|
Voiced by Amazon Polly |
Overview
Moving to the cloud helps companies optimize the IT cost and ability to get rid of most hardware and software. Also, maintaining the low latency for architecture is complex and challenging. As a result, AWS created Local Zones, which let you use specific AWS resources, such as computing and storage services, closer to more end customers, giving them access to the locally operating apps with extremely low latency. Applications running in AWS Local Zones have quick, secure, and seamless access to the rest of AWS services. AWS Local zones also connect to the parent region, giving applications running in Local Zones via Amazon’s redundant, extremely high bandwidth private network.
In this blog, we’ll go through the basics of AWS Local Zones and the configuration required for AWS Local Zones.
Pioneers in Cloud Consulting & Migration Services
- Reduced infrastructural costs
- Accelerated application deployment
Introduction
AWS Local Zones places AWS compute, storage, database, and other selected AWS services closer to end users to run latency sensitive applications.
To start with AWS Local Zones, you must first enable the AWS Local Zones for your AWS account. After that, you can deploy resources to them. Once you enable AWS Local Zones, they will be available along with all of the other AZs, and you will be able to access and manage AWS Local Zones.
Use cases of AWS Local Zones
- Run low-latency apps at the edge location —Build and deploy apps near end users to enable real-time gaming, live streaming, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), virtual workstations, and more.
- Ease the process of hybrid cloud migrations — Move your applications to an AWS Local Zone in your area while maintaining the low-latency requirements of hybrid deployment.
- Comply with strict criteria for data residency — Comply with local and state data residency regulations in fields like government, iGaming, healthcare, and finance.
How does AWS Local Zones Work?
AWS Local Zone consists of one or more AZs, physically separated data centers with independent power, cooling, and networking infrastructure.
AWS Local Zones are mainly designed for applications with ultra-low latency requirements, such as multimedia creation, real-time, and financial services. AWS Outposts, a fully managed service that extends AWS infrastructure, services, tools, and APIs to customer premises, can be used with AWS Local Zones.
As of the time of writing this blog, there are 33 AWS AWS Local Zones, about half in the US and half in other countries.
Below is a diagram describing an AWS account with a VPC in the US-east-1 Region, extended to a Local Zone called “Houston”. The zones within the VPC have a subnet each (with separate Amazon EC2 instances).

Prerequisites
AWS Account with a valid subscription
Steps to Configure AWS Local Zones
- Log in to your AWS Account and go to the Amazon EC2 console, and from the left side, under Settings, select
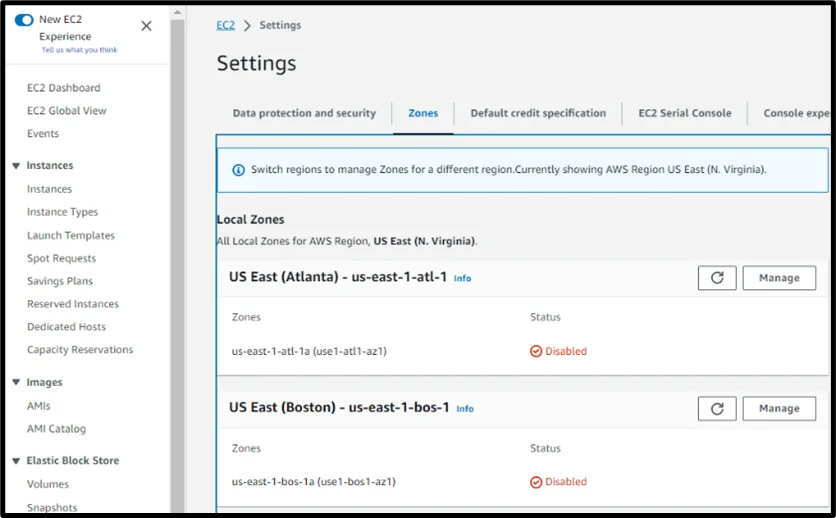
- Change the region with the AWS Local Zones option. For example, move to us-east-1 (N. Virginia) and enable the Local Zone (Houston) by clicking Manage.

- Once successfully enable the AWS Local Zone is completed, the status will change to Enabled

- Now again, go to the Amazon EC2 console and click on Launch instances, and under the Network settings section, select the appropriate Amazon VPC. Under the subnet section, click Create new subnet.

- Now, the Create subnet tab will open. Select the appropriate Amazon VPC in the VPC ID After that, enter the subnet name and select Houston AZ from the Availability Zone dropdown, provide the valid CIDR for the subnet from the VPC range, and click Create Subnet.

- Now go back to the instance launch wizard, refresh the Network settings section by clicking the refresh icon, and select the newly created subnet in Houston from the Subnet dropdown list.

- Now, you can create an Amazon EC2 instance in the Houston Local Zone and launch other resources as required.
Conclusion
In this blog, we’ve learned about AWS Local Zones, the basics, how to get started with AWS Local Zones, when to use AWS Local Zones, some of the benefits and use cases of Local Zones, there’s no additional charge for enabling AWS Local Zones. You pay only for the resources you deploy in your AWS Local Zones.
Drop a query if you have any questions regarding AWS Local Zones and we will get back to you quickly.
Making IT Networks Enterprise-ready – Cloud Management Services
- Accelerated cloud migration
- End-to-end view of the cloud environment
About CloudThat
CloudThat is an award-winning company and the first in India to offer cloud training and consulting services worldwide. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner, AWS Advanced Tier Training Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, CloudThat has empowered over 850,000 professionals through 600+ cloud certifications winning global recognition for its training excellence including 20 MCT Trainers in Microsoft’s Global Top 100 and an impressive 12 awards in the last 8 years. CloudThat specializes in Cloud Migration, Data Platforms, DevOps, IoT, and cutting-edge technologies like Gen AI & AI/ML. It has delivered over 500 consulting projects for 250+ organizations in 30+ countries as it continues to empower professionals and enterprises to thrive in the digital-first world.
FAQs
1. When can we use AWS Local Zones?
ANS: – You should use AWS Local Zones to deploy workloads close to your location for low-latency requirements. Resources produced in the Local Zone can provide low-latency services to nearby end users since AWS Local Zones have internet connection and support AWS Direct Connect.
2. How do AWS Local Zones and Amazon VPC interact?
ANS: – By establishing a new subnet and designating it to the AWS Local Zone, you can extend any VPC from the parent region into those zones. When you create a subnet in an AWS Local Zone, your VPC is expanded to include that AWS Local Zone and your Amazon VPC will treat the subnet the same as any other subnet in any other AZ, automatically adjusting any necessary gateways and route tables, etc.
3. How are AWS Local Zones and Availability Zones different from each other?
ANS: – While Availability Zones give access to the full range of AWS services, Local Zones are made to bring the key services required for the latency-sensitive elements of your workload closer to end users. In contrast to other AWS services like Amazon S3 and Amazon Aurora, which are only accessible privately via VPC over the AWS private network, local AWS services like Amazon EC2, Amazon EBS, Amazon VPC, and others can be utilized to serve end users close to one another with incredibly low latency. You can create high-availability applications using both AWS Local Zones and Availability Zones.

WRITTEN BY Mayank Bharawa


 Login
Login


 September 20, 2023
September 20, 2023 PREV
PREV











Comments