|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Introduction
Imagine orchestrating multiple AI agents to work together seamlessly, each handling specialized tasks while maintaining clear dependencies and information flow. The Graph Multi-Agent Pattern makes this possible by treating agents as nodes in a directed graph, where execution flows deterministically based on defined edges. Whether you’re building research pipelines, content generation workflows, or complex decision-making systems, graphs provide the structure needed to coordinate multiple agents effectively.
Traditional approaches to multi-agent coordination often struggle with complexity, sequential chains are too rigid, while completely parallel systems lack coordination. Graphs solve this by offering a middle ground: structured workflows with clear dependencies, yet flexible enough to support parallel processing, conditional branching, and even feedback loops. This enables sophisticated multi-agent systems that can adapt, iterate, and scale.
The pattern shines in scenarios that require clear dependency management and a deterministic execution order. Need research completed before analysis begins? Want multiple specialists to work simultaneously, then aggregate their findings? Require quality checks with revision loops? Graphs handle all these scenarios elegantly. By combining AI agents with custom business logic nodes, you can build hybrid systems that leverage AI creativity for complex tasks while using deterministic code for performance-critical operations, data validation, and business rule enforcement.
What makes graphs particularly powerful is their composability. You can nest entire multi-agent systems (like Swarms) within graph nodes, creating hierarchical orchestration in which specialized teams handle subtasks autonomously. This modularity, combined with multi-modal support for text, images, and documents, makes graphs the go-to pattern for building production-grade multi-agent systems.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Key Features
- Deterministic Execution – Graphs execute nodes in a predictable order according to edge dependencies, ensuring consistent, reliable workflows. This makes debugging easier and results more reproducible.
- Flexible Topologies – Support for both acyclic (DAG) and cyclic graphs means you can build everything from simple linear pipelines to complex feedback loops with iterative refinement. Sequential pipelines, parallel processing, branching logic, and review cycles are all possible.
- Conditional Edges – Add dynamic decision-making to your workflows with conditional edges that determine whether to traverse based on intermediate results. This enables adaptive workflows that respond to content, quality checks, or business rules.
- Nested Patterns – Combine multiple orchestration patterns by embedding Swarms or entire Graphs as nodes within parent Graphs. This modularity enables the construction of complex hierarchical systems in which specialized multi-agent teams handle specific subtasks.
- Custom Nodes – Extend beyond AI agents by creating custom nodes that execute deterministic Python functions. This hybrid approach combines AI creativity with business logic, data validation, and performance-critical operations that don’t require LLM calls.
- Multi-Modal Support – Process diverse inputs, including text, images, and documents, using ContentBlocks. A single graph can handle PDFs, extract images, analyze them with vision-capable agents, and synthesize findings into comprehensive reports.
- Real-Time Streaming – Monitor execution with streaming events that provide visibility into node execution, parallel processing, and nested system behavior. Track running nodes, view intermediate results, and collect performance metrics throughout execution.
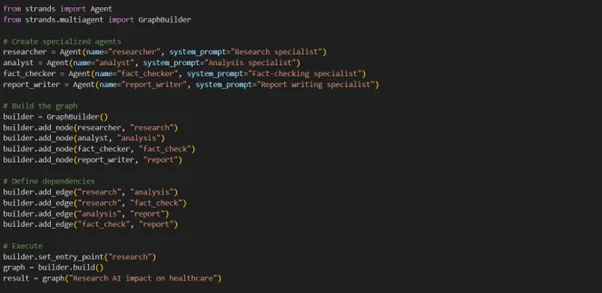
Code Examples: Research and Analysis Pipeline
Here’s a practical example of building a research workflow:
Real-World Use Cases
- Content Generation Pipeline – Media companies use graphs to orchestrate content creation. A research agent gathers trending topics, then specialized writers work in parallel, creating articles, social posts, and newsletters simultaneously. An editor reviews outputs, routing quality content to publishing while sending revisions back through feedback loops. This parallel processing dramatically reduces production time while maintaining standards.
- Financial Analysis System – Investment firms deploy graphs that market data agents use to collect information concurrently from stock exchanges, news feeds, and economic indicators. Analysis agents process different asset classes simultaneously, equities, bonds, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Risk assessment agents evaluate findings while recommendation engines synthesize actionable strategies. Deterministic execution ensures regulatory compliance and clear audit trails.
- Customer Support Automation – E-commerce platforms route tickets through classifier agents to specialized handlers working in parallel, technical support, billing, and logistics. Quality checks validate responses before delivery, while escalation agents flag complex cases for human intervention. Custom nodes integrate with CRM systems and enforce business rules.
- Medical Diagnosis Assistant – Healthcare systems process patient data through symptom analysis agents, while research agents reference medical literature in parallel. Specialist agents, cardiology, neurology, and radiology, provide simultaneous expertise. Multi-modal support analyzes medical images, lab results, and patient narratives together, synthesizing comprehensive diagnostic recommendations for physicians.
Conclusion
The Graph Multi-Agent Pattern provides a powerful framework for coordinating specialized agents with deterministic execution and flexible topologies.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding Graph Multi-Agent Pattern and we will get back to you quickly.
Empowering organizations to become ‘data driven’ enterprises with our Cloud experts.
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Timely data-driven decisions
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. How do graphs differ from simple sequential agent chains?
ANS: – Graphs support parallel execution, conditional branching, and cyclic patterns. While chains execute agents sequentially, graphs allow multiple agents to run simultaneously and make dynamic routing decisions based on intermediate results, enabling more sophisticated workflows.
2. Can I combine graphs with other multi-agent patterns?
ANS: – Yes! Nest Swarms within graphs or use entire graphs as nodes in larger graphs. This modularity enables hierarchical systems in which specialized multi-agent teams handle specific subtasks within broader workflows.
3. How do I prevent infinite loops in cyclic graphs?
ANS: – Use set_max_node_executions() to limit total executions and set_execution_timeout() for maximum runtime. Design conditional edges with clear exit conditions and enable reset_on_revisit(True) to reset node state during iteration.

WRITTEN BY Livi Johari
Livi Johari is a Research Associate at CloudThat with a keen interest in Data Science, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). She is passionate about building intelligent, data-driven solutions that integrate AI with connected devices to enable smarter automation and real-time decision-making. In her free time, she enjoys learning new programming languages and exploring emerging technologies to stay current with the latest innovations in AI, data analytics, and AIoT ecosystems.


 Login
Login

 February 9, 2026
February 9, 2026 PREV
PREV











Comments