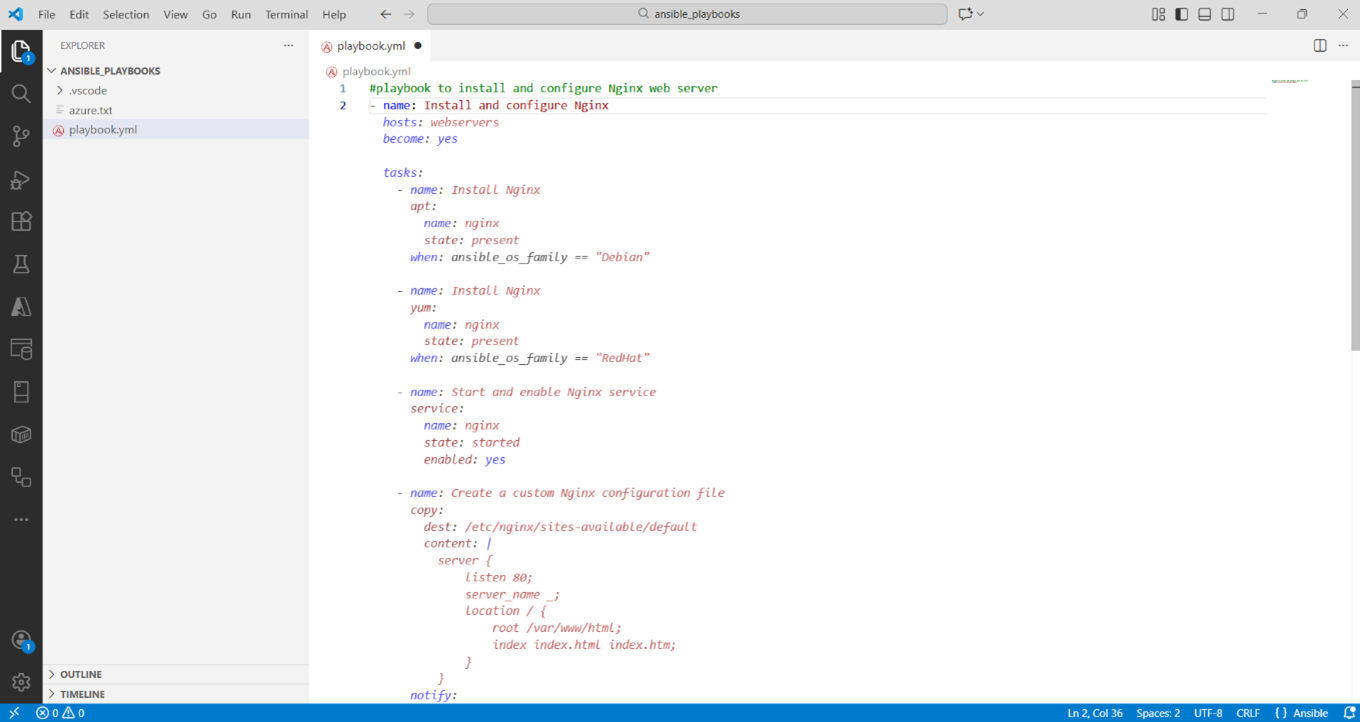
Copilot auto-generates Ansible playbooks from intent, cutting YAML boilerplate and errors.
Notice how Copilot understood your intent from the natural language comment and selected the appropriate modules. One of the significant benefits of combining GitHub Copilot with Ansible playbooks is that you spend less time worrying about syntax or module naming and more time thinking about what you want to automate.
Using Copilot for more advanced patterns
You can escalate complexity by prompting more descriptive comments, for example:
# Copy custom index.html to Apache doc root and restart service only if the file changed
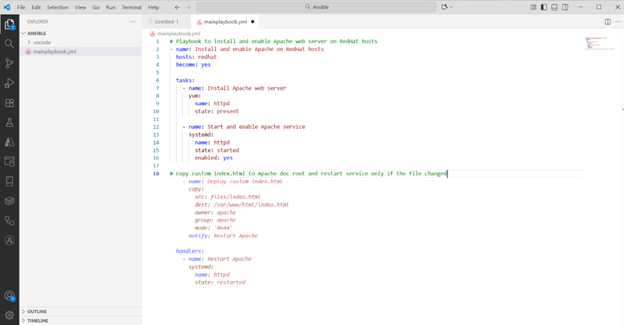
Copilot generates Ansible handlers to restart Apache only when index.html changes.
Copilot may propose this snippet:
What’s valuable here is that the generated playbook includes the notify/handlers pattern, capturing the “restart only on change” idiom. You can then refine or customize the suggestion further (e.g., parametrising src, dest, adding conditions like when: ansible_facts[‘os_family’] == ‘RedHat’).
Building roles and reusable structure
Moving from a simple playbook to a role-based structure is a further step in the automation workflow. You might prompt Copilot with something like:
# Create a reusable role called webserver for Apache installation and configuration
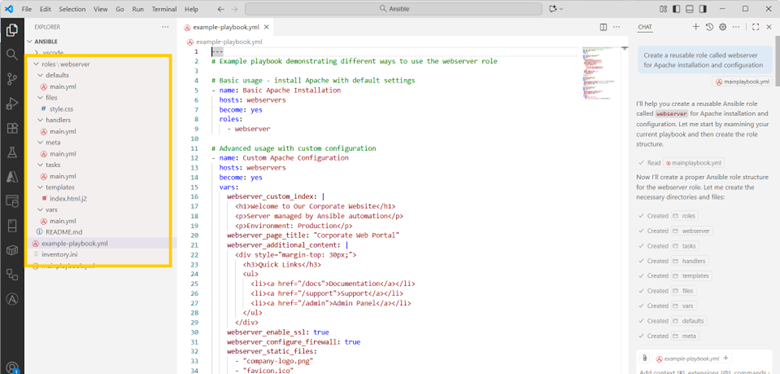
Copilot scaffolds reusable Ansible roles and playbooks for Apache automation.
Copilot might generate:
│ example-playbook.yml
│ inventory.ini
│ mainplaybook.yml
│├───.vscode
│ apache.yml
│ settings.json
└───roles
└───webserver
│ README.md
├───defaults
│ main.yml
├───files
│ style.css
├───handlers
│ main.yml
├───meta
│ main.yml
├───tasks
│ main.yml
├───templates
│ index.html.j2
└───vars
main.yml
You then open tasks/main.yml and ask Copilot to write the installation steps. You open templates/httpd.conf.j2 and ask Copilot for a Jinja2 template that uses variables document_root, listen_port, etc
Best practices when using Copilot with Ansible playbooks
While GitHub Copilot adds speed and suggestions, you must still apply judgment. Here are the best practices to incorporate into your workflow:
- Always review the generated code. Copilot may choose outdated module names or omit error handling.
- Use ansible-lint or ansible-playbook –syntax-check to validate your playbooks before running them in production.
- Use the ansible.builtin.* namespace explicitly. Copilot sometimes uses legacy module names (for example, yum instead of ansible.builtin.yum).
- Ensure security considerations: when using, become: yes, handle credentials or vaults properly.
- Parametrize templates and roles rather than hard-coding values. Use variables, defaults and conditionals.
By following these practices, your automation workflow becomes more reliable.
Accelerating Ansible Automation
Writing Ansible playbooks has always been about describing the desired infrastructure state rather than scripting every step. By introducing GitHub Copilot into your workflow, you gain speed, clarity and the ability to focus on designing logic rather than plumbing. The automation workflow becomes more efficient, you spend more time on value-adding tasks and you produce cleaner, role-based, maintainable code.
For anyone involved in DevOps training or looking to standardize server fleets and services, combining Ansible playbooks with GitHub Copilot offers a compelling path. Use the suggestions, review them critically and refine the output into production-ready automation.
Upskill Your Teams with Enterprise-Ready Tech Training Programs
- Team-wide Customizable Programs
- Measurable Business Outcomes
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.

WRITTEN BY MD Azhar Uddin
Azhar is a Microsoft Certified Trainer (MCT) and multicloud expert with a Master’s degree in computer applications. With a proven track record of training over 10,000 professionals worldwide, he specializes in cloud, DevOps, and system administration- emphasizing scalable, secure and cost-effective solutions. He brings deep expertise in Azure, AWS and Oracle Cloud, skillfully integrating complex multicloud environments and designing modern cloud-native architectures using microservices and containers. Recognized among the Top 100 MCTs globally acclaimed for delivering real-world, high-impact training in Microsoft Data & AI and cloud technologies.


 Login
Login


 December 18, 2025
December 18, 2025 PREV
PREV










Comments